Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Data on the impact of body weight and body mass index (BMI) on the response to biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) including ankylosing spondylitis (AS) are still contradictory. Data on the impact of different components of the body composition on the treatment response are lacking. The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of body composition on the response to biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARD) in patients with AS after 6 months of treatment.
Methods: Patients with AS (radiographic axSpA), fulfilling the modified New York criteria and starting a bDMARD therapy were recruited between 2015 and 2019 in an extension of the prospective German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (GESPIC-AS). All patients were required to be candidates for bDMARD therapy at baseline with high disease activity (BASDAI >=4 and/or ASDAS >=2.1) despite previous treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Disease activity measures (BASDAI, CRP, ASDAS), as well as body composition parameters were assessed at baseline and after 6 months of bDMARD treatment. Body composition was assessed by the bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Weight, body mass index (BMI), fat mass index (FMI), fat free mass index (FFMI), skeletal muscle mass value (SMM), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), total body water (TBW), and extracellular water (ECW) values were collected. The primary measure of the treatment response was ASDAS change at month 6 as compared to baseline.
Results: A total of 129 patients with AS were included in this cohort. BIA was performed in 77 patients. There were 71.4% males, and 85.7% were HLA-B27 positive. At baseline, BASDAI was 5.4±1.4, CRP was 12.8±16.5 mg/l, and ASDAS – 3.0±1.0. The baseline BMI was 25.0±4.3 kg/m2. A total of 75 patients were treated with TNFi, 2 patients received an IL-17 inhibitor.
A higher BMI at baseline was associated with a worse response to bDMARD therapy that was attributable to both, the fat mass as reflected by FMI and to the fat-free mass reflected by FFMI, but not to SMM or VAT or water components – Table. This effect was independent of age, sex, symptom duration, HLA-B27 status and ASDAS at baseline.
Conclusion: Both fat mass and fat free mass have an impact on the response to bDMARDs after 6 months of treatment in patients with AS. Interestingly, skeletal muscle mass, visceral fat as well as water components showed no association with treatment response.
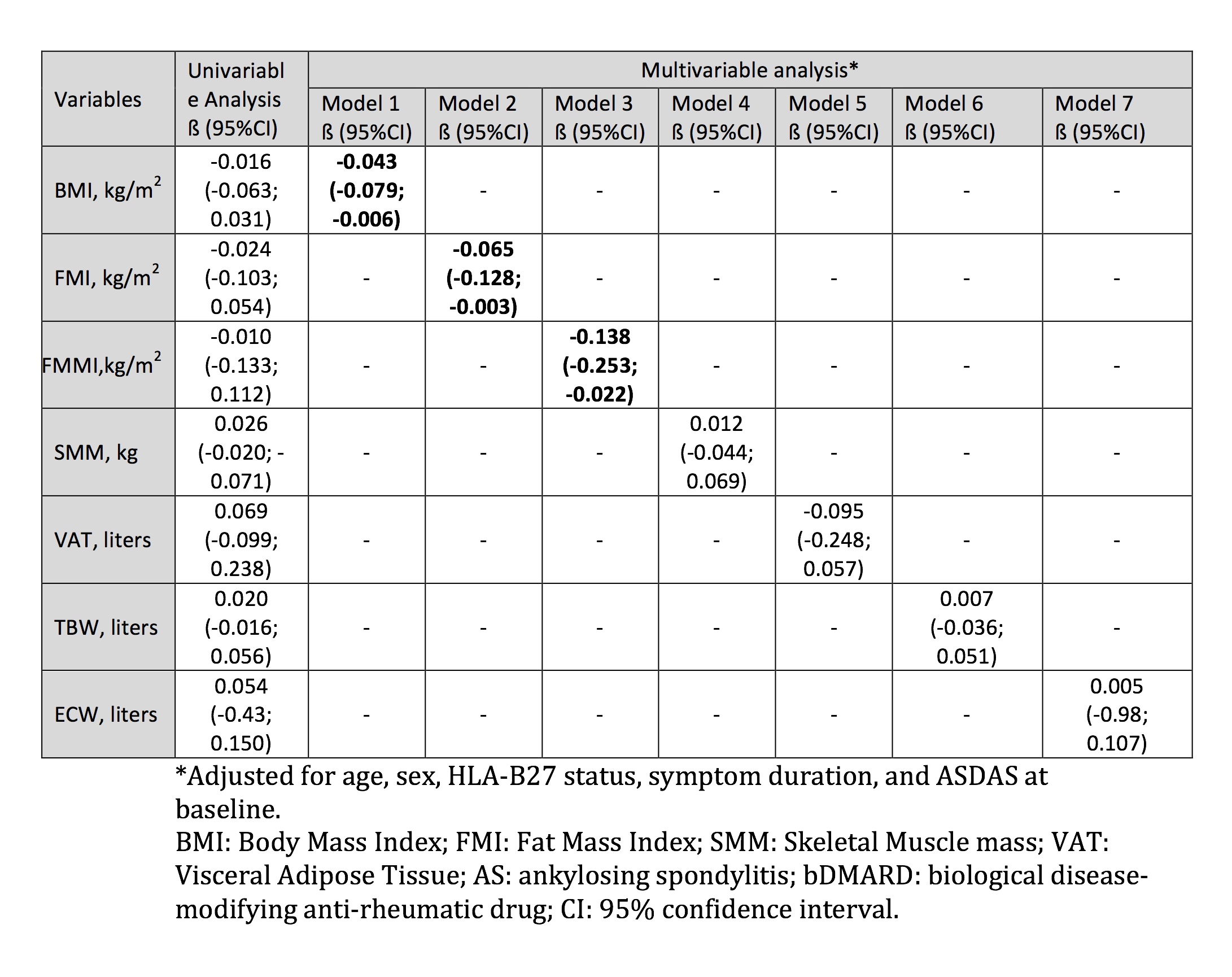 Table. Univariable and multivariable linear regression analysis of the association between response to bDMARD treatment (change in the ASDAS score after 6 months) and body composition parameters in patients with AS (n=77)
Table. Univariable and multivariable linear regression analysis of the association between response to bDMARD treatment (change in the ASDAS score after 6 months) and body composition parameters in patients with AS (n=77)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rios Rodriguez V, Protopopov M, Proft F, Rademacher J, Muche B, Weber A, Lüders S, Haibel H, Verba M, Sieper J, Poddubnyy D. Impact of Body Composition Measures on the Response to Biological Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-body-composition-measures-on-the-response-to-biological-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-body-composition-measures-on-the-response-to-biological-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
