Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a condition characterized by a sepsis-like condition and laboratory abnormalities such as high ferritin, low ESR, and low fibrinogen which has a mortality rate of up to 60%. Patients with SARS-CoV-2 can develop CRS (SARS-CoV-2-CRS). There have been reports of features of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, lupus and Kawasaki disease occurring in SARS-CoV-2 patients, but no other study has looked at these features in patients with CRS. Studies are needed to determine if immunological laboratory abnormalities occur in SARS-CoV-2-CRS patients, and can help predict poor outcomes. Institution-mandated rheumatology treatment protocols for SARS-CoV-2-CRS were developed at a university medical center and county Hospital (Figure 1, Table 1). This study aims to establish if immunological abnormalities and poorer outcomes are present in SARS-CoV-2-CRS patients when compared to those without CRS.
Methods: SARS-CoV-2 patients referred to Rheumatology SARS-CoV-2-CRS for CRS evaluation (March 15-May 30, 2020) were included in this retrospective chart review. Demographics (age, sex, and ethnicity) and histories of diabetes, autoimmune disease, and medications were noted. Laboratory data reviewed included white blood cell count, hemoglobin, platelets, ferritin, fibrinogen, liver enzymes, complement, immunoglobulin levels, antinuclear antibody and antiphospholipid antibody panels and interleukin 6. Clinical outcomes tracked included oxygen and ventilation requirements, development of infections, and mortality. Descriptive statistics were used.
Results: 150 patients were included in this chart review. Majority were 109 (73%) males, with a mean age of 61.6. 28 (19%) were health facility residents, 11 (7%) health care workers, and 34 (23%) inmates. Ethnicities included 44 (30%) white non-Hispanic, 64 (43%) Hispanic, 24 (16%) Asian, 14 (9%) Black, and 2 (1%) other. 71 (47%) of patients were diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2-CRS. Compared to patients without CRS, greater proportions of patients with CRS were noted to have lower Ig, complement and platelet levels, higher liver enzyme, triglyceride, ferritin, IL6 and IL2 receptor levels, positive antiphospholipid antibody tests, (Table 2). Bacterial co-infections were actually higher among non-CRS patients. CRS patients had a higher rate of death and thrombosis compared to those without CRS.
