Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Healthcare and work-loss costs are markedly higher in RA patients than in the general population. The EuroQol 5-Dimensions (EQ-5D) instrument, commonly applied to measure utility and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) in health-economic evaluations, is based on a questionnaire, asking respondents to value 5 health dimensions (mobility; self-care; usual activities; pain/discomfort; anxiety/depression) on a 3-leveled scale. In this study, we aimed to compare how these 5 EQ-5D components relate to healthcare, work-loss, and total societal costs in RA.
Methods: Clinical visits of anti-TNF treated RA patients, monitored in the observational South Swedish Arthritis Treatment Group register 2005-2011, were included (11674 visits in 2246 patients; >95% fulfillment of 1987 ACR criteria in a prior validation). EQ-5D questionnaire responses at visits were linked to register-derived costs of anti-rheumatic drugs, out- and inpatient care, and work-loss due to sick leave or disability pension from 30 days before to 30 days after each visit. Associations of the 5 EQ-5D components to healthcare (patient care and drugs), work-loss (in patients <65 years), and total societal costs (healthcare + work-loss costs; <65 years) were studied in separate, adjusted, generalized estimating equations regression models, comparing standardized β coefficients by nonparametric bootstrapping to assess which component best reflects costs.
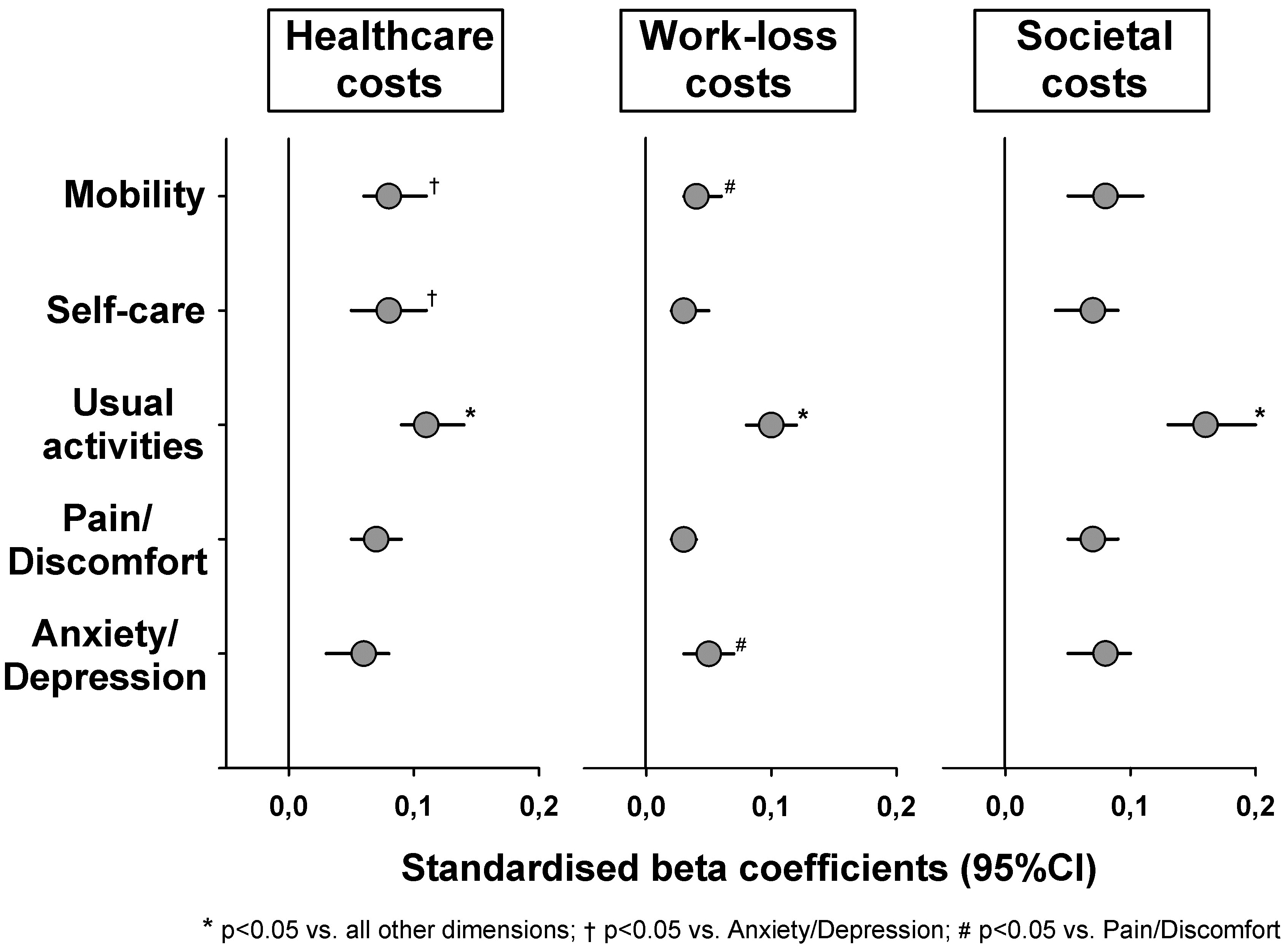
Results: The strongest associations with both healthcare and work-loss (and thus also societal) costs were observed for the usual activites component (p<0.05 vs. all other components; Figure). Apart from that, the mobility and self-care components were more closely associated with healthcare costs than anxiety/depression, while stronger associations with work-loss costs were revealed for mobility and anxiety/depression than for pain/discomfort. For comparison, cost associations with the composite EQ-5D utility score (United Kingdom peference set) were (standardized β (95%CI)): -0.11 (-0.14 to -0.09) for healthcare, -0.07 (-0.08 to -0.05) for work-loss, and -0.12 (-0.15 to -0.09) for societal costs.
Conclusion: Of the 5 EQ-5D components, problems to perform one’s usual daily activities was most strongly related to both healthcare and work-loss (as expected) costs. Moreover, the associations of the usual activities component to costs were on par with those observed for the composite EQ-5D utility score, making it an interesting simple marker of total societal costs in RA. Somewhat unexpectedly, relatively weak cost associations were observed regarding the pain/discomfort component.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gülfe A, Olofsson T, Söderling JK, Neovius M, Wallman JK. Impact of the Five Components of the Euroqol 5-Dimensions Instrument on Healthcare and Work-Loss Costs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Observational Data from Southern Sweden [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-the-five-components-of-the-euroqol-5-dimensions-instrument-on-healthcare-and-work-loss-costs-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-observational-data-from-southern-sweden/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-the-five-components-of-the-euroqol-5-dimensions-instrument-on-healthcare-and-work-loss-costs-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-observational-data-from-southern-sweden/