Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The objective of this real-world
analysis was to examine the impact of the interleukin-6 receptor α
inhibitor tocilizumab (TCZ) on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in a US observational
cohort of > 40,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA; Corrona).
Methods: Between October 1, 2010, and March 31,
2015, patients with RA who newly initiated TCZ monotherapy while not in
remission (based on Clinical Disease Activity Index) and had a follow-up visit
at 1 year (± 3 months) were identified. Changes in
PROs, assessed 1 year from baseline and stratified by prior tumor necrosis
factor inhibitor (TNFi) use, included patient global assessment of disease,
pain and fatigue (0-100); morning stiffness (hours); modified Health Assessment
Questionnaire (mHAQ; 0-3); and Euro Quality of Life 5 dimensions questionnaire
(EQ-5D). Improvement in EQ-5D domains was defined as patients improving from
moderate to no disability or severe to moderate or no disability. Outcomes
between the 1 and ≥ 2 prior TNFi groups were compared using chi-square or
t-tests, as appropriate.
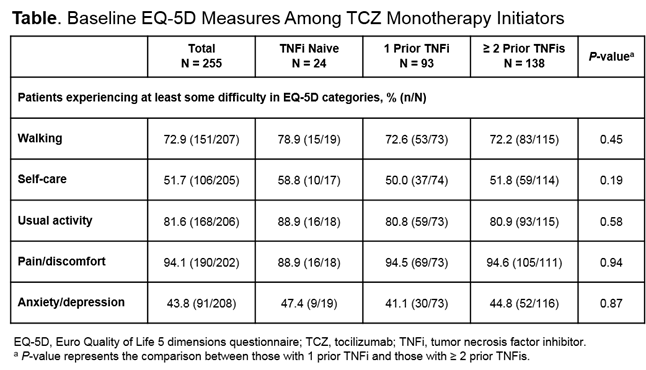
Results: Of the 255 TCZ monotherapy initiators included,
24 (9%) were TNFi naive, 93 (37%) received 1 prior TNFi and 138 (54%) received
≥ 2 prior TNFis. Baseline PROs showed that patients were substantially
impacted by their disease, with similar scores reported across TNFi exposure
groups (Table). Patients reported median (IQR) global disease activity,
pain, fatigue and mHAQ scores of 55 (40-75), 60 (40-76), 60 (33-80) and 0.63
(0.25-1.00), respectively, and a median (IQR) of 1 (0.5-2.5) hour of morning
stiffness at baseline. Baseline proportions of patients reporting difficulties
in EQ-5D domains are shown (Table). At 12 months, improvements were
reported in all PROs with no significant differences across TNFi exposure
groups. Median (IQR) improvements in patient global, pain and fatigue were 10
(-5-30), 10 (-5-30) and 5 (-10-23), respectively. 46% of
patients reported no reduction in morning stiffness, 35% reported 1-60 minutes
reduction and 19% reported > 60 minutes reduction. Improvement in EQ-5D is
shown (Figure). A significantly lower proportion of patients with
≥ 2 prior TNFis had improvement in walking and usual activities compared
with patients with 1 prior TNFi.
Conclusion: Real-world data showed that quality of
life in patients with RA newly initiating TCZ monotherapy was substantially
impacted by their disease. Improvements at 1 year were reported in all
measures, regardless of prior TNFi history; however, patients who received TCZ
therapy earlier in the line of treatment had better response with respect to walking
and usual activities than those treated with ≥ 2 prior TNFis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harrold L, John A, Reed GW, Karki C, Li Y, Kremer JM, Haselkorn T, Greenberg JD. Impact of Tocilizumab Monotherapy on Patient-Reported Quality of Life Outcomes in the US Corrona Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tocilizumab-monotherapy-on-patient-reported-quality-of-life-outcomes-in-the-us-corrona-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tocilizumab-monotherapy-on-patient-reported-quality-of-life-outcomes-in-the-us-corrona-registry/