Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Phosphatidylserine-specific phospholipase A1 (PS-PLA1) is a secreted lipase that is proposed to be a producing enzyme for lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS), which is an emerging lipid mediator with a number of immunomodulative effects. The aim of the present study was to assess the utility of serum levels of PS-PLA1 in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
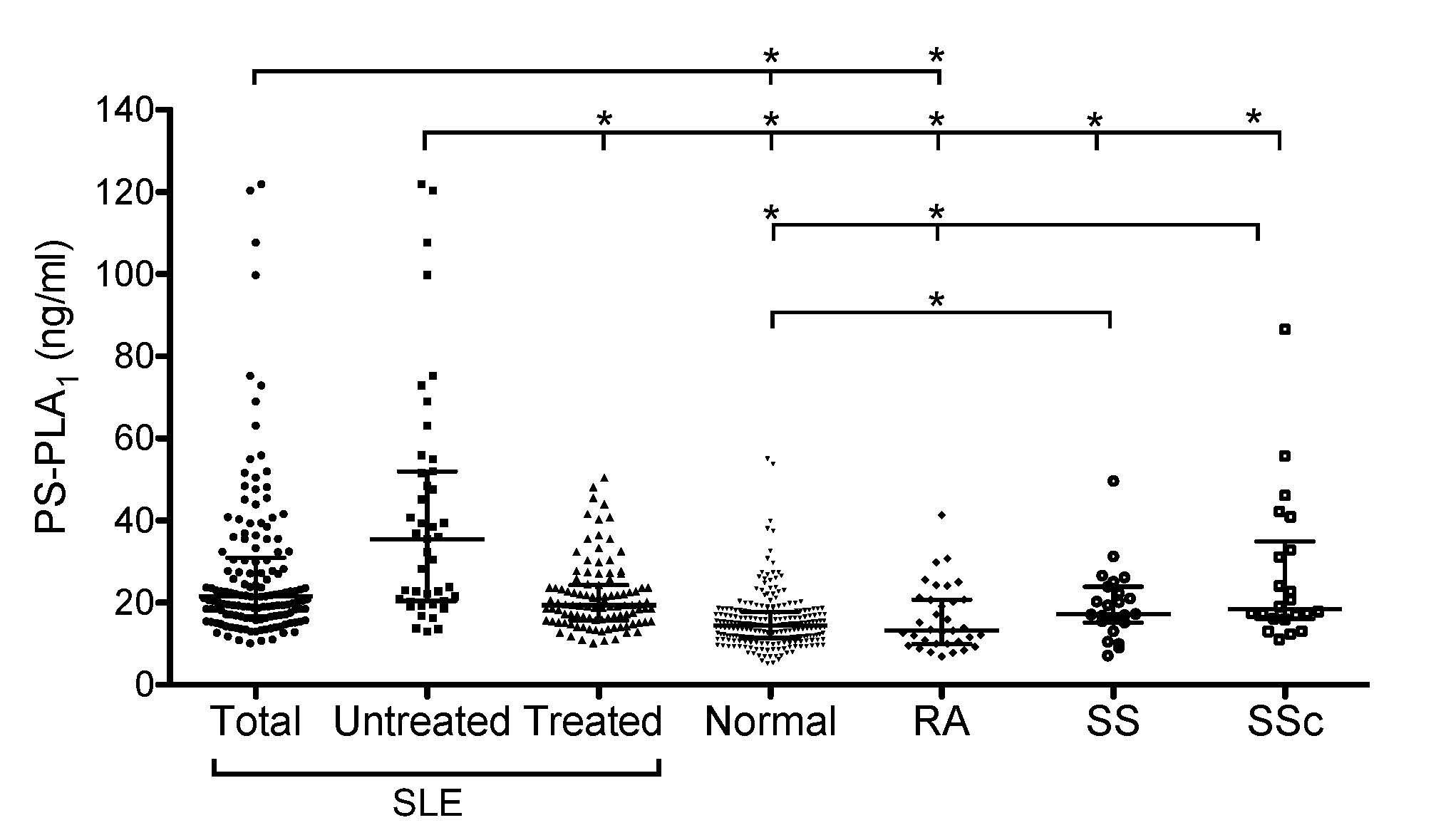
Methods: Serum PS-PLA1 was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 146 patients with SLE (including 43 untreated patients), 80 disease controls (35 active rheumatoid arthritis [RA], 23 Sjögren’s syndrome [SS], and 22 systemic sclerosis [SSc]), and 237 healthy controls.
Results: Serum PS-PLA1 was significantly higher in SLE patients than in healthy controls and RA patients. Although serum PS-PLA1 was significantly elevated in SSc and SS patients compared with healthy controls, serum PS-PLA1 was significantly higher in untreated SLE patients than in treated SLE patients and disease control patients. Receiver operating characteristic analysis revealed that a cut-off value of 17.9 ng/mL distinguished untreated SLE from disease control, with sensitivity and specificity of 88.4% and 57.0%, respectively. Serum PS-PLA1 was significantly correlated with SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and IgG with a correlation coefficient of 0.56 and 0.31, respectively, and inversely correlated with white blood cell counts, lymphocyte counts, total complement hemolytic activity (CH50), complement C3, and C4 with a correlation coefficient of -0.32, -0.26, -0.42, -0.39, and -0.18, respectively, in SLE patients overall. Stepwise multiple regression analysis identified SLEDAI, CH50, and IgG as significant parameters. In SLEDAI-based disease activity groups, serum PS-PLA1 was significantly higher in SLE patients with high disease activity than in those with low disease activity. Serum PS-PLA1 decreased significantly in parallel with SLEDAI in 25 SLE patients whose paired serum samples were available pre- and post-treatment.
Conclusion: Serum PS-PLA1 was associated with disease activity of SLE, suggesting that serum PS-PLA1 may be useful as a biomarker for monitoring disease activity of SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sawada T, Kurano M, Shirai H, Iwasaki Y, Tahara K, Hayashi H, Igarashi K, Fujio K, Aoki J, Yatomi Y. Importance of Serum Phosphatidylserine-Specific Phospholipase A1 (PS-PLA1) as a Novel Disease Activity Biomarker of Systemic Lupus Erythematous [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/importance-of-serum-phosphatidylserine-specific-phospholipase-a1-ps-pla1-as-a-novel-disease-activity-biomarker-of-systemic-lupus-erythematous/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/importance-of-serum-phosphatidylserine-specific-phospholipase-a1-ps-pla1-as-a-novel-disease-activity-biomarker-of-systemic-lupus-erythematous/