Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: 5T095: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorder – Basic Science (2744–2749)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Iguratimod is a novel disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug that has been approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis in East Asia. Transcription factor early growth response 1 (Egr1) is one the most down-regulated genes in with iguratimod treatment. Egr1 forms a positive feedback loop with TGFβ and is overexpressed in lesional skin from systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients. This study is aim to investigate the anti-fibrotic effect of iguratimod in scleroderma models and patient skin grafts.
Methods: We used iguratimod to treat TGFβ-stimulated human skin fibroblast, bleomycin induced mice, tight skin 1 (TSK-1) mice and SSc skin grafts. The bleomycin model contained pre-establish fibrosis and late onset treatment. The skin grafts came from three SSc patients and was planted into irradiated nude mice.
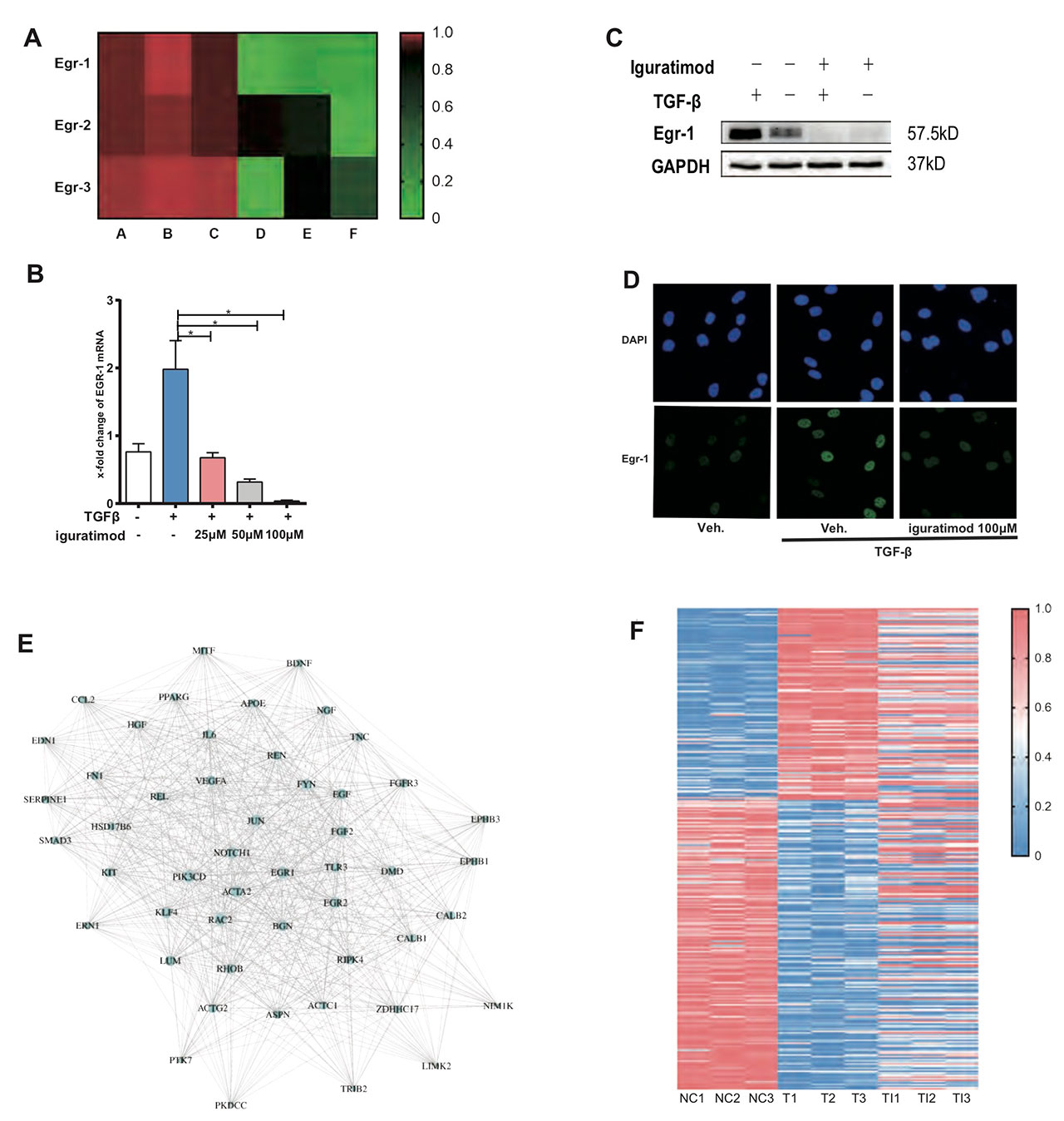
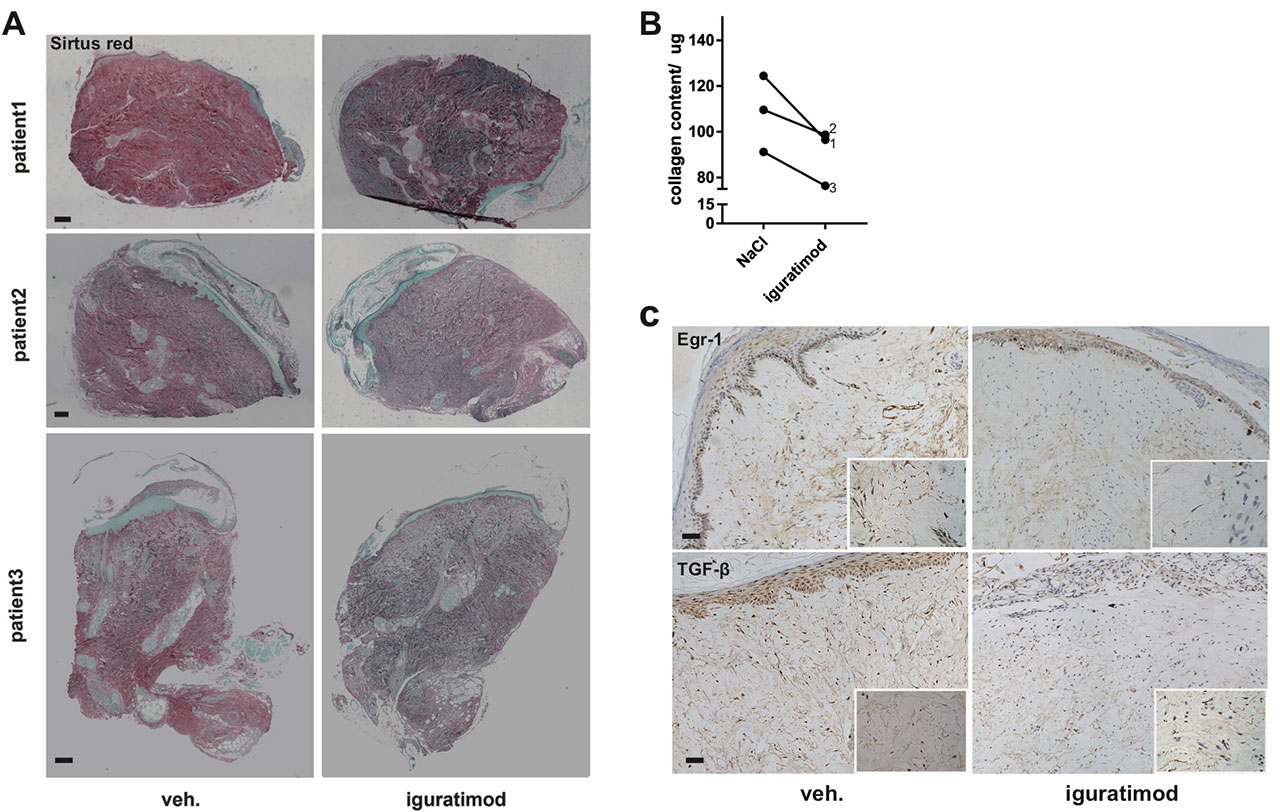
