Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: CT-P41 has been developed as a proposed biosimilar of the reference denosumab (DEN), a fully human monoclonal antibody that binds the cytokine receptor activator of NF-κb ligand (RANKL). The anti-drug antibody (ADA) incidence in DEN historical studies showed less than 1% of patients treated with DEN for up to 5 years tested positive for ADA using an electrochemiluminescent (ECL) bridging immunoassay (DEN Prescribing Information 2024). Although the incidence rate cannot be directly compared because a different assay was used in this study compared to the one used in the DEN historical studies, most patients had at least 1 positive ADA result after treatment. However, the ADA incidence and titer values were comparable among the treatment groups both in Treatment Period (TP) I and II (in total, 97.9% and 93.3% of patients were ADA positive in TP I and II, respectively). No patients had a positive neutralizing antibody result. In this report, further impact analysis was performed on the study data to determine any correlation between immunogenicity and clinical outcomes in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (PMO).
Methods: The ADA against denosumab (CT-P41 and DEN) was detected using a Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) – ECL assay which can detect ADA at low levels in all samples regardless of residual serum drug (25 ng/mL of ADA in the presence of 50 μg/mL of CT-P41 and DEN in PMO). It indicates that the ADA assay is considered to achieve adequate sensitivity for detecting clinically meaningful ADA levels. To investigate the impact of ADA on pharmacokinetic (PK), efficacy, and safety, the ADA status and titer were categorized into 5 groups; ADA negative, ADA positive, ADA titer=100, ADA titer=300, and ADA titer≥900 (900, 2700, 8100).
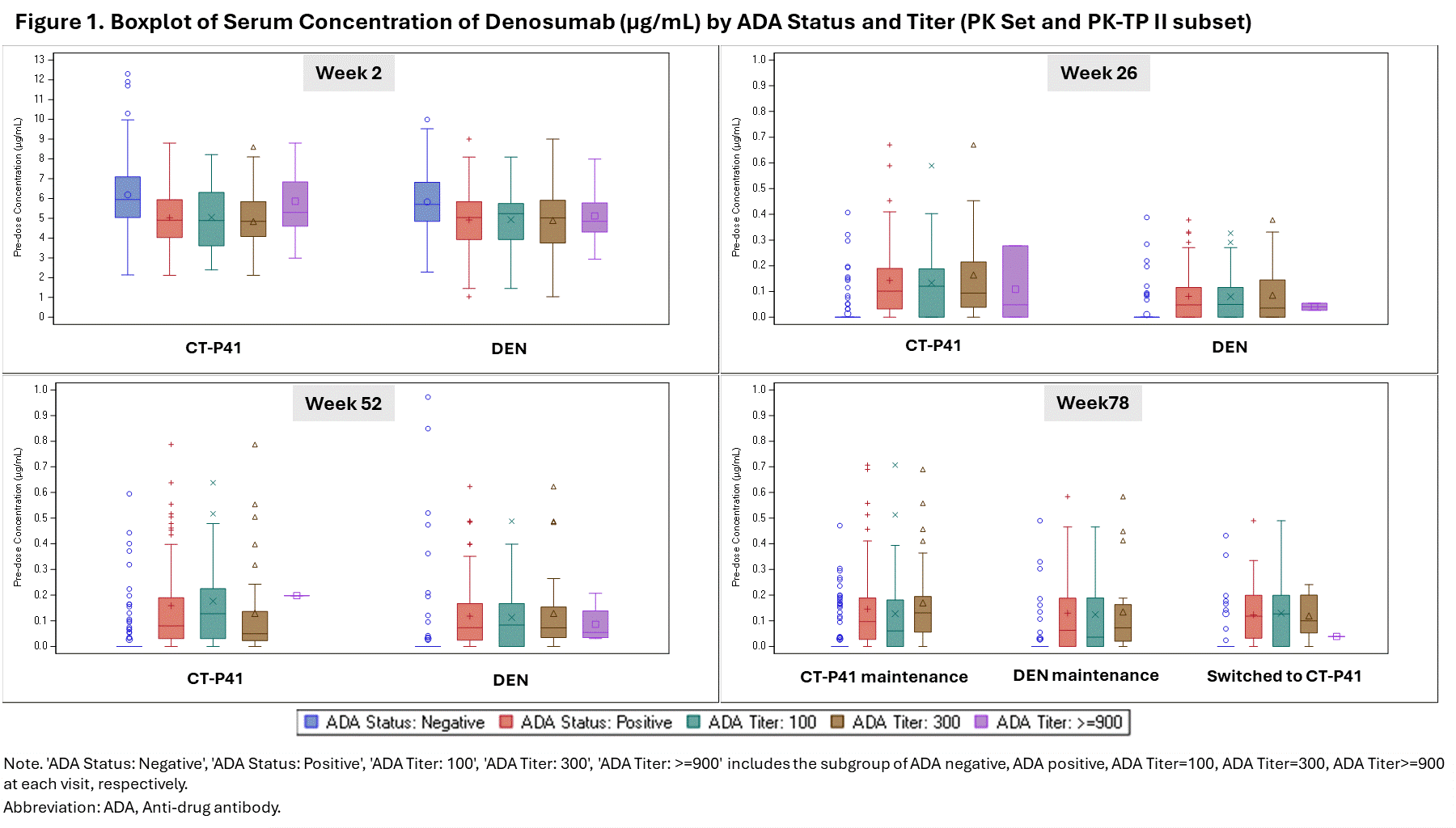
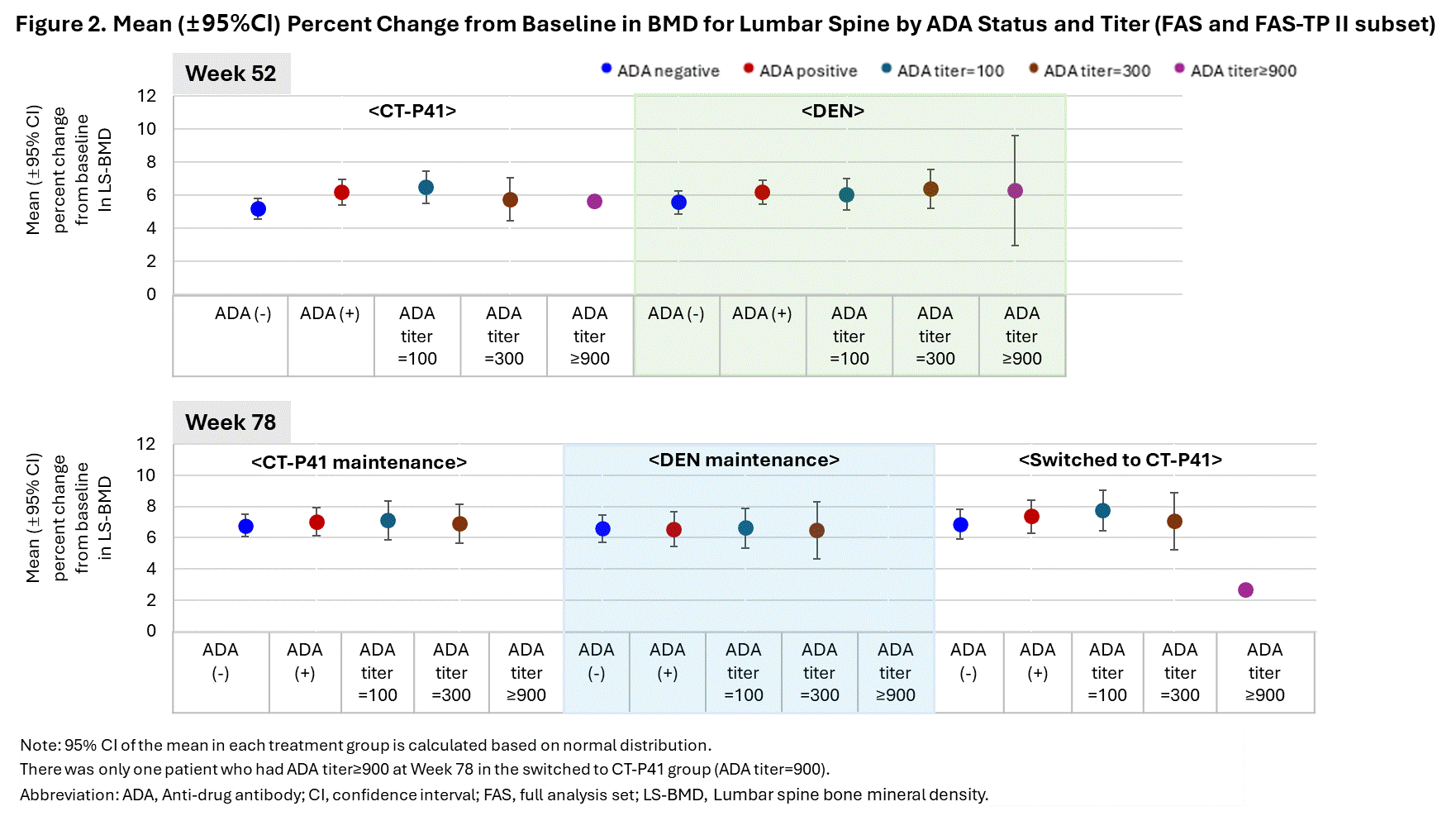
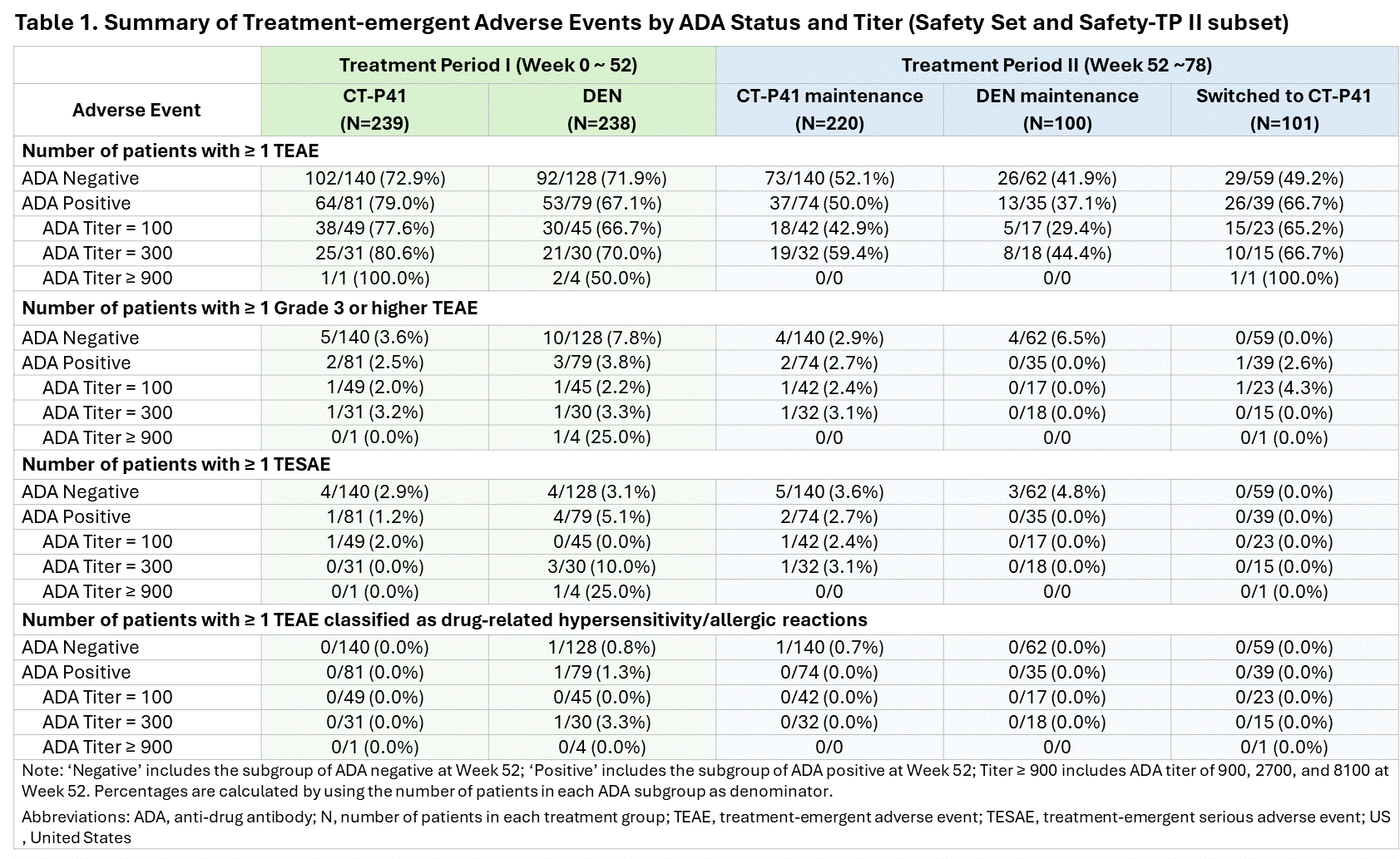
Results: The predose serum concentrations of denosumab at Week 2 (the most similar timepoint to when the maximum serum concentration of denosumab was observed after the first study drug administration) were higher in the ADA negative group than the ADA positive group. However, the results at Week 26, Week 52 (the same timepoint with the primary efficacy endpoint), and Week 78 (end of study visit) showed the opposite trend, with lower levels in the ADA negative group. Both ADA status and ADA titer