Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Obesity is highly prevalent in PsA (~45%),1 and has previously been associated with a reduced response to TNF inhibitors.2 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA. This post hoc analysis assessed tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with PsA, by baseline (BL) BMI category.
Methods: Data were pooled from two placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind, Phase 3 studies in pts with active PsA and an inadequate response to ≥ 1 conventional synthetic DMARD (OPAL Broaden [12 months; NCT1877668]) or to ≥ 1 TNF inhibitor (OPAL Beyond [6 months; NCT01882439]).3,4 This analysis included pts randomized to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), tofacitinib 10 mg BID, or PBO, stratified by BL BMI: < 25 kg/m2, ≥ 25 – < 30 kg/m2, ≥ 30 – < 35 kg/m2, or ≥ 35 kg/m2. Efficacy and safety were reported to Month M3. Efficacy outcomes included ACR20/50/70, HAQ-DI, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI)75 responses, dactylitis and enthesitis absence rates, and changes from BL in Short Form-36 Version 2 (SF-36v2) Physical (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) scores at M3. Safety outcomes included adverse events (AEs), such as cardiovascular (CV) events, and changes in liver function tests (LFTs) and lipid levels.
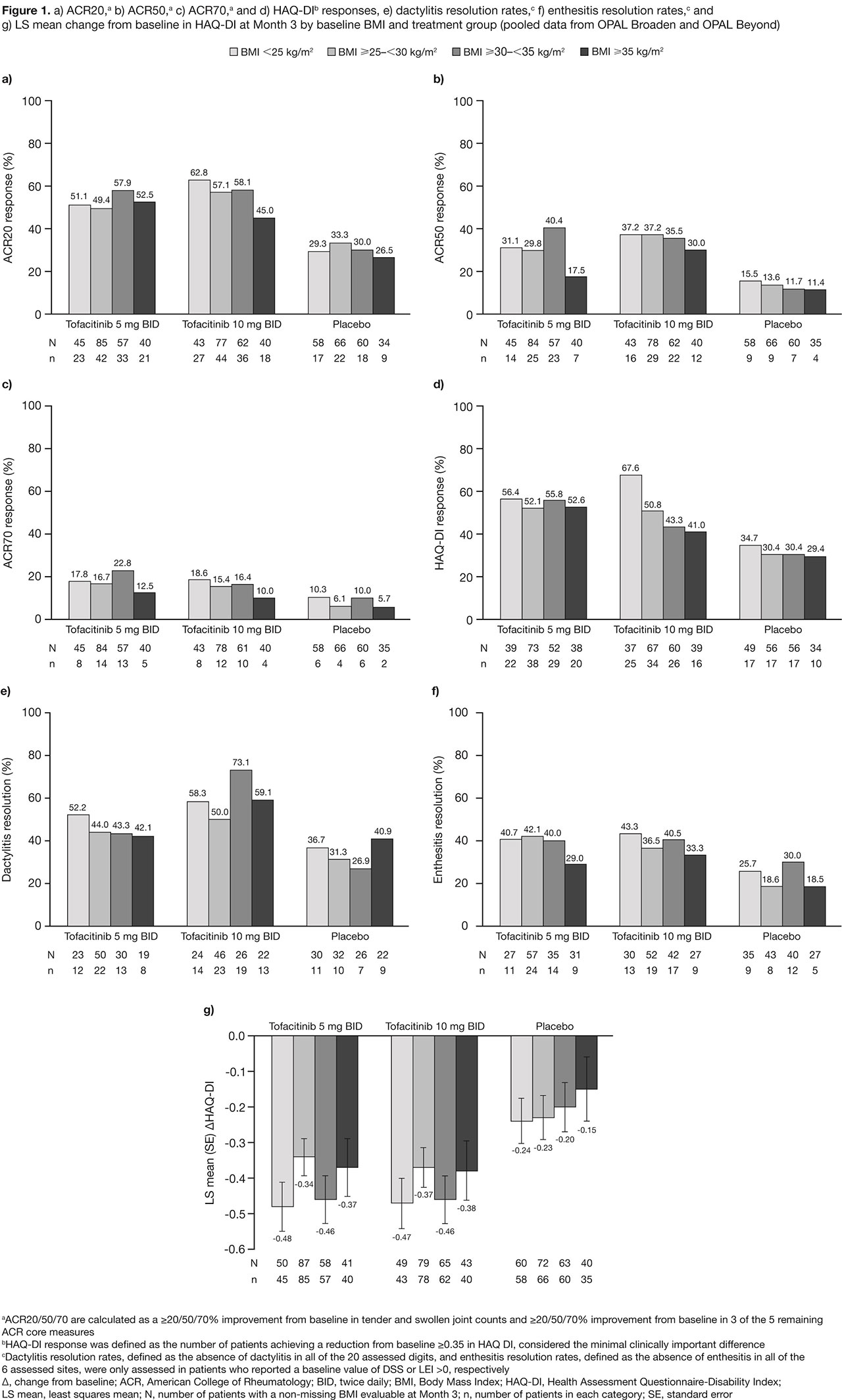
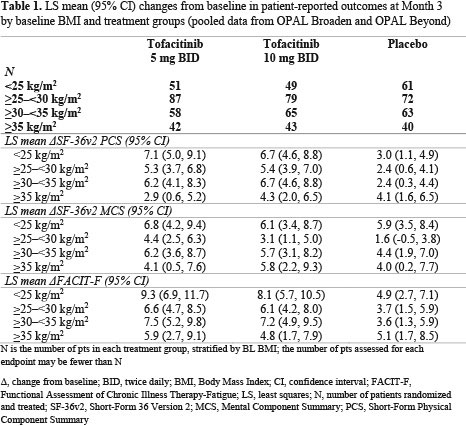
Results: This analysis included 710 pts; 43.8% were obese (BMI ≥ 30). At BL, 161 pts had a BMI < 25, 238 had a BMI ≥ 25 – < 30, 186 had a BMI ≥ 30 – < 35 and 125 had a BMI ≥ 35. Most pts were white (92.5–96.8%), middle-aged (44.5–51.2 yrs) and female (49.5–65.6%). Compared with the rest of the world, there were greater proportions of obese pts in Russia/Eastern Europe (35.1%) and US/Canada (31.8%). Higher BL BMI appeared correlated with increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome (4.3% in