Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: 4M125: Pediatric Rheumatology: Outcomes & Quality of Life (1920–1925)
Session Type: ACR/ARP Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Use of certain biologic medications increases the risk of reactivation of hepatitis B. Therefore, screening for hepatitis B viral (HBV) infection is recommended prior to initiation of biologic agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Although children are routinely vaccinated for hepatitis B in the US, vaccine seroprotection may be reduced or lost in immunocompromised patients. We sought to evaluate our compliance with HBV screening before starting biologic therapies.
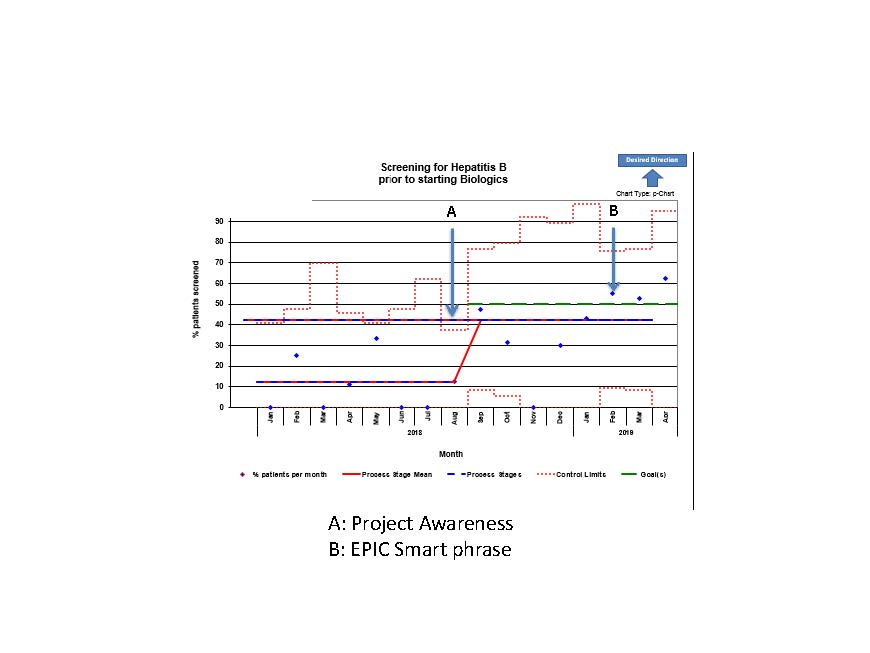
Methods: We used Quality Improvement methodologies with an aim to increase HBV screening rates in patients starting injectable biologic agents from 12.5% to greater than 50% in 6 months and to 80% in 1 year. Using a multidisciplinary team approach, we identified the root causes of incomplete HBV screening including: lack of provider awareness of guidelines, lack of access to vaccination records and prompts in the electronic health record (EHR), and concern about delay in therapy. To address these root causes, we performed multiple PDSA cycles including education of providers and engaging the clinical pharmacy staff, who were involved with the prior authorization for these Specialty medications. We created smart phrases for providers to use at the time of request for prior authorization for new injectable biologic medications, which included all required HBV screening tests. Another smart phrase enabled pharmacy staff to notify providers of patients missing screening. Flyers were posted in clinic rooms to remind prescribers and patients of the need to perform HBV screening.
Results: At the start of the project, only 1 of 7 providers (14%) stated that they routinely screened patients for HBV before starting a new biologic and only 12.5% of patients in the rheumatology clinic were screened for HBV with hepatitis B surface antigen prior to initiating biologic therapy. Through the PDSA cycles, monthly HBV screening rate for patients starting injectable biologics increased from 12.5% to 42.5% by 7 months. Further improvement is being seen with implementation of the EHR smart phrase. Since testing was incorporated in to the prior authorization process, initiation of therapy was not delayed.
Conclusion: Despite falling short of the initial project aim, our interventions resulted in a significant improvement in the number of patients screened for a potentially serious complication than in the pre-intervention period, as seen by the center line shift in the control chart (Fig 1). Inclusion of pharmacists in the improvement process was successful in reminding providers of missed opportunities for testing. Future directions include analysis for percentage of patients without evidence of immunity to hepatitis B with plans for booster vaccination when indicated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sivaraman V, Wise K, Bley E, Dawson M, DeSalvo J, Lazaroff S, Neiger M, Shisler E, Lemle S, Ardura M. Improvement in Hepatitis B Screening Prior to Initiation of Biologic Therapy in the Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-in-hepatitis-b-screening-prior-to-initiation-of-biologic-therapy-in-the-pediatric-rheumatology-clinic/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-in-hepatitis-b-screening-prior-to-initiation-of-biologic-therapy-in-the-pediatric-rheumatology-clinic/