Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Power doppler ultrasound (PDUS) is superior to clinical examination in the detection of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although dynamic and cheap it is impractical to scan large numbers of joints in routine clinical settings. MRI, whilst sensitive for synovitis, is expensive, and routine use is limited to targeted joints. Bone scintigraphy produces whole body images but due to lower specificity is not routinely used to detect synovitis
99mTc-maraciclatide (Serac Healthcare) is a radio-labelled tracer which binds with high affinity to integrin αvβ3, a cell-adhesion molecule up-regulated on neoangiogenic blood vessels. It therefore has the potential to image synovial inflammation at the whole-body level. We previously showed in a pilot study that uptake was seen in the inflamed joints of 5 RA patients and that this correlated with PDUS1. This study explores correlation with PDUS in a larger groups of patients with a range of disease activities
Methods: 25 patients with RA, fulfilling ACR 2010 classification criteria, were recruited. Patients underwent 66/68 swollen/tender joint counts followed by an ultrasound scan of 38 joints with grey scale (GS) and PD quantification. As per OMERACT guidelines, each joint was scored on a scale of 0-3 for GS and PD with a total score calculated for each patient. Within 3 hours of the ultrasound, patients were injected with 740 MBq of 99mTc-maraciclatide. Using a gamma camera, whole body planar views and dedicated hand and foot views were taken 2 hours after injection. Acquisition time was 20 minutes for whole body, and 20 minutes for hand and foot views. Nuclear medicine images were scored as positive or negative uptake for each joint (binary score). Binary scores were summed individually to derive a total score for each patient. Ultrasound and 99mTc-maraciclatide scores were tested for correlation with Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Significance was set at p< 0.05
Results: Strong correlation was seen between total PDUS and binary scores (r=0.93, r2=0.86, p< 0.001). In the wrists and ankles 99mTc-maraciclatide uptake was seen not only in synovitic joints but in inflamed tendons/ tendon sheaths. The imaging procedure was well-tolerated
Conclusion: 99mTc-maraciclatide uptake was highly correlated with PDUS highlighting its potential as a viable alternative imaging modality. 99mTc-based planar imaging has the unique capacity to image the whole body and hence the total synovial inflammatory load in a quick acquisition. Furthermore the imaging equipment to perform these scans is already widely available in nuclear imaging departments. Interpretation of scans is also much simpler compared to US and MRI. It could therefore have a role in key decision-making points in pathways for diagnosis, treatment failure, and remission prior to dose tapering. Recruitment is underway to expand the data to a larger group of patients