Results: Iguratimod strongly inhibited egr1 expression in human skin fibroblast, with moderate down-regulation of Egr2/3. Iguratimod neutralized effects of TGFβ on 232/327 Egr1 inducible genes according to transcriptome sequencing. Further protein interaction analysis showed that Egr1 was one of the hub genes of iguratimod working network. Collagen production and α-SMA production were decreased by iguratimod. Knocking down Egr1 using siRNA could mimic these effects. Both oral and topical iguratimod could treat dermal thickening and collagen deposition in bleomycin induced skin fibrosis. α-SMA (+) myofibroblast counts, as well as Egr1 (+) and TGFβ (+) fibroblast counts were significantly reduced by iguratimod. Similarly, topical iguratimod ameliorated dermal fibrosis in TSK-1 mice. Of note, 5-week iguratimod local injection remarkably reduced collagen content in skin grafts from three SSc patients, with simultaneous inhibited Egr1 and TGFβ staining.
Conclusion: We found the potential of iguratimod to treat SSc, which was characterized as the interruption of Egr1/TGFβ loop. Further clinical investigations for its safety and efficacy is warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yan Q, Shen L, Chen X, Lu L. Iguratimod Treated Scleroderma with Interrupted Egr1/TGF-β Loop [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/iguratimod-treated-scleroderma-with-interrupted-egr1-tgf-%ce%b2-loop/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/iguratimod-treated-scleroderma-with-interrupted-egr1-tgf-%ce%b2-loop/