Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
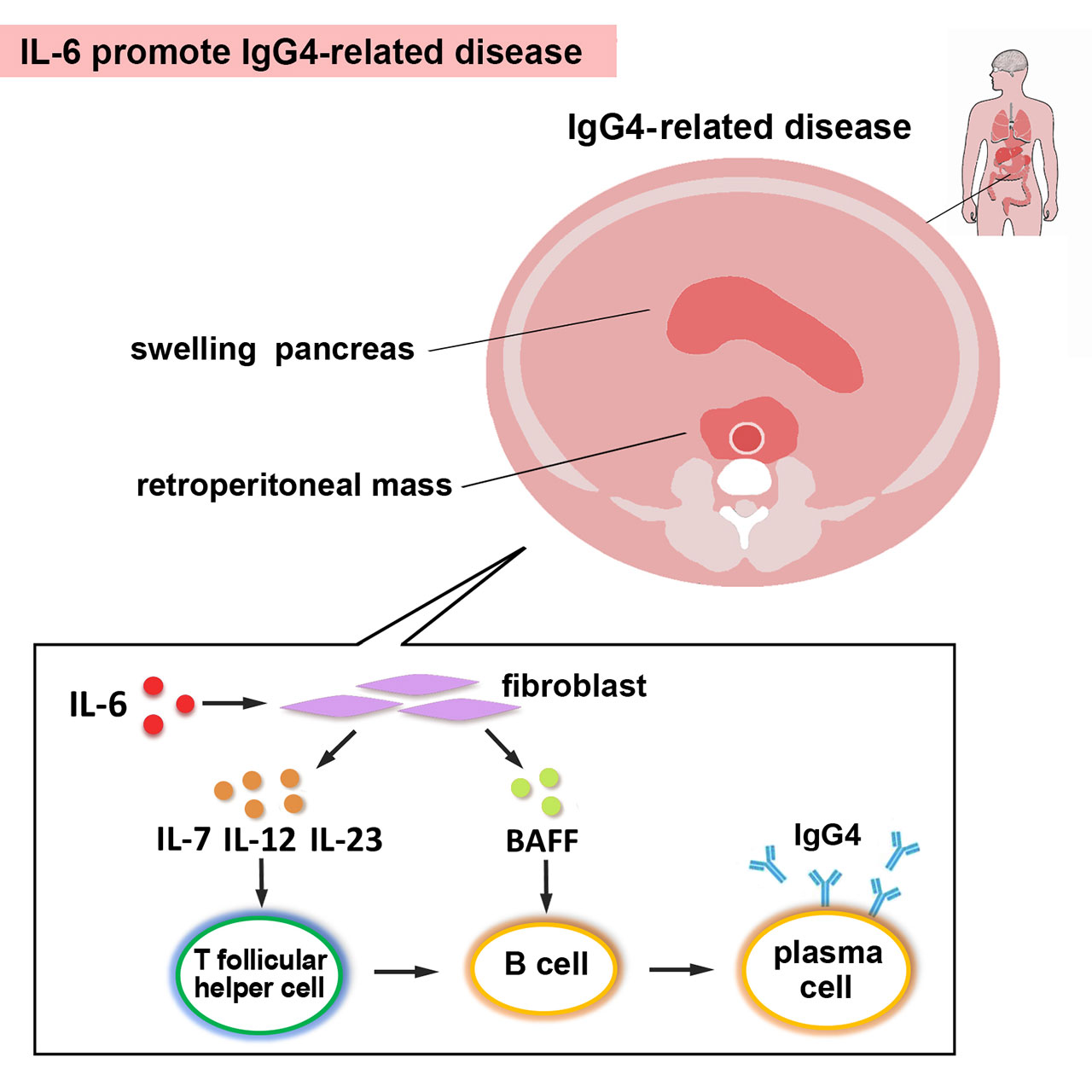
Background/Purpose: Considering the unsatisfied effect of conventional therapy, to investigate the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is crucial to explore novel treatment strategies. This study aims to clarify the pathogenesis of interleukin 6 (IL-6) in IgG4-RD through the induction of fibroblast-dependent Tfh cell and B cell differentiation factors and find the new therapeutic target.