Reference:
1. Garrood T, Morrison M, Shivapatham D, Chaabo K, Ul-Hassan F, Ballinger J, Cook G, Cope AP. Whole-Body Synovial Uptake of a 99mtc-Labelled RGD Peptide Is Highly Correlated with Power Doppler Ultrasound [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10)
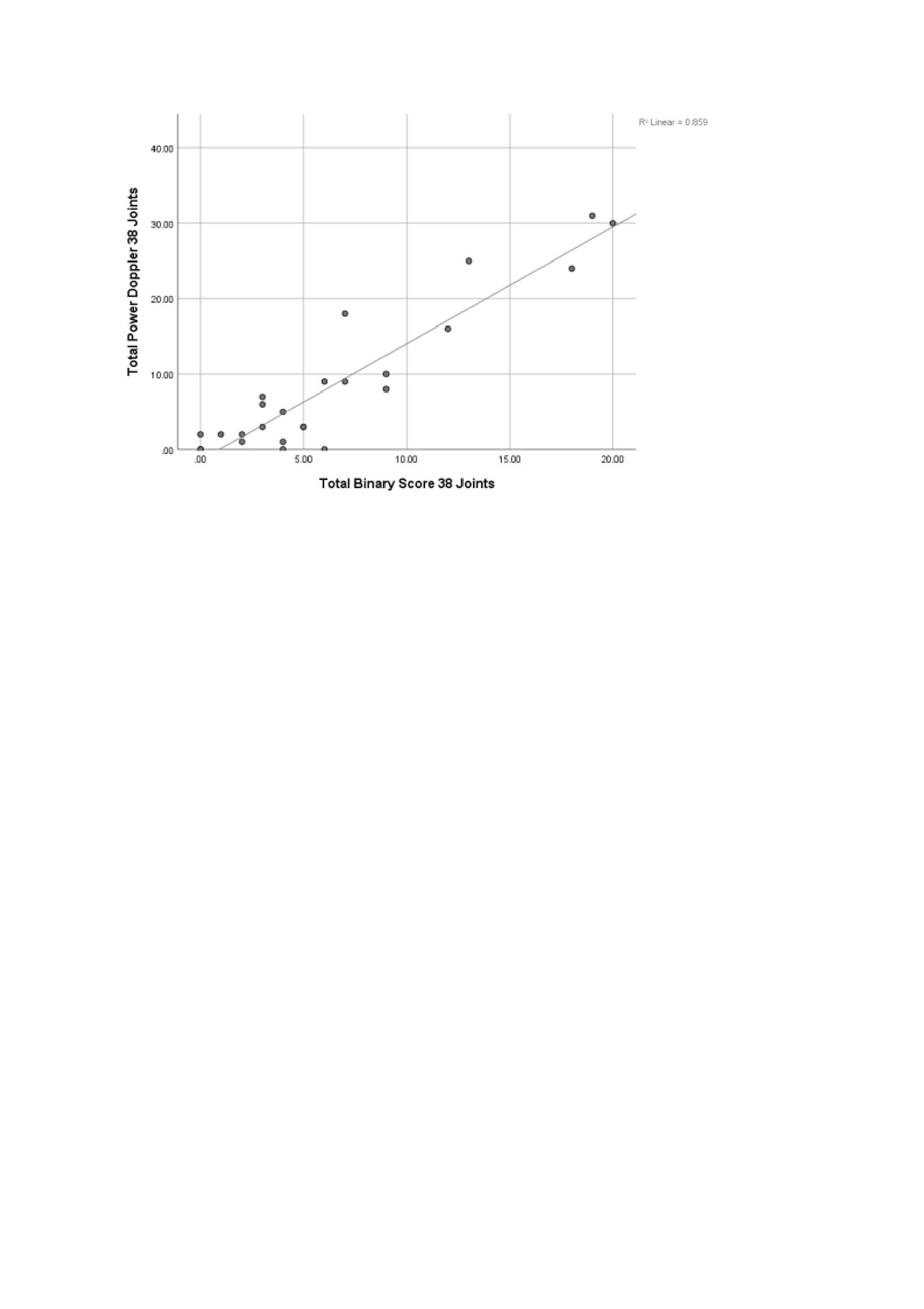
figure 1 pd vs binary acr 2019
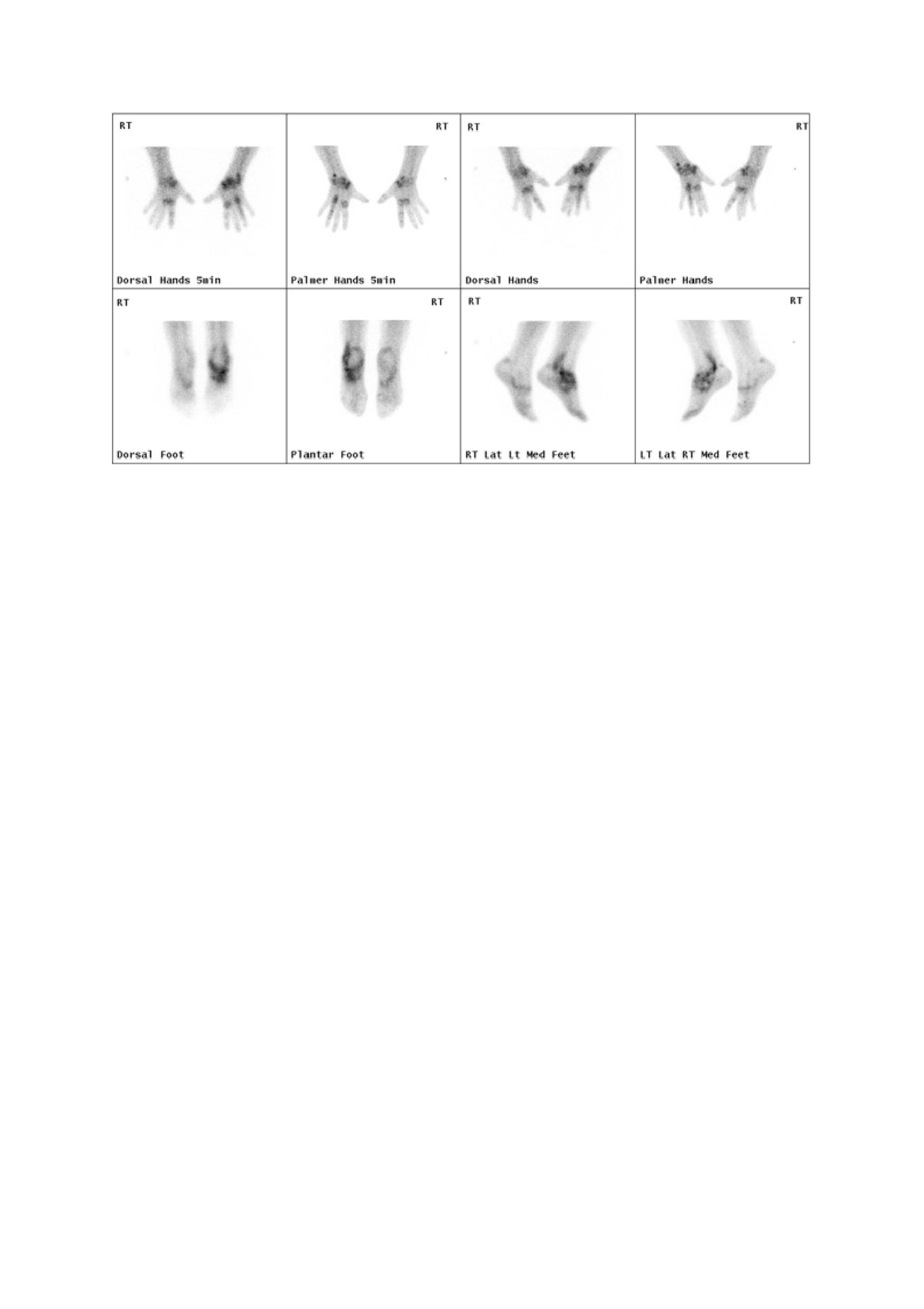
figure 2 hand and foot images acr 2019
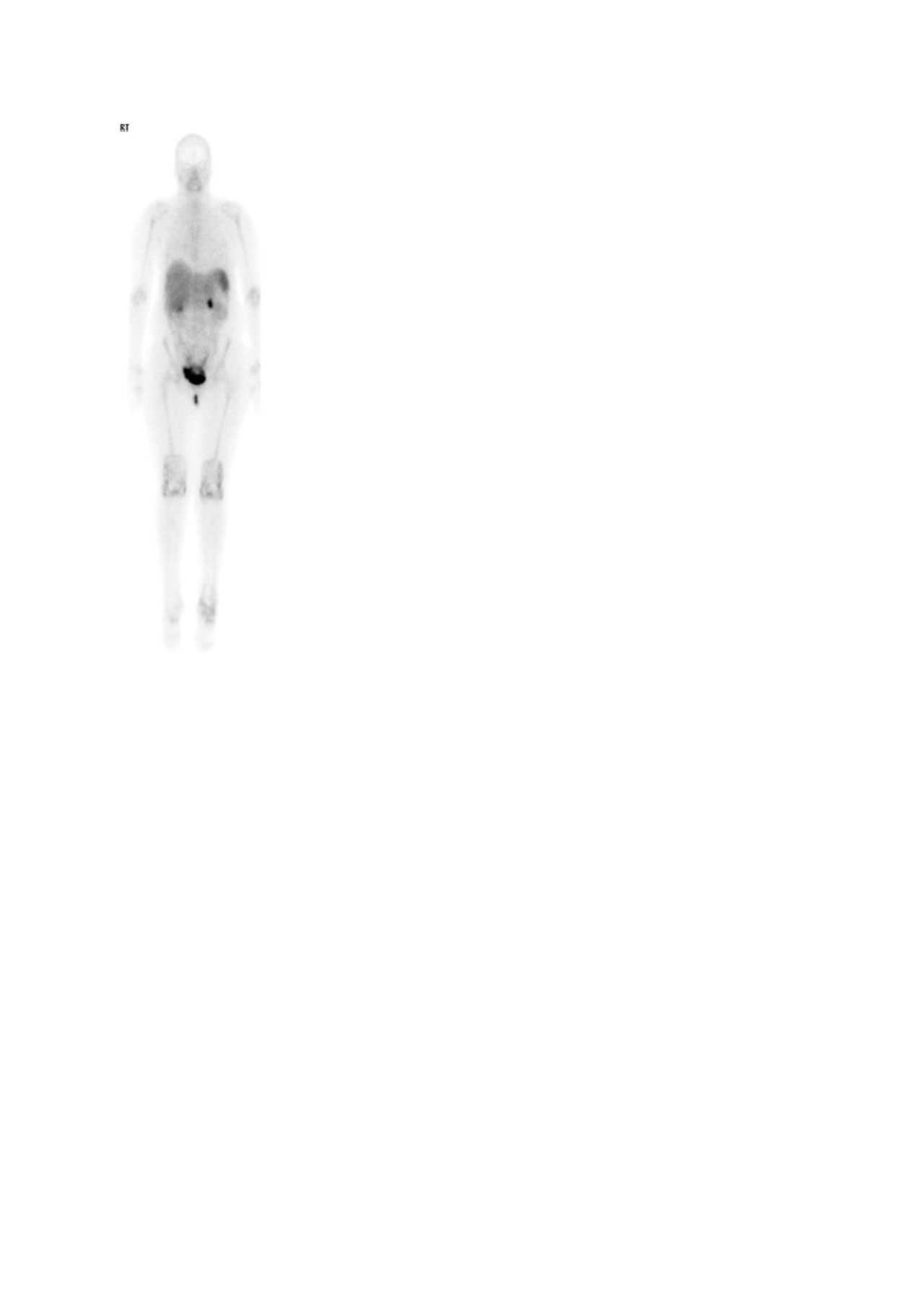

figure 3 whole body image acr 2019
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Attipoe L, Garrood T, Subesinghe S, Opena M, Blanco-Gil C, Rosser M, Cook G, Cope A. Imaging Neoangiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis (INIRA): Whole-Body Synovial Uptake of a 99mTc-Labelled RGD Peptide Is Highly Correlated with Power Doppler Ultrasound [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-inira-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-a-99mtc-labelled-rgd-peptide-is-highly-correlated-with-power-doppler-ultrasound/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-inira-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-a-99mtc-labelled-rgd-peptide-is-highly-correlated-with-power-doppler-ultrasound/
