Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
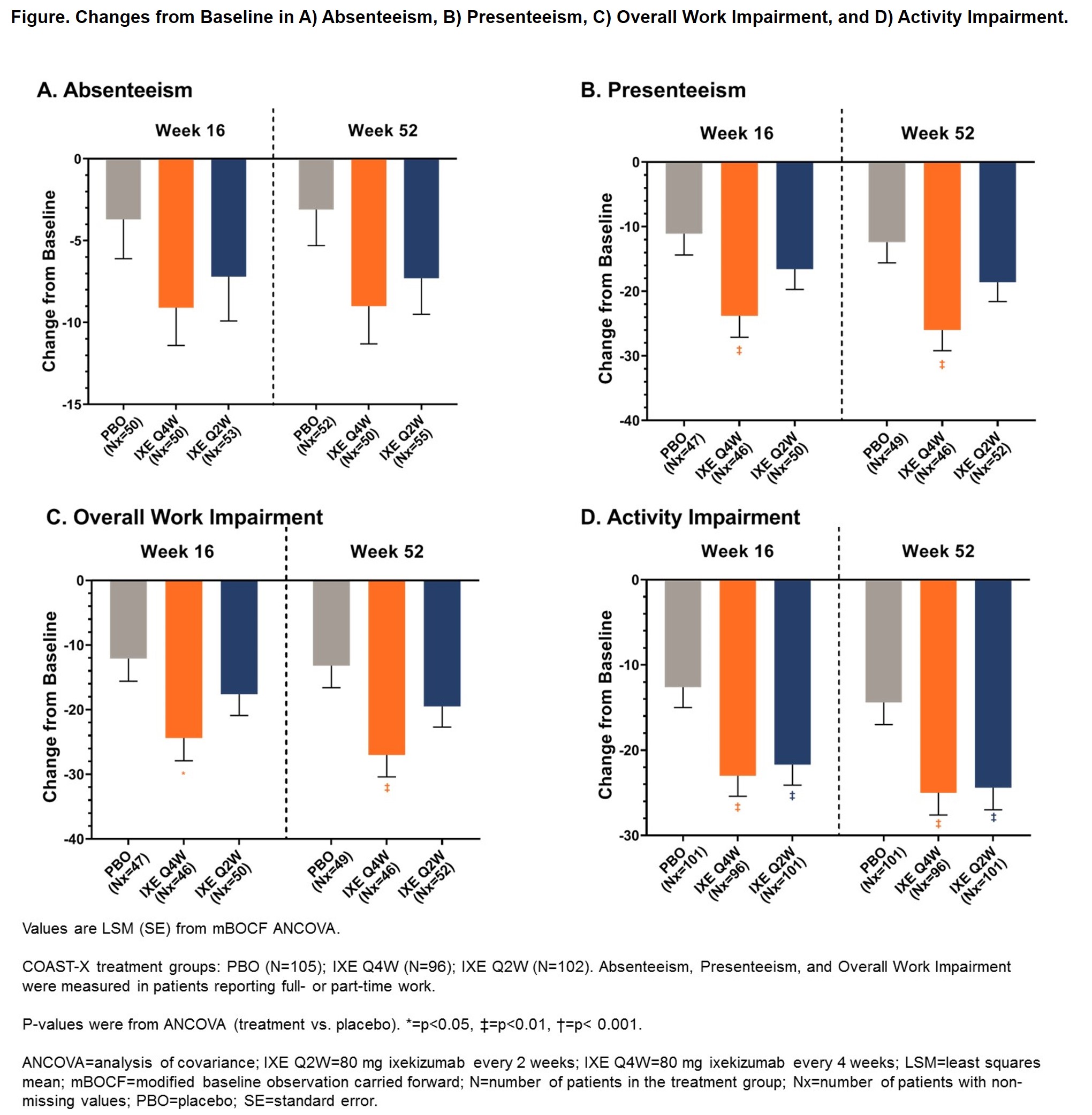
Background/Purpose: Patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) experience impairments in health-related quality of life comparable to those seen in ankylosing spondylitis, including impacts on work productivity. Ixekizumab (IXE) is a high-affinity monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin-17A and effectively treats axial spondyloarthritis.1-3 This analysis evaluated the effect of IXE treatment for 52 weeks on work productivity and activity impairment as measured by absenteeism, presenteeism, overall work impairment, and activity impairment in patients with active nr-axSpA.
Methods: COAST-X (NCT02757352) was a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group outpatient study investigating the efficacy and safety of 80 mg IXE every 2 weeks (Q2W) and every 4 weeks (Q4W) compared to placebo (PBO) in 303 patients naïve to biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs with active nr-axSpA during a 52-week treatment period. From Weeks 16 through 44, if patients’ disease activity required escalation of treatment at investigator discretion, patients were switched to open-label IXE Q2W or subsequent tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment. Analysis was performed for the intent-to-treat population, which included data up to the time of biologic switching. Patients who switched to open-label IXE were considered non-responders. Changes from baseline in work productivity were measured for patients reporting full- or part-time work at Weeks 16 and 52 with the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) Questionnaire for Spondyloarthritis and analyzed with an analysis of covariance model including treatment, geographic region, screening magnetic resonance imaging and C-reactive protein level status, and baseline value as factors. Missing data was imputed using the modified baseline observation carried forward.
Results: A majority of patients (63.5–65.7%) reported part-time or full-time paid work at baseline, with baseline scores for presenteeism and overall work activity slightly higher for patients in the PBO arm (p< 0.05). Patients treated with IXE Q4W had significantly greater improvement than PBO in activity impairment at Weeks 16 (p=0.003) and 52 (p=0.004), presenteeism at Weeks 16 (p=0.007) and 52 (p=0.003), and overall work impairment at Weeks 16 (p=0.014) and 52 (p=0.005; Figure). Patients treated with IXE Q2W had significantly greater improvement than PBO in activity impairment at Weeks 16 (p=0.007) and 52 (p=0.006; Figure). Patients treated with either IXE regimen had numeric improvements in all WPAI measures compared to those receiving PBO at Weeks 16 and 52 (Figure).
Conclusion: Patients with nr-axSpA treated with either IXE regimen had significant improvements in activity impairment compared to PBO. Patients receiving IXE Q4W also had significant improvements in presenteeism and overall work impairment.
References:
1. Sieper J, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(6):975-83.
2. Van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet. 2018;392(10163):2441-51.
3. Deodhar A, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(4):599-611.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Mease P, Gensler L, Rahman P, Navarro-Compán V, Marzo-Ortega H, Hunter T, Sandoval D, Kronbergs A, Zhu B, Leung A, Strand V. Impact of Ixekizumab on Work Productivity in Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients: Results from the COAST-X Trial at 52 Weeks [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-ixekizumab-on-work-productivity-in-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-results-from-the-coast-x-trial-at-52-weeks/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-ixekizumab-on-work-productivity-in-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-results-from-the-coast-x-trial-at-52-weeks/