Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Peripheral manifestations (arthritis, enthesitis and dactylitis) are frequent in patients with Spondyloarthritis (SpA). However, little is known regarding the impact of these manifestations on patients’ disease perception and treatments. In this analysis, we aimed to evaluate the impact of the presence of peripheral manifestations on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and treatment.
Methods:
Data from the ASAS-COMOSPA study were analysed. Patients who reported peripheral arthritis were divided into three groups: current, past history and no history. The impact of the presence of peripheral arthritis on VAS-G (Global Visual Analogue Scale), BASDAI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Activity Index), BASFI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index), work and activity impairment was evaluated through the use of the ANOVA one factor test. Finally, NSAIDs, corticosteroids and DMARDs intake were compared among patients with and without peripheral articular involvement.
A similar statistical analysis was performed for enthesitis and dactylitis.
Results:
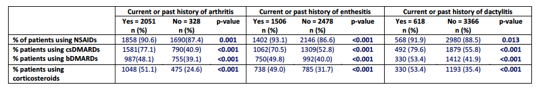
Among the 3984 patients included in the ASAS-COMOSPA study, 1333 (33.5%), 718 (18%) and 1933 (48.5%) patients had current, past history and no history of peripheral arthritis, respectively. Patients with current peripheral arthritis showed higher levels in VAS-G, BASDAI, BASFI, as well as in work and activity impairment, in comparison to the other two groups, being these differences statistically significant (p<0.01). Patients with peripheral articular involvement at the time of the visit showed higher mean scores in all questions of the BASDAI questionnaire, in contrast to those with past history and/or no history (p<0.001). Impact on treatment is shown in table 1.
Regarding enthesitis, 642 (16.1%), 864 (21.7%) and 2478 (62.2%) patients had current, past history and no history of enthesitis, respectively. Patients with current enthesitis showed significant higher levels in all PROs against the other two groups of patients (p<0.05), as well as higher scores in all the BASDAI questions (p<0.001).
Finally, 171 (4.3%), 447 (11.2%) and 3366 (84.5%) patients had current, past history and no history of dacylitis, respectively. The same results as the other two peripheral manifestations were obtained regarding impact on PROs and BASDAI questions
Conclusion:
The presence of any of the three peripheral manifestations at the time of the visit was associated to higher scores in all PROs. Patients with peripheral involvement showed greater use of NSAIDs, corticosteroids and DMARDs than those without peripheral manifestations.
Table 1. Impact on treatment
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López-Medina C, Molto A, Dougados M. Impact of Peripheral Manifestations on Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs) and Treatment in Spondyloarthritis. Data from ASAS-Comospa [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-peripheral-manifestations-on-patient-reported-outcomes-pros-and-treatment-in-spondyloarthritis-data-from-asas-comospa/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-peripheral-manifestations-on-patient-reported-outcomes-pros-and-treatment-in-spondyloarthritis-data-from-asas-comospa/