Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster II: Co-morbidities and Complications
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Citrullinated BiP is a newly described target for cyclic citrullinated peptide(CCP). BiP in both serum and synovial fluid is over-expressed in RA patients and correlates with CCP1. Serum BiP causes T cell expansion and increases interferon during incubation of the QuantiFERON-Gold tuberculosis in-tube test (QFT-G TB) which can result in a false positive TB test. The QFT-G TB has never been validated where interferon is increased, as for example RA.
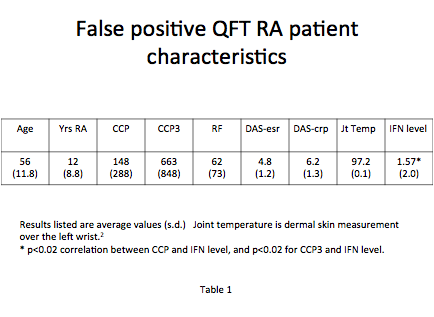
Methods: Positive CCP RA patients (n=126) were tested prior to initiating biologic therapy with QFT-G TB (Cellestis). TB evaluation at baseline and annually for two years included history, physical, standard blood tests, chest radiograph, PPD and control skin testing. RA patients had CCP, RF, Wesr, CRP, DAS, wrist temperature, tender and swollen joint counts at baseline (table 1). Three healthy middle-aged female controls with no arthritis were tested with QFT-G TB. Their serum was later tested with BiP added, with 2 ug/ml, 5ug/ml, 10ug/ml, and 20ug/ml, levels seen in RA. (Sourced BiP Novus Biologicals.)
Results: Of 126 CCP+ patients, 16 tested positive for TB (13%) by QFT-G TB, despite no known risk factors for TB (no travel, low endemic rural area, no exposure history), negative chest radiograph, negative PPD with positive candida control, normal blood testing, no symptoms or signs of TB. The CDC established local TB rate is 0.0007%. All 16 had high levels of CCP and active inflammation (mean DAS-esr 6.17). With consultation of an Infectious Disease specialist, all 16 patients received biologic therapy with no INH prophylaxis. In follow up after 24 months, none developed TB and QFT-G TB reverted to negative in 5 patients, correlating with the RA control on biologic therapy. (The other 11 did not have repeat QFT-G.) Mean QFT-G interferon levels in test tubes were 1.57 IU for TB, 0.18 IU for nil, and >10 IU for the mitogen tube. Positive TB defined by the lab kit was > 0.35 IU. False TB interferon levels correlated with CCP level (p<0.02). Three healthy women with no arthritis or TB exposure had negative QFT-G TB. These three subjects tested positive every time for TB correlating to the dose of BiP added, at concentrations of 2 ug/ml, 5 ug/ml, 10 ug/ml, and 20 ug/ml (fig 1).
Conclusion: BiP is naturally found in the majority of CCP+RA patients and presence of BiP in serum can result in a false positive QFT-G TB. Patients with the highest CCP had the highest QFT-G TB interferon levels. Subsequent undertreatment of RA, if biologic therapy is withheld, and overtreatment of presumed latent TB may harm patients. 1. Arth Rheum 2015;67:1171-1181.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ball J, Greenwald K, Deodhar AA, Winthrop KL. Immunoglobulin Binding Protein (BiP), an Antigen for CCP Sero-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Can Result in a False Positive Quantiferon-Gold Tuberculosis Test [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunoglobulin-binding-protein-bip-an-antigen-for-ccp-sero-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-can-result-in-a-false-positive-quantiferon-gold-tuberculosis-test/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunoglobulin-binding-protein-bip-an-antigen-for-ccp-sero-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-can-result-in-a-false-positive-quantiferon-gold-tuberculosis-test/