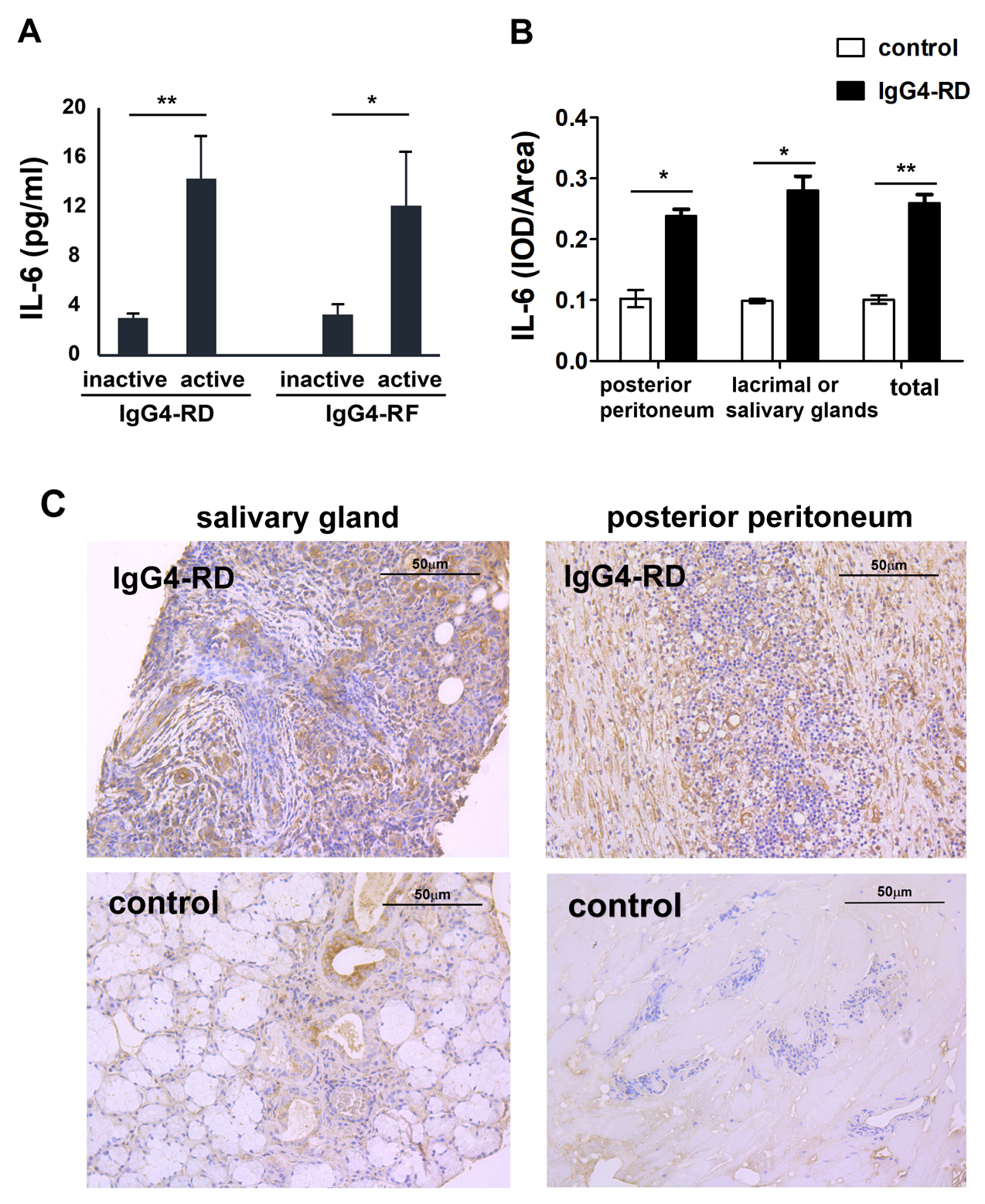
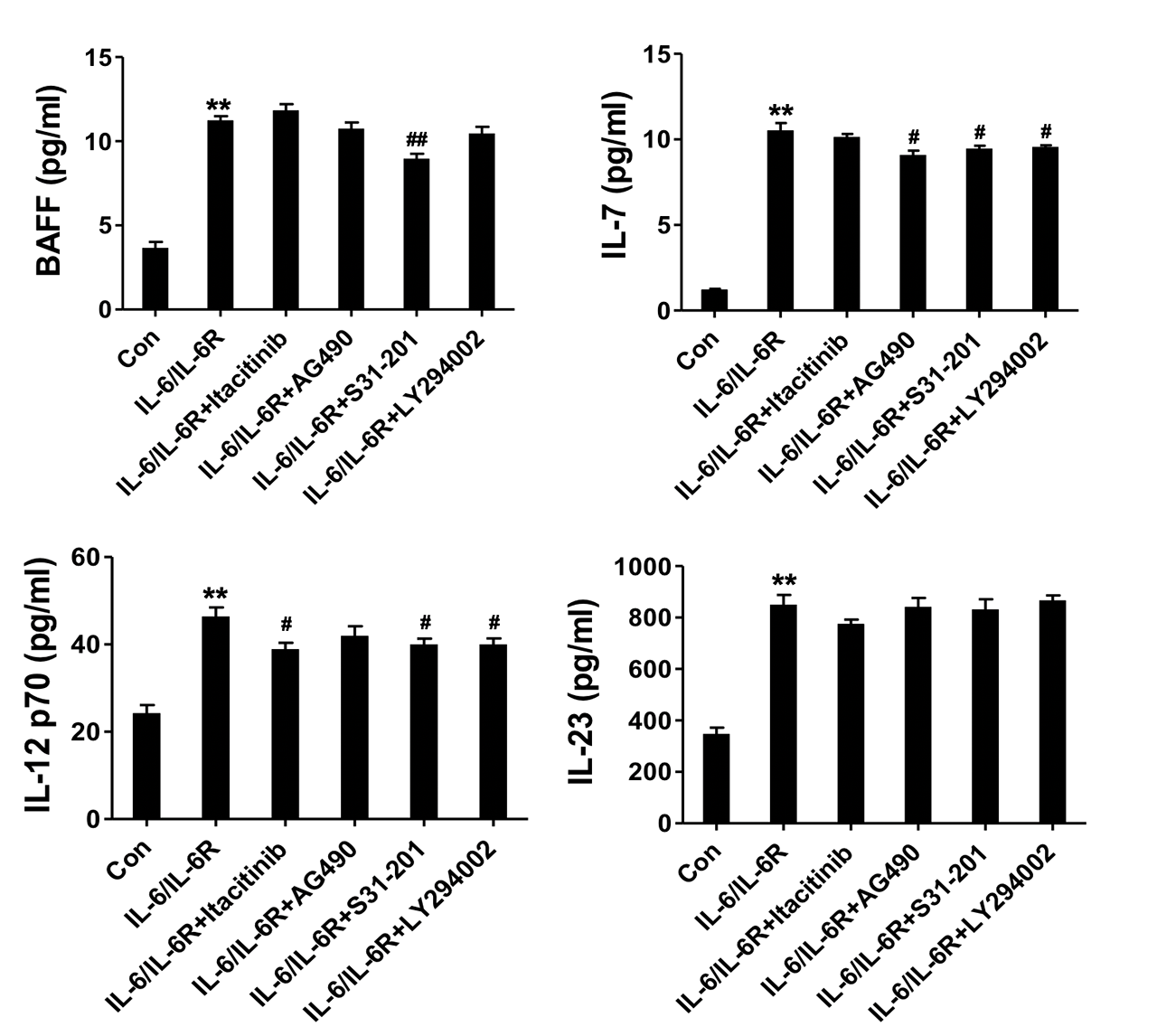
Methods: The IL-6 expression in the serum and tissues of patients with IgG4-RD and healthy controls were detected by ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, respectively. Human aorta adventitial fibroblasts (AAFs) were cultured and stimulated with IL-6/IL-6 receptor (IL-6R). The effect of IL-6/IL-6R on AAFs was determined by CCK-8 and Luminex assays.
Results: The level of serum IL-6 was elevated in active IgG4-RD patients and was positively correlated with IgG4-RD reactive index (RI). The expression of IL-6 in the tissue of IgG4-RD patients was also significantly higher than that in the normal tissue. IL-6-producing fibroblasts were found to co-localize with IgG4+ plasma cells in the tissue of IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis (IgG4-RF). Co-localization of α-SMA and B cell differentiation cytokines (i.e., B cell activating factor (BAFF)), α-SMA and T follicular helper (Tfh) cell differentiation cytokines (e.g., IL-7, IL-12, and IL-23) were present in the local lesions. IL-6/IL-6R significantly promoted the production of BAFF, IL-7, IL-12, and IL-23 in AAFs in a dose-dependent manner. This effect was blocked by JAK1, JAK2, STAT3, and Akt inhibitors, respectively.
Conclusion: IL-6 promotes IgG4-RD by inducing fibroblast-dependent Tfh and B cell differentiation factors via the JAK2/STAT3, JAK1/STAT3, and JAK2/Akt pathways. Thus, IL-6 and JAK1/2 inhibitors may be therapeutic targets for IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ji Z, Chen R, Cui X, Ma L, Kong X, Ma L, Sun Y, Dai X, Zhang Z, Chen H, Jiang L. IL-6 Promotes IgG4-related Disease by Inducing Fibroblast-dependent Tfh Cell and B Cell Differentiation Factors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-6-promotes-igg4-related-disease-by-inducing-fibroblast-dependent-tfh-cell-and-b-cell-differentiation-factors/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-6-promotes-igg4-related-disease-by-inducing-fibroblast-dependent-tfh-cell-and-b-cell-differentiation-factors/