Conclusion: A larger proportion of SARS-CoV-2-patients who developed CRS had certain immunological laboratory abnormalities when compared to those without CRS. This data serves as preliminary analysis of an ongoing study. More detailed analysis of categorized deviations of laboratory abnormalities relative to the timed occurrence of adverse outcomes (i.e. death) and to the use of therapies, and how these correlate with other features such as physical exam findings and imaging results are needed. Autopsy data also need to be included. Follow up of survivors are being done to determine if these abnormalities persist, and if other clinical features suggestive of autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency disorders develop.
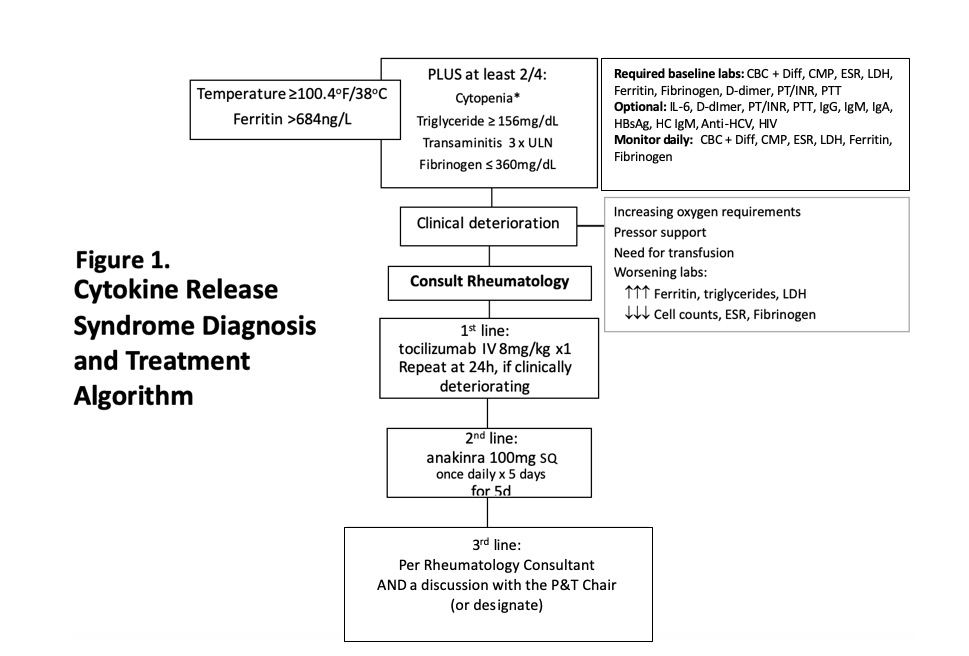 Figure 1. Cytokine Release Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm
Figure 1. Cytokine Release Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm
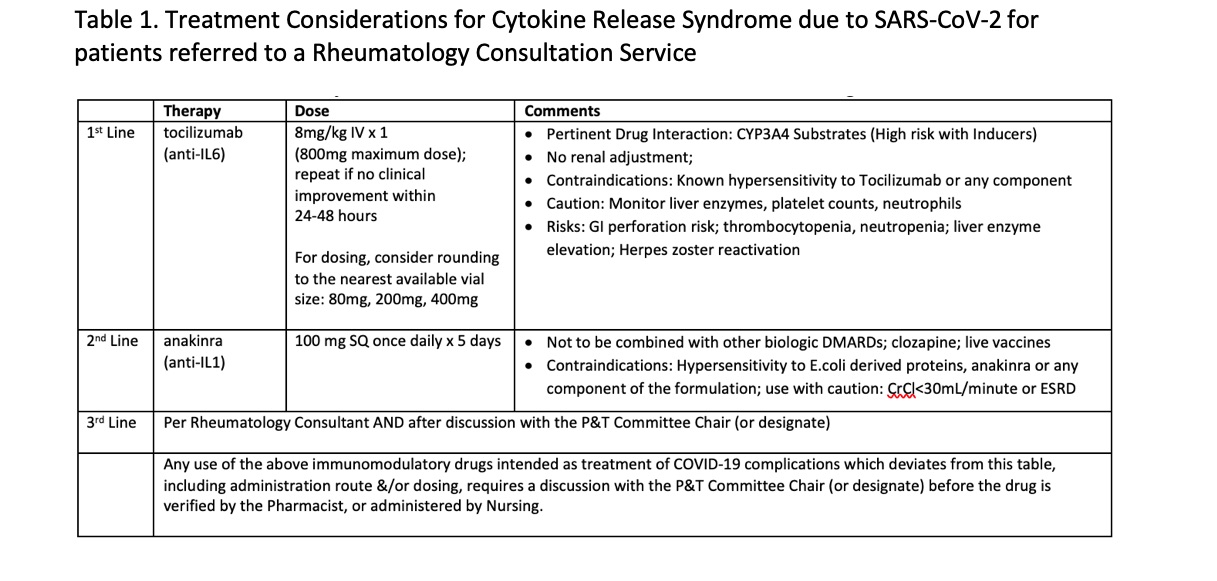 Table 1.Treatment Considerations for Cytokine Release Syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 for patients referred to a Rheumatology Consultation Service
Table 1.Treatment Considerations for Cytokine Release Syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 for patients referred to a Rheumatology Consultation Service
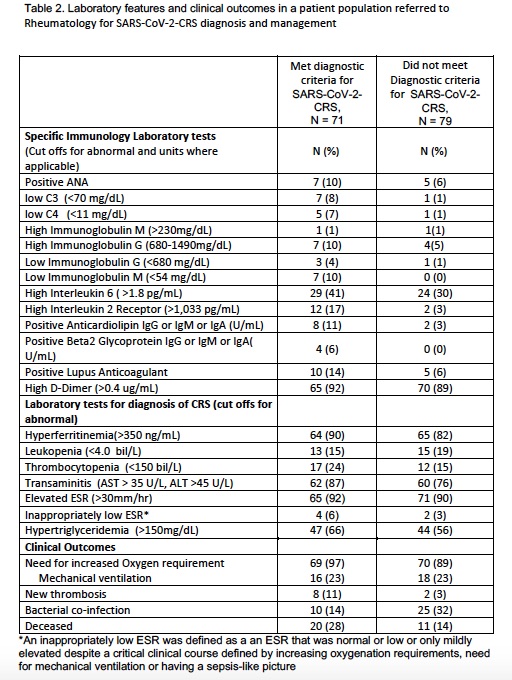 Table 2. Laboratory features and clinical outcomes in a patient population referred to Rheumatology for SARS-CoV-2-CRS diagnosis and management
Table 2. Laboratory features and clinical outcomes in a patient population referred to Rheumatology for SARS-CoV-2-CRS diagnosis and management
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Injean P, Lee S, Chiruvolu N, Karim M, Doo L, Ragesh Panikkath D, Jose D, Yu M, Lafian A, Sandhu V, Torralba K, Downey C, Cabling M, Hojjati M. Immunological Abnormalities in a SARS-CoV-2-Cytokine Release Syndrome Rheumatology Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunological-abnormalities-in-a-sars-cov-2-cytokine-release-syndrome-rheumatology-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunological-abnormalities-in-a-sars-cov-2-cytokine-release-syndrome-rheumatology-cohort/
