Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:15AM-11:30AM
Background/Purpose: The heel is a frequently affected anatomical site for enthesitis in spondyloarthritis (SpA).1 Recently, the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) group developed and validated the Heel Enthesitis MRI Scoring system (HEMRIS) that takes both inflammatory and structural features of enthesitis into account.2 ACHILLES (NCT02771210) is a prospective randomized controlled trial, investigating both clinical and imaging endpoints in patients (pts) with SpA and heel enthesitis.3 Here, we report a post hoc analysis applying HEMRIS system in blinded and centrally read MRI data of the heel from the ACHILLES trial (N=204).
Methods: ACHILLES included pts (≥18 years) with active psoriatic arthritis or axial SpA, with clinical and MRI-positive heel enthesitis, refractory to standard treatment (either Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or Tumor necrosis factor-inhibitors). Pts were randomized to receive s.c. secukinumab (SEC) 150 mg, 300 mg or placebo (PBO) at baseline, Weeks (Wks) 1, 2, 3, and 4, followed by once every 4 wks. At Wk 24, pts on PBO were switched to SEC 150 or 300 mg. MRI-positive heel enthesitis was confirmed in all pts by local investigators and was defined as tendinitis and/or bone marrow edema (BME) in the area of the Achilles’ tendon and/or the plantar aponeurosis. MRIs were performed at three time points: screening (SCR), Wks 24, and 52. In the present analysis, all MRIs were re-evaluated by two blinded central readers in a consensus read fashion for a priori defined MRI parameters based on HEMRIS system.
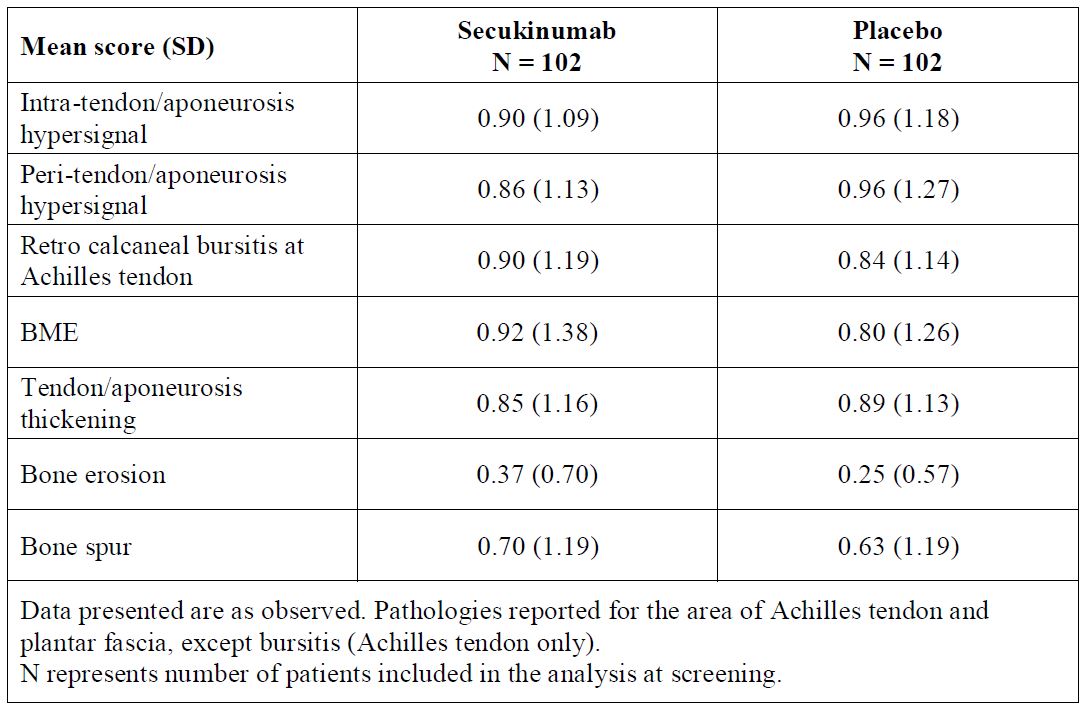
Results: Structural and inflammatory parameters at SCR are shown in Figure. At SCR, 156/204 (76.5%) pts presented with total entheseal inflammation score >0, 131/204 (64.2%) with total structural damage score >0, and 171/204 (83.8 %) with any entheseal inflammation and/or structural damage, considering both Achilles tendon and plantar fascia. The mean total entheseal inflammation score at SCR was 3.58 (N=204) and the mean change (SD) from SCR to Wk 24 and to Wk 52 was -1.05 (2.11) and -1.26 (2.28) in the SEC group vs -0.74 (2.21) and -1.17 (2.73) in the placebo group, respectively. The mean total structural damage score at SCR was 1.85 (N=204) and the mean change (SD) from SCR to Wk 24 and to Wk 52 was -0.01 (0.71) and -0.09 (0.66) in the SEC group vs 0.12 (0.56) and 0.06 (0.83) in the PBO-SEC group, respectively. Mean scores at SCR and mean change over time for individual parameters are given in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively.
Conclusion: Based on the newly developed HEMRIS system, entheseal inflammation and/or structural damage was not confirmed for 16.2% of pts with SpA enrolled in the ACHILLES trial. The mean improvements in total inflammation and total structural damage scores were higher in the SEC-treated pts compared to placebo. The observed magnitude of improvement for the SEC-treated pts was more pronounced for the peri-tendon/aponeurosis hypersignal, bursitis and bone erosion.
References:
1. Schett G, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13:731–41.
2. Mathew AJ, et al. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:1232–8.
3. Behrens F, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71 (suppl 10). Abstract 2503.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Sewerin P, De Miguel E, Pournara E, Kleinmond C, Shekhawat A, Wiedon A, Behrens F. Imaging Characteristics in Patients with Spondyloarthritis Using a Novel Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring (HEMRIS) System: Post-hoc Analysis of a Phase 3 Secukinumab Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-characteristics-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-using-a-novel-heel-enthesitis-magnetic-resonance-imaging-scoring-hemris-system-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3-secukinumab-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-characteristics-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-using-a-novel-heel-enthesitis-magnetic-resonance-imaging-scoring-hemris-system-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3-secukinumab-trial/