Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's – Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The DETECT calculator has been freely available as a tool for earlier detection and diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) since 2014. Here, we aimed to evaluate its impact on PAH incidence rates, risk profile and functional class (FC) of patients at time of PAH diagnosis.
Methods: The study cohort included all patients in the prospective Oslo University Hospital (OUH) SSc cohort who performed an incident right heart catheterization (RHC) from 2009 and onwards. We grouped the patients in an early cohort with RHC conducted in 2009-2013, and a DETECT cohort with RHC from 2014-17. PH diagnosis was made by an experienced cardiologist according to the updated ESC guidelines with mean (m) PAP ≥ 25 mmHg measured by RHC and borderline PH with a mPAP >19mmHg. Pre and post capillary PHT was defined by PCW above or below 15 mmHg. Risk stratification at time of diagnosis was done using the low, intermediate and high risk grouping system suggested by ESC in 2016. Patients with ≥ 1 parameter of poor prognosis were considered at high risk and with ≥ 1 parameter of intermediate prognosis, at intermediate risk.
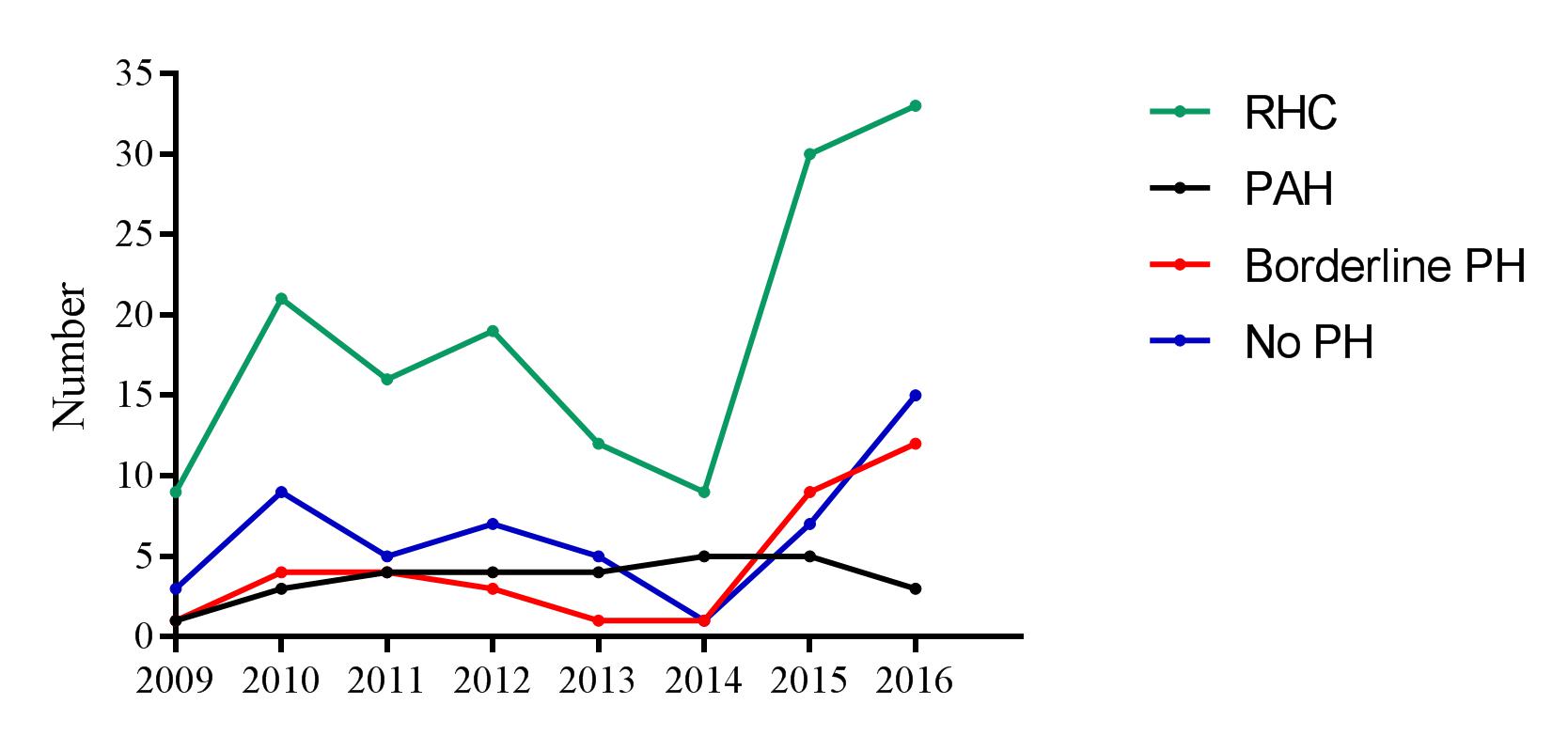
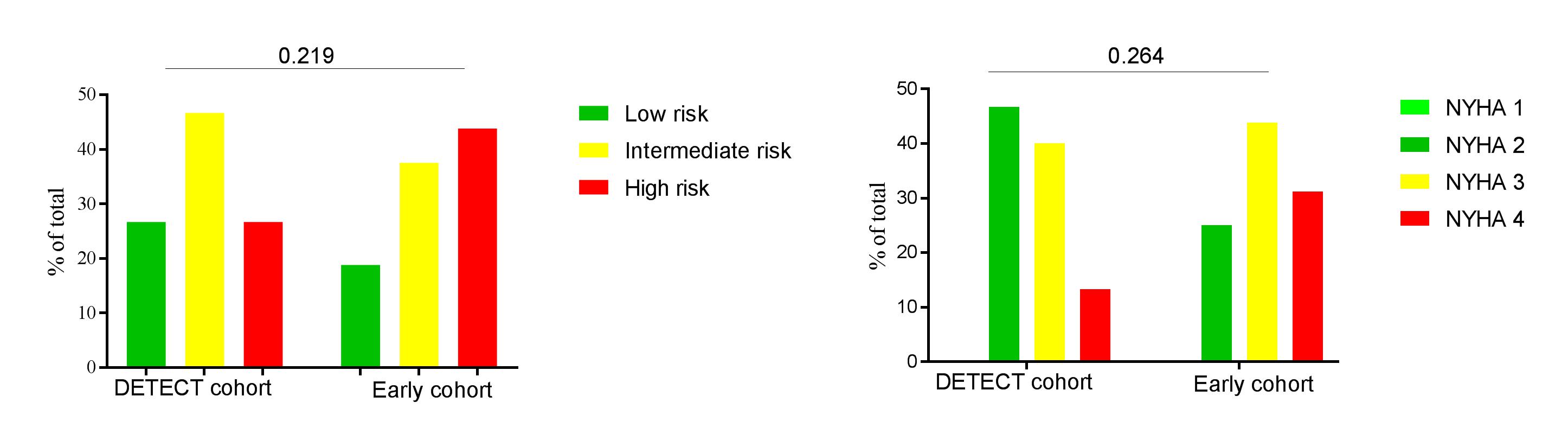
Results: An incident RHC was available in 161 patients, 77 from the early cohort and 84 from the DETECT cohort. Clinical and demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. Absolute numbers of RHC, PAH and borderline PH cases in the years 2009-2017 are shown in Figure 1. At the time of PAH diagnosis, 27% of the DETECT cohort were in the low risk group compared to 19% in the early cohort, while 27% and 47% respectively belonged in the high risk groups (p-value 0.219) (Figure 2). We also observed a trend towards lower functional class in the DETECT cohort (Figure 2).
Conclusion: We show that the number of new PAH cases per year has been stable since 2009, with no apparent change following the introduction of the DETECT algorithm. From 2014 and onwards, we observed a, not significant, increase in amount of newly diagnosed PAH cases with low risk group, and better functional class status. The total number of RHC increased from 2014 and onwards, with a concomitant increase in the number of borderline PH cases.
