Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment has improved considerably over the years. However, patient compliance remains critical to treatment outcomes. Patient compliance still poses challenges in day-to-day care of RA patients and treatment outcomes. In a technology driven era, with more people having access to smart phones, unique opportunities exist for use of phone based technologies to improve patient care in chronic diseases. This study aims to investigate the impact of smart phone application (HealthCius) on inflammatory disease activity and quality of life in RA patients receiving standard treatment.
Methods: 75 consecutive patients fulfilling the 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria for RA were recruited in this observational study. Subjects were randomized into 2 groups. First, having access to a smart phone were assigned to the intervention group using the Healthcius application (n=45) and second, the control group not using the application (n=30). The patients in two groups received standard treatment for RA. The application was designed after obtaining feedback from health care providers, patient counselors and RA patients using a questionnaire. To the patients, the app was their individual treatment plan. It helped them comply with the plan by providing an easy to refer checklist, reminders, alerts and a visual dashboard of their progress through the day. The app served as the doctor’s virtual assistant inside the patient’s smart phone. For the doctor, it was a live dashboard of all patients and their real time compliance levels. The data reported by the patients was available to the doctor in the form of time sliced charts and trend lines. Therefore, this app is designed to leverage technology to shift the patients’ focus every day on to their treatment plan thereby driving up compliance and better health outcomes. Outcome measures included erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-Reactive protein (CRP), disease activity score (DAS28) and health assessment questionnaire (HAQ-DI) at baseline and after 1 year.
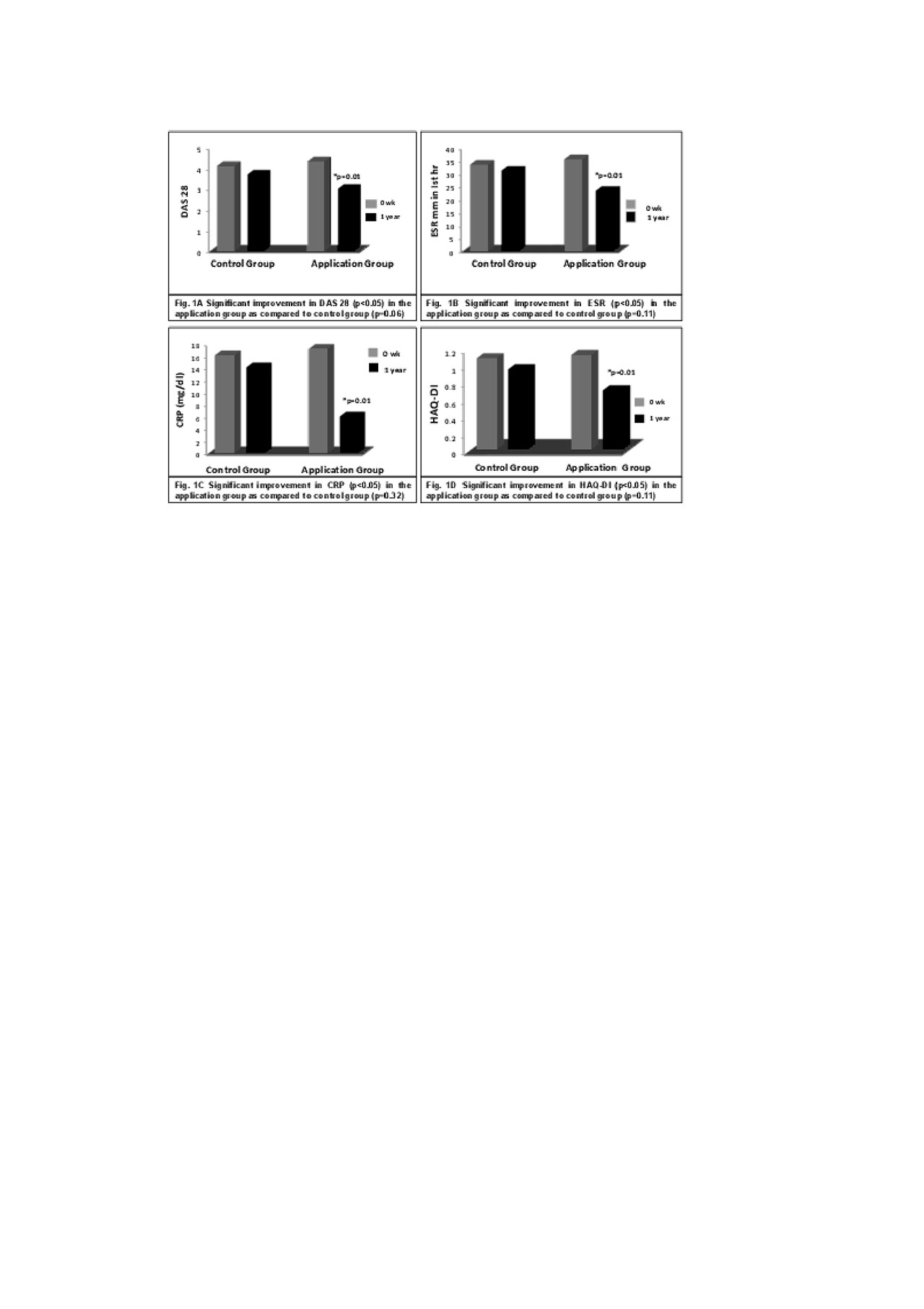
Results: The two groups did not differ significantly for baseline characteristics. There was a significant difference between the control and intervention group for DAS28 (p < 0.05), ESR (p≤0.05), CRP (p≤0.05) and HAQ-DI (p≤0.5) after 1 year in favor of smart phone application. Analysis within the groups revealed significant improvement in DAS28 (p< 0.05) (Fig.1A), ESR (p=0.01) (Fig.1B), CRP (p=0.001) (Fig.1C) and HAQ-DI (p=0.01) (Fig.1D) in the application group as compared to control group. Impact of DMARDs usage was also evaluated at the end of the study and it was found that the average drug usage of DMARDs was more in control group than the intervention group.
Conclusion: The study suggested that there was greater improvement in inflammatory disease activity and quality of life in smart phone application assisted RA patients suggesting that smart phone technology can be used to leverage health benefits in RA.
Acknowledgement: We acknowledge the development of App used in the present study by HealthCius Services Pvt Ltd. However, App developer did not not have any say in study protocol, abstract or submission. none of the authors have any financial relationship with company.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Syngle A, Garg N, Bhatia R, Rattan S, Chauhan K. Impact of Smartphone Application Based Management in Rheumatoid Arthritis: SMART- RA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-smartphone-application-based-management-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-smart-ra-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-smartphone-application-based-management-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-smart-ra-study/