had no discernible impact on PK (Figure 1). At Week 52, the percent change from baseline (%CFB) in lumbar spine bone mineral density (LS-BMD) was slightly higher in the ADA positive group compared to the ADA negative group, whereas the results at Week 78 were generally similar between the ADA status groups. The %CFB in LS-BMD in the ADA titer groups showed no apparent trend in TP I and II (Figure 2). Overall, there was no clear correlation between the incidences of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and ADA status or titer. The TEAE incidences were comparable between the treatment groups in the ADA status groups (Table 1).
Conclusion: The result showed no discernible impact of ADA on PK, efficacy, and safety. Despite the high ADA incidence compared to the DEN historical studies, it can be concluded that ADA to CT-P41 and DEN has no clinical impact considering the high sensitivity and specificity of the assay and further evaluation of immunogenicity impact.
Disclosures: J. Reginster: Celltrion, Inc, 2; S. Silverman: Amgen, 5, Celltrion, Inc., 2, Radius, 5, Tissuegene, 5; E. Czerwinski: Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Celltrion, Inc., 5; P. Borowy: Amgen, 6, Astra Zeneca, 6, Celltrion, Inc., 5, Pierr Fabre, 6; T. Budlewski: Celltrion, Inc., 5; J. Kwiatek: Celltrion, inc., 5; S. Postol: Celltrion, Inc., 5; A. Põder: Celltrion, Inc., 5; J. Supronik: Celltrion, Inc., 5; S. Kim: Celltrion, Inc., 3; J. Suh: Celltrion, Inc., 3; G. Yang: Celltrion, Inc., 3; N. Han: Celltrion, Inc., 3; N. Kim: Celltrion, Inc., 3; S. Bae: Celltrion, Inc., 3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reginster J, Silverman S, Czerwinski E, Borowy P, Budlewski T, Kwiatek J, Postol S, Põder A, Supronik J, Kim S, Suh J, Yang G, Han N, Kim N, Bae S. Impact of Immunogenicity on Clinical Outcomes in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Study to Compare CT-P41 (Proposed Denosumab Biosimilar) and Reference Denosumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-immunogenicity-on-clinical-outcomes-in-postmenopausal-women-with-osteoporosis-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-study-to-compare-ct-p41-proposed-denosumab-biosimilar-and-refere/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-immunogenicity-on-clinical-outcomes-in-postmenopausal-women-with-osteoporosis-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-study-to-compare-ct-p41-proposed-denosumab-biosimilar-and-refere/