Table 1: Demographics and clinical characteristics
|
|
Total cohort (n=161) |
2009-13 (n=77) |
2014-17 (n=84) |
p-value |
|
Age at RHC, yrs (SD) |
61 (11.8) |
59.6 (12.2) |
62.4 (11.3) |
0.137 |
|
Time onset to RHC, yrs (SD) |
6.6 (8.2) |
6.3 (8.3) |
6.9 (8.1) |
0.634 |
|
Follow-up, yrs (SD) |
2.9 (2.4) |
4.6 (2.2) |
1.2 (0.8) |
<0.001 |
|
Females, no (%) |
126 (78.8) |
60 (77.9) |
66 (78.6) |
0.582 |
|
Ever smoker, no (%) |
67 (41.9) |
28 (36.4) |
39 (46.4) |
0.064 |
|
Limited cutaneous SSc, no (%) |
125 (78.1) |
63 (81.8) |
63 (75) |
0.502 |
|
Anti-centromere Ab, no (%) |
78 (48.8) |
37 (48.1) |
34 (40.5) |
0.848 |
|
Digital ulcers, n (%) |
61 (38.1) |
31 (40.3) |
30 (35.7) |
0.911 |
|
Scleroderma renal crisis, n (%) |
7 (4.4) |
4 (5.2) |
3 (3.6) |
0.562 |
|
Baseline modified Rodnan skin score |
9.9 (8.8) |
9.8 (10.5) |
9.9 (9.8) |
0.934 |
|
Pulmonary hypertension, n (%) |
65 (40.6) |
35 (45.5) |
30 (35.7) |
<0.001 |
|
PAH total, n (%) |
31 (19.4) |
16 (20.8) |
15 (17.9) |
|
|
PH-ILD, n (%) |
20 (12.5) |
14 (18.2) |
6 (7.1) |
|
|
Post capillary PH, n (%) |
14 (8.8) |
5 (6.5) |
9 (10.7) |
|
|
Borderline PH, n (%) |
38 (23.8) |
19 (24.7) |
27 (32.1) |
|
|
No PH, n (%) |
57 (35.6) |
23 (29.9) |
27 (32.1) |
|
|
Myocardial infarction, n (%) |
14 (8.8) |
8 (10.4) |
6 (7.1) |
0.557 |
|
Angina pectoris, n (%) |
14 (10.1) |
9 (11.7) |
5 (6) |
0.414 |
Figure 1: Frequency of conducted incident RHC, PAH, borderline PH and no PH
Figure 2: Risk stratification and functional class
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Fretheim H, Heiervang Tennøe A, Midtvedt O, Garen T, Gude E, Andreassen AK, Molberg Ø. Impact of Detect on Right Heart Catheterization Referral and Results; Data from a Prospective, Unselected, Systemic Sclerosis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-detect-on-right-heart-catheterization-referral-and-results-data-from-a-prospective-unselected-systemic-sclerosis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-detect-on-right-heart-catheterization-referral-and-results-data-from-a-prospective-unselected-systemic-sclerosis-cohort/