Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal antibody that simultaneously blocks IL-17A, IL-17F, and their heterodimer, key cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Unlike other therapies targeting IL-17A alone, BKZ has demonstrated rapid and sustained efficacy in both joint and skin manifestations in clinical trials. Benefits have been observed in both biologic-naïve patients and those previously exposed to treatment, with a favorable safety profile. This study aims to broaden real-world experience with BKZ by evaluating its persistence, effectiveness, and patterns of use in routine clinical practice.
Methods: This is an observational, ambispective and multicenter study conducted in Spain. The study included patients >18 years diagnosed with SpA (according to ASAS classification criteria and/or the modified New York criteria) or PsA (according to CASPAR classification criteria) who initiated treatment with BKZ between January 1, 2024, and December 31, 2024. Demographic and clinical characteristics, as well as treatment patterns and response to BKZ were described using data from the electronic database. Changes in musculoskeletal (MSK) disease activity indices at 6 months and psoriasis (PsO) from baseline (start of BKZ treatment) were assessed.
Results: A total of 124 patients receiving BKZ were identified (41.1% SpA, 57.2% PsA), mainly women in both groups, with a median age of 53.6 ± 11 years and a long disease duration averaging 11.1 ± 9.3 years. Eleven patients presented active or previous neoplasms (8.8%). The most frequent MSK domain was mixed (peripheral and axial) in 44.3% of patients, and enthesitis was present in 52.9%, slightly more common in SpA. Patients had previously received a mean of 2.6 ± 2 b/tsDMARDs, mainly TNF inhibitors (85.4%) and IL-17 inhibitors (49.2%), with similar patterns in SpA and PsA. Most patients initiated BKZ as third-line therapy or beyond (67.7%), with concomitant DMARD use in nearly half of cases. The main reason for prescription was MSK involvement, though one-third also had active PsO (Table 2). At the 6-month follow-up (n=88/124 patients; 33 SpA, 55 PsA), an overall retention rate of 86.3% (n=76/88) for BKZ was observed, being greater in SpA (90.9%; n=30/33) compared to PsA (83.6%; n=46/55). BKZ was discontinued in 10 patients (3 SpA/ 8 PsA): 7 due to loss of effectiveness and 3 due to adverse events. Among the patients with effectiveness data available for MSK disease at 6 months (Table 2), 42% (45% PsA, 30,3% SpA) achieved low disease activity and 9% (3% SpA, 12,7% PsA) achieved remission. A significant improvement in MSK outcomes was observed across all axial and peripheral measures (axial and peripheral VAS, BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP, DAPSA, 68/66 joint counts all p< 0.01). In patients with PsO and data available, a significant (p< 0.01) reduction in PASI (n=20) and BSA (n=28) was observed at 6 months.
Conclusion: BKZ was mainly used in patients with long-standing, refractory SpA/PsA, with prior IL-17 inhibitor use in half of the cases. Despite this, the 6-month retention rate was high (86.3%), with favorable efficacy across all domains.
