Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Health Services Research Poster II: Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
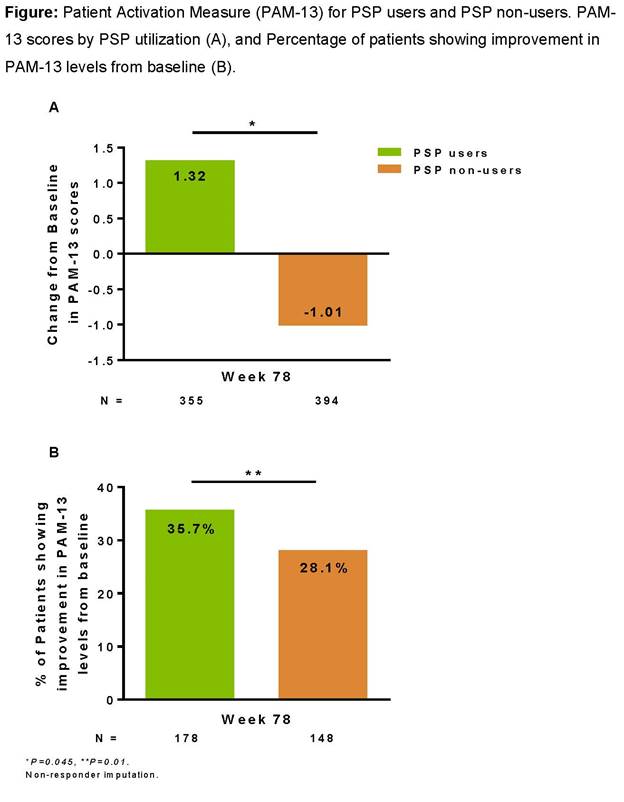
Background/Purpose : AbbVie’s Patient (pt) Support Program (PSP) is offered to pts who are prescribed adalimumab (ADA) for their Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The purpose of this analysis was to assess the association of Patient Activation Measure (PAM)-13 scores with PSP utilization among pts with moderate to severe RA initiating ADA who had option to enroll in the PSP.
Methods : PASSION (NCT01383421) was a 78-week post-marketing observational study of pts with RA receiving ADA in routine clinical care. Pts from the EU, Israel, Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Australia with an insufficient response to ≥1 disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) newly initiating ADA (1 prior biologic DMARD was allowed) were enrolled. Pts were offered a panel of “Core elements” (starter pack, call center/hotline, nursing services, educational material, and injection guide; offered in all participating countries) and “Other elements” (e.g, refill reminders, email communications, newsletters, support groups, home medication delivery, and financial assistance; vary by country) of PSP. Pts were divided in 2 groups based on their participation in the PSP: ever (PSP users) vs never (PSP non-users). The PAM-13 scores were collected at baseline (BL) and at week 78. PAM-13 scores evaluate knowledge, skills, and confidence essential to a pt managing his/her own health. PAM-13 scores were classified a priori into 4 levels (higher level = greater pt involvement in disease management). Multivariate inferential analysis was used to examine the associations between PSP utilization (yes/no) and PAM-13 scores after adjusting for the following BL characteristics: age, gender, race, RA disease duration, prior use of biologic DMARD, BL Health Assessment Questionnaire Disease Index (HAQ-DI), and BL PAM-13 score. The response variable of the model was PAM-13 scores change from BL.
Results : PSP users had significantly larger increase in the PAM-13 scores (2.33, 95% CI 0.05 – 4.61, P=0.045) compared to the BL than the PSP non-users after adjusting for relevant BL characteristics (Figure 1A). Percentage of pts that demonstrated improvement in PAM-13 levels were significantly higher among PSP users vs PSP non-users at week 78 compared to BL (35.7% vs 28.1%, P=0.01) (Figure 1B). Additionally, lower PAM-13 and HAQ-DI BL scores were statistically significantly associated with increases in the PAM-13 scores at week 78 compared to BL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Den Bosch F, Wassenberg S, Östör A, Wang C, Garg V, Kalabic J. Impact of Patient Support Program Utilization on Patient Activation Measure Scores Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-patient-support-program-utilization-on-patient-activation-measure-scores-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-patient-support-program-utilization-on-patient-activation-measure-scores-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/