BMI < 25 to 76.0% in BMI ≥ 35) and CRP levels > 2.87 mg/L (49.1% in BMI < 25 to 84.0% in BMI ≥ 35). Higher proportions of pts (42.5–47.9%) in BL BMI categories < 35 reported no prior biologic DMARD use, vs pts with a BL BMI ≥ 35 (33.6%). At M3, efficacy improvements were generally greater in tofacitinib-treated pts, vs PBO-treated pts (Figure 1). In pts with a BL BMI ≥ 35, there was a trend towards fewer pts responding (Figure 1), and mean changes from baseline in SF-36v2 PCS, MCS and FACIT-F appeared lower (Table 1), vs pts in lower BL BMI categories. Up to M3, the proportions of pts with AEs, lipid levels, and percentage change from BL in LFTs, were generally similar across all BL BMI categories. There were three CV events: non-fatal cerebrovascular accident, transient ischemic attack (both tofacitinib 5 mg BID, BMI ≥ 30 – < 35), and artery revascularization (PBO; BMI ≥ 35).
Conclusion: Regardless of BL BMI, tofacitinib demonstrated greater efficacy than PBO in pts with PsA. Similar to other advanced therapies,2 reduced efficacy was generally observed in tofacitinib and PBO pts with a BL BMI ≥ 35. Tofacitinib safety appeared consistent across all BL BMI categories.
- Labitigan M et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2014;66:600-7.
- Singh S et al. PloS one 2018;13:e0195123-e0195123.
- Mease P et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1537-50.
- Gladman D et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1525-36.
Medical writing support was provided by Mark Bennett of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ritchlin C, Ogdie A, Giles J, Gomez-Reino J, Helliwell P, Stockert L, Young P, Joseph W, Mundayat R, Graham D, Woolcott J, Romero A. Impact of Baseline Body Mass Index on the Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-body-mass-index-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-body-mass-index-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/