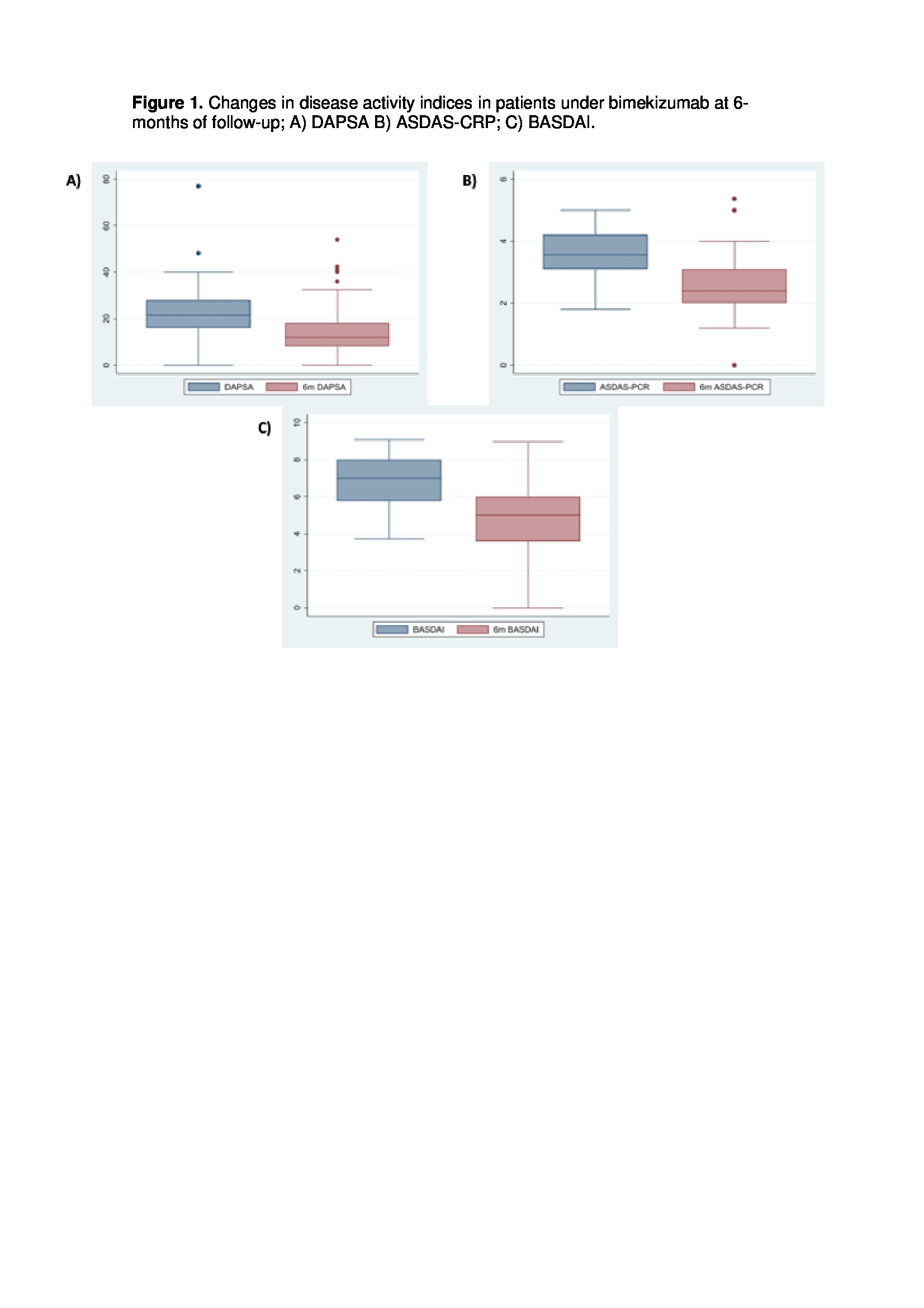 Table 1. Demographic, clinical and treatment-related characteristics at baseline
Table 1. Demographic, clinical and treatment-related characteristics at baseline
.jpg) Table 2. Bimekizumab treatment characteristics and disease activity data
Table 2. Bimekizumab treatment characteristics and disease activity data
.jpg) Figure 1. Changes in disease activity indices in patients under bimekizumab at 6-months of follow-up; A) DAPSA B) ASDAS-CRP; C) BASDAI.
Figure 1. Changes in disease activity indices in patients under bimekizumab at 6-months of follow-up; A) DAPSA B) ASDAS-CRP; C) BASDAI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Valero C, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Paredes Romero M, Montes S, Marin J, Rubio A, Macía-Villa C, Gonzalez Hombrado L, Gonzalez Gomez M, Ortega de la O M, Morcillo Valle M, Garcia Vicuña R, TOMERO MURIEL E, Peiteado D, JOVEN B. Impact of Bimekizumab Use in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis: Persistence Study in Routine Clinical Practice in Spain (BIMPACT study) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-bimekizumab-use-in-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-persistence-study-in-routine-clinical-practice-in-spain-bimpact-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-bimekizumab-use-in-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-persistence-study-in-routine-clinical-practice-in-spain-bimpact-study/
