Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Interstitial
lung disease (ILD) represents one of the most frequent causes of death in systemic
sclerosis (SSc) patients. Yet, there are no approved drugs for treatment of SSc-ILD.
At present, data on immunosuppressive therapy in patients with ILD and limited
cutaneous (lc) involvement are missing.
Methods:
The European
Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database was established in 2004 to annually
collect data on specialized care of patients with SSc. Data from patients with lc
SSc and ILD, where immunosuppressive therapy can be assumed to be mainly
intended to treat ILD, were analyzed to describe current use of immunosuppressants
and to recognize patterns of treatment choices.
Results:
Out of a
cohort of 12,536 SSc patients, we identified 1,814 adult patients fulfilling
the 1980 ACR or the 2013 ACR-EULAR criteria, with lc involvement and signs of ILD
(either on chest X-ray or high resolution computed tomography) with at least
one valid report on immunosuppressive treatment.
Mean age
was 58.7±13.1
years, with 88.9%
females and a mean SSc disease duration of 10.2±8.6 years. Mean mRSS was 6.1±4.7.
Compared to
the 1,119 (62%) patients who had at least one episode of immunosuppressive
therapy the 695 (38%) patients without use of immunosuppressants ever were on
average 5 years older, had a 2.4 years longer median disease duration, higher
DLCO (single breath) and FVC values and consequently less often a pulmonary
restrictive defect.
The
immunosuppressants most frequently used were prednisolone (pred; 52.6%),
azathioprine (aza; 13.9%), cyclophosphamide (cyc; 13.8%), methotrexate (mtx; 11.7%),
and mycophenolate mofetil (mmf; 11.0%); all others were prescribed in less than
2%. With regard to highest treatment intensity ever received, 31.6% of the patients
got monotherapies and 26.3% combinations of two drugs, while triple therapy was
comparably rare with 3.6%. Overall, immunosuppressive treatment was less
frequent than in diffuse cutaneous type (82%), this was true for mmf or cyc
monotherapy and any combination therapies.
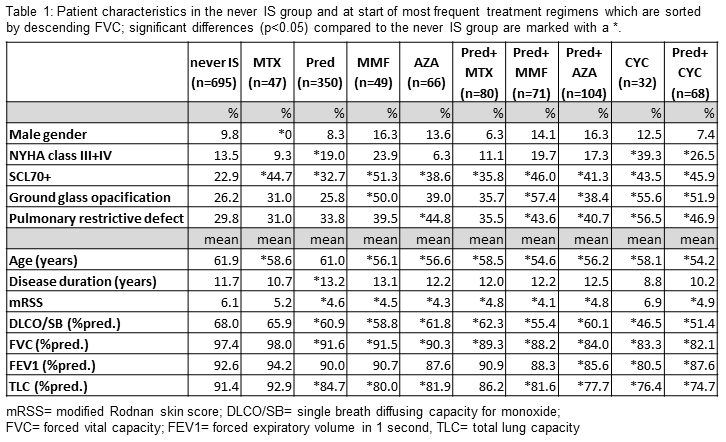
When comparing
patient characteristics at the treatment start of the most frequent regimens, differences
compared to the “never IS” group and between treatment arms become apparent
with regard to age, NYHA class, Scl70 antibodies, mRSS, ground glass
opacification, lung function parameters and the proportion with pulmonary
restrictive defect (table 1).
Conclusion:
“Everyday”
use of immunosuppressants is frequent in SSc-ILD patients with lc involvement,
showing a wide variety of single and combined immunosuppressive therapies with
distinct patient patterns between treatment regimens. However, prospective
studies are still necessary to define indications and outcomes. The EU-funded
international FP7 DeSScipher research project was initiated to achieve this
goal, comprising 5 prospective observational trials addressing the most
frequent medical problems in SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huscher D, Adler S, Siegert E, Abignano G, Allanore Y, Avouac J, Becker K, Czirjak L, Del Galdo F, Denton CP, Distler O, Foeldvari I, Garay-Toth B, Guiducci S, Jaeger VK, Lóránd V, Matucci-Cerinic M, Maurer B, Müller-Ladner U, Nihtyanova SI, Tarner IH, Valentini G, Vettori S, Walker UA, Riemekasten G. Immunosuppressive “Routine”� Treatment of SSc Patients with Limited Cutaneous Involvement and Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunosuppressive-routine%ef%bf%bd-treatment-of-ssc-patients-with-limited-cutaneous-involvement-and-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunosuppressive-routine%ef%bf%bd-treatment-of-ssc-patients-with-limited-cutaneous-involvement-and-interstitial-lung-disease/