Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The activation of the Th-1 and Th-17 lymphocytes response seems to be one of the causes associated with PsA onset. During this process cytokines like TNF-α and Il-6 play an important role in chronic inflammatory response. However, their role in clinical manifestations and comorbidity is less known.
Purpose: To relate the IL-6 and TNF-α serum levels with clinical spectrum, presence of dactylitis, enthesitis, disease activity and comorbidity in a group of patients with PsA.
Methods: A Cross-sectional study with 194 PsA patients (diagnosed by the CASPAR criteria). IL-6 and TNF-α serum levels were determined by ELISA. The clinical variables measured were: clinical spectrum (peripheral, axial or mixed), presence of dactylitis, enthesitis, psoriasis (measured by PASI score) and HLA-B27. Disease activity was measured with the minimal disease activity criteria (MDA). In regards to comorbidity, we measured cardiovascular risk markers such as waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), Apolipoprotein A, Apolipoprotein B, Lipoprotein A, Insulin, Insulin resistance and microalbuminuria; hepatic steatosis was measured by ultrasound and fatigue by FACIT-F questionnaire.
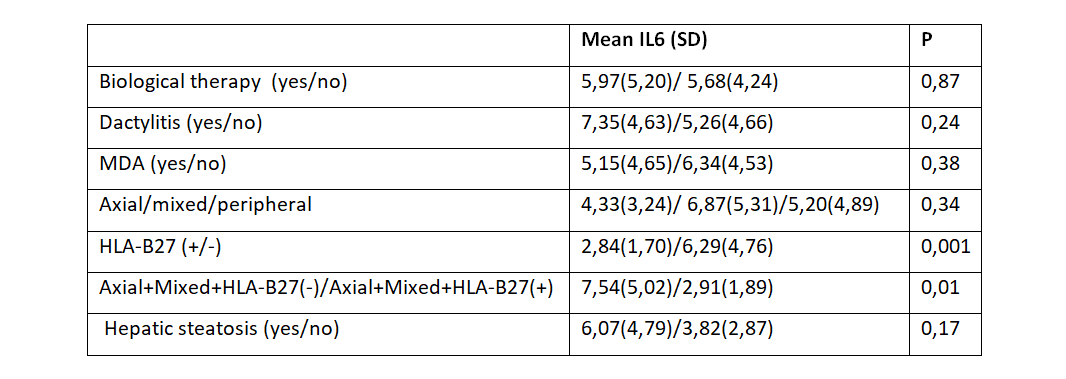
Results: Of the 194 patients, 107 were men (55.2%) and 87 (44.8%) female. The mean of age was 53.33 years (SD: 10.86). 14.9% were receiving biological therapy. Eighteen patients had an exclusive axial affectation, 72 mixed and 104 peripheral only. 17.5% were HLA-B27 positive and 52.1% had a MDA. Regarding IL-6, we found no correlation with the number of entheses affected, SJC, PASI, ESR, WHR, Apolipoprotein A, Apolipoprotein B, Lipoprotein A, Insulin, Insulin resistance, microalbuminuria, nor FACIT-F. We found a positive correlation between IL6 levels and CRP (R=0.41, p< 0.0001). The rest of the results are shown in Table1.
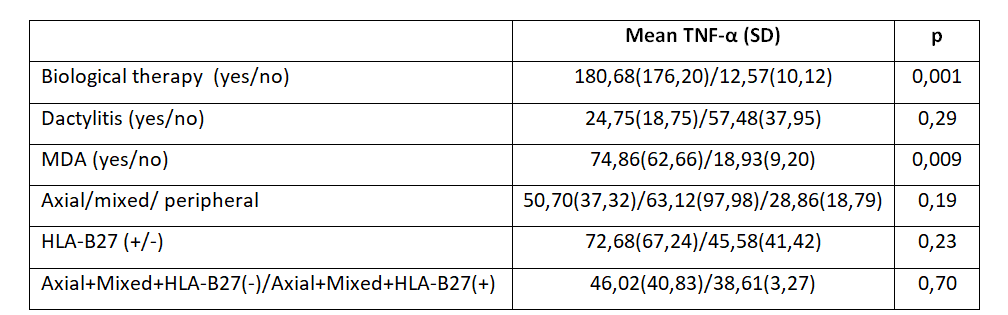
Regarding TNF-α, we found no correlation with number of entheses affected, SJC, PASI, ESR, CRP, WHR, Apolipoprotein A, Apolipoprotein B, Lipoprotein A, insulin, insulin resistance, microalbuminuria nor FACIT-F. The rest of the results are shown in Table2.
Due to the close correlation between the use of biologicals and TNF-α serum levels, we analyzed them between TNF-i and Ustekinumab/Secukinumab (242.18 SD: 207.71 vs. 32 SD: 27.32, p < 0.007). In the analysis excluding patients treated with biologicals, we only found a positive correlation with microalbuminuria (R:0.72, p< 0.001), even when excluding patients with a history of hypertension or diabetes (R: 0.37, p< 0.004). We found no correlation between IL-6 and TNF-α levels (R:-0.01, p< 0.85).
Conclusion: Excluding CRP, we found no correlation between IL-6 levels and clinical disease activity or comorbidity. In our results HLA-B27 influenced IL-6 levels, but it is unknown the pathogenesis on which this relationship is based, however findings that correlate IL-6 polymorphisms with HLA-B27 may indicate that the relationship obtained is not casual. On the other hand, blockade of TNF-α causes higher TNF-α serum levels. TNF-α was associated with subclinical kidney damage in PsA patients with or without diabetes. Even though this cytokine is known to be involved in kidney damage this correlation has not been documented in non-diabetic PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Acosta M, Gomez-Lechon L, Manzano Canabal G, Compan O, Hidalgo C, Martinez O, Turrión A, del Pino J, Montilla C. IL-6 and TNF-α Influence on Clinical Manifestations, Activity and Comorbidity in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-6-and-tnf-%ce%b1-influence-on-clinical-manifestations-activity-and-comorbidity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-6-and-tnf-%ce%b1-influence-on-clinical-manifestations-activity-and-comorbidity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/