Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with RA are at increased risk of myocardial infarction and stroke not fully explained by usual cardiovascular (CV) risk factors. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Small, dose-dependent increases from baseline in total, LDL-c, and HDL-c have been noted in some pts. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) are infrequent in the tofacitinib clinical program. The Framingham and Reynolds risk scores calculate the 10-year risk of developing CV disease; Reynolds risk score includes high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) as a variable, Framingham risk score does not. We scored pts receiving tofacitinib to investigate the impact of changes in lipids and hsCRP on CV risk scores.
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of 6 Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (disease-modifying antirheumatic drug [DMARD]-inadequate responders [IR] in ORAL Standard [NCT00853385; N=471]; ORAL Sync [NCT00856544; N=729]; ORAL Solo [NCT00814307; N=574]; ORAL Scan [NCT00847613; N=739]; ORAL Step [NCT00960440; N=353]; methotrexate [MTX]-naïve pts in ORAL Start [NCT01039688; N= 906]). Pts received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID either as monotherapy (ORAL Solo, ORAL Start), with background MTX (ORAL Standard, ORAL Scan, ORAL Step), or csDMARDs (ORAL Sync). All trials were placebo (pbo) controlled except ORAL Start (tofacitinib vs MTX). Pts with diabetes were excluded from this analysis. Framingham and Reynolds CV risk scores were calculated at baseline (BL) and Month 3. Change from baseline was assessed using a linear mixed model for repeated measures, controlling for treatment.
Results: 2/5 trials in DMARD-IR pts (ORAL Sync [tofacitinib 5 mg p=0.012; tofacitinib 10 mg p=0.042] and ORAL Step [tofacitinib 10 mg only p=0.041]), showed a significantly higher change from BL to Month 3 in Framinghan risk score with tofacitinib vs pbo (Figure); Reynolds risk scores were significantly (all <0.05) reduced from BL to Month 3 with both doses of tofacitinib vs pbo except ORAL Step, in which there was no significant difference in change from BL to Month 3 between tofacitinib 5 mg BID and pbo (Figure). Change from BL to Month 3 in Framingham risk score was significantly higher with tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg vs MTX in ORAL Start; however, for Reynolds risk score there was no significant difference between either dose of tofacitinib and MTX.
Conclusion: In this analysis, the 10-year Framingham CV risk score was not significantly increased with tofacitinib vs pbo in 3 out of 5 Phase 3 trials, although a higher CV risk score was identified vs MTX. The 10-year CV risk calculated by Reynolds risk score, which includes hsCRP as a variable, was significantly reduced with tofacitinib vs pbo and there was no difference vs MTX. CV risk with RA treatment is a function of lipid changes and/or hsCRP. An ongoing study will investigate the incidence of MACE with tofacitinib vs etanercept or adalimumab.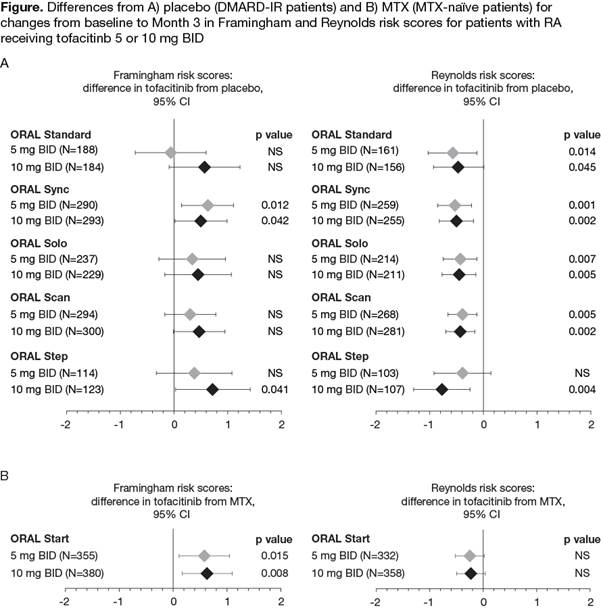
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nurmohamed M, Choy E, Charles-Schoeman C, Kitas G, Accossato P, Szczypa P, Chouchouli K, Lukic T, Biswas P. Impact of Tofacitinib Treatment Compared with Placebo or Methotrexate on Cardiovascular Risk Scores in Six Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tofacitinib-treatment-compared-with-placebo-or-methotrexate-on-cardiovascular-risk-scores-in-six-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tofacitinib-treatment-compared-with-placebo-or-methotrexate-on-cardiovascular-risk-scores-in-six-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trials/
