Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) including their granulocyte (Gr-MDSCs) and monocyte (Mo-MDSCs) subtypes constitute a cellular subset with potent immune regulatory capacity. An augmented proportion of MDSCs has been described in patients with cancer, infections and autoimmune diseases, nevertheless the presence of MDSCs in Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) has not been explored. The aim of this study is to evaluate the proportion of myeloid derived suppressor cells and their relationship with clinical characteristics of patients with IIM.
Methods: Twenty-two adult patients with the diagnosis of IIM according to the ACR/EULAR criteria and active disease were recruited. The disease activity, damage accrual and disability were evaluated with the myositis disease activity assessment tool (MDAAT), the manual muscle test 8 (MMT8), the myositis damage index (MDI) and the health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). MDSCs were measured by flow cytometry in the peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) fraction after separation of blood with density gradients. Gr-MDSCs were defined as those CD33dim, CD11b+, CD66b+, HLA-DR–. Gr-MDSCs were classified as mature if they expressed CD16 (CD16+) and immature if they were CD16–. Mo-MDSCs were defined as those CD33+, HLA-DR– and CD14+. Also, the proportion and expression of arginase 1+ and PDL1+ in MDSCs was evaluated by their mean fluorescence intensity. The proportion of MDSCs and their expression of arginase 1 and PDL1 was compared with 14 healthy donors. Quantitative variables were expressed as medians and interquartile range (IQR). The difference between independent medians was assessed with the Mann-Whitney U test and the correlation between variables was evaluated with the Spearman Rho.
Results: Twelve patients with IIM were women (54.5%). The median of age was 40 (26-42.5) years and patients had a time since diagnosis of 6 (4.5-9.75) months. The most frequent diagnosis was dermatomyositis (72.7%) and most patients had positive anti-Ro52 (36.4%), anti-MDA5 and anti-Mi2 (18.2% each) antibodies. At the time of evaluation 68.2% of patients were taking prednisone, 31.8% methotrexate, 9.1% azathioprine, 18.2% mycophenolate mofetil and 31.8% hydroxychloroquine. Sixteen patients (76.2%) had cutaneous manifestations, 47.6% had dysphagia and 23.8% had interstitial lung disease. Five healthy donors were women (35.7%). The median of age was 27.5 (25-33) years. There was not a statistically significant difference in the age and gender of the study groups.
As shown in table 1, the proportion of MDSCs and their expression of arginase 1 and PDL1 was higher in patients with IIM, except for the proportion of Mo-MDSCs. The proportion of immature Gr-MDSCs was correlated with the cutaneous damage (Rho=0.486, P=0.048). There was not a relationship between immunosuppressive therapy and MDSCs.
Conclusion: Patients with IIM have a higher proportion of Gr-MDSCs with an immature phenotype and a higher expression of arginase 1 and PDL1+. Further studies are required to evaluate their suppressor capacity and their relationship with other clinical features including the presence of neoplasia.
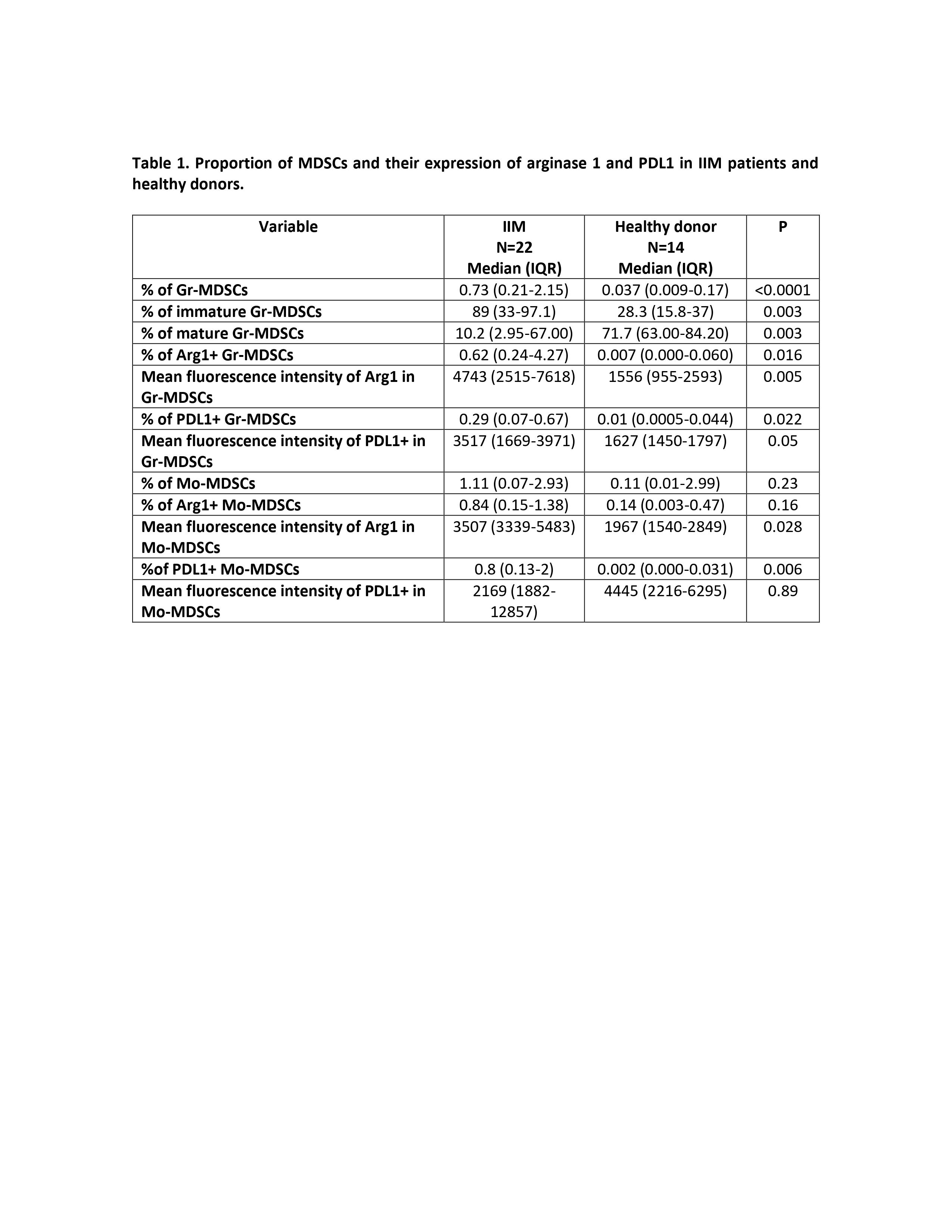 Table 1. Proportion of MDSCs and their expression of arginase 1 and PDL1 in IIM patients and healthy donors.
Table 1. Proportion of MDSCs and their expression of arginase 1 and PDL1 in IIM patients and healthy donors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Culebro H, Torres-Ruiz J, Cassiano Quezada F, Perez Fragoso A. Immunophenotypic Characterization of Myeloid Derived Supressor Cells (MDSCs) and Their Relationship to the Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunophenotypic-characterization-of-myeloid-derived-supressor-cells-mdscs-and-their-relationship-to-the-clinical-characteristics-of-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunophenotypic-characterization-of-myeloid-derived-supressor-cells-mdscs-and-their-relationship-to-the-clinical-characteristics-of-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathies/
