Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster I: Patient-Reported Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a complex disease with high impact on quality of life (QoL). The PsA core domain set1 includes pain, patient (pt) global assessment, physical function, QoL and fatigue. To evaluate the impact of PsA on health domains, a global survey was developed; we report results in the context of the PsA Impact of Disease (PsAID) questionnaire due to its high content validity for pts.2
Methods: A pt-based survey was conducted online from Nov 2 2017 to Mar 12 2018. Eligible pts (≥18 yrs) had PsA for >1 yr, had visited a rheumatologist/dermatologist in the past 12 months and reported using ≥1 synthetic/biologic DMARD for PsA. Pts reported current symptoms and impact of PsA on daily life. Post-survey, responses were aligned with PsAID health domains. Analyses included descriptive statistics and binomial tests.
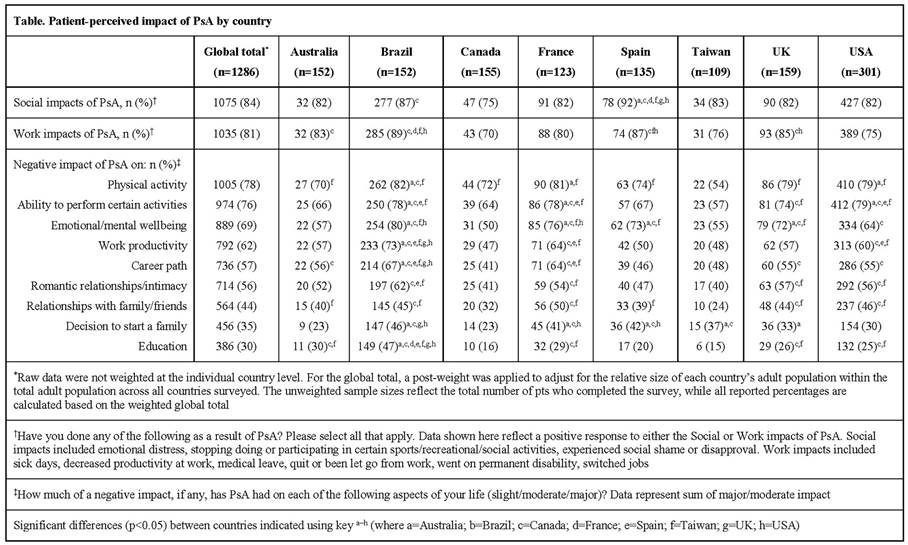
Results: 1286 pts were surveyed across 8 countries; mean age 41 yrs, 52% female, 84% reported moderate/severe PsA. Pt-perceived PsA social and work impacts were reported by 1075 (84%) and 1035 (81%) pts; 56% stopped participating in certain sports/recreational activities and 42% reported decreased work productivity. The most commonly reported major/moderate impacts of PsA were on physical activity (78%), ability to perform activities (76%), and emotional/mental well-being (69%). A greater proportion of pts in Brazil, France, Spain and UK reported negative impact on emotional well-being compared with Australia, Canada and Taiwan (p<0.05; Table). Social impacts included emotional distress (58%), social shame or disapproval (32%), and ceased participation in social activities (45%). Most respondents (62%) reported a major/moderate impact on work productivity. A greater proportion of pts in Brazil, France and USA reported negative impact on work productivity compared with Canada, Spain and Taiwan (p<0.05). Overall, 97% of pts reported musculoskeletal symptoms in the past year, most commonly joint pain, tenderness, swelling, stiffness or inflammatory back pain (IBP) (79%, 60%, 60%, 57%, 53%, respectively). Of these, joint pain and IBP were considered most bothersome (32%, 12% respectively), and 53% pts currently taking prescription medication reported joint pain. Skin/nail symptoms occurred in 80% of pts (skin patches/plaques, 58%; skin discomfort, 55%; nail changes, 34%) and unusual fatigue in 52% of pts.
Conclusion: All health domains that pts reported on were impacted by PsA in this survey aligning with life impact domains of the pt-derived PsAID questionnaire. Most pts reported an impact of PsA on social, work, and physical life aspects. These results highlight the impact of PsA on multiple health domains from a pt perspective that should be considered during shared decision-making processes between physicians and pts.
1. Orbai AM et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2017; 76: 673-80
2. Gossec L et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73: 1012-9
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates LC, Orbai AM, Azevedo VF, Cappelleri JC, Moser J, Lippe R, Lim I, Eder L, Richette P, Weng MY, Queiro R, Fallon L. Impact of Psoriatic Arthritis from the Patient’s Perspective in the Context of the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID) Questionnaire: An Online Global Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-psoriatic-arthritis-from-the-patients-perspective-in-the-context-of-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid-questionnaire-an-online-global-survey/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-psoriatic-arthritis-from-the-patients-perspective-in-the-context-of-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid-questionnaire-an-online-global-survey/