Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: 3S088 ACR Abstract: Spondyloarthritis Incl PsA–Clinical I: Axial SpA Epidemiology (892–897)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Big data research in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is limited by a lack of adequate methods for identifying axSpA patients, since there are no billing codes for most subtypes of axSpA. The objective of this study was to develop accurate axSpA identification methods to enable previously impractical observational research in axSpA.
Methods: The population included 600 Veterans with risk factors for axSpA in the Veteran Health Administration (January 1, 2005 through June 30, 2015). Clinical experts reviewed medical records to determine axSpA status. axSpA identification algorithms were developed in a subset of 451 patients (training set) and tested in the remaining 149 patients (testing set). Forty-nine variables anticipated by clinical experts to be predictive of an axSpA diagnosis were selected for algorithm development. The variables included demographics, billing codes, provider utilization patterns, medication dispensations, laboratory results, and affirmative language for key disease features (spondyloarthritis, sacroiliitis, and HLA-B27 positivity) that was extracted from the free text of documents with natural language processing (NLP). Three algorithms were developed: the Spond NLP Algorithm (NLP algorithm as a single variable), High Feasibility Algorithm (16 coded variables), and Full Algorithm (all coded and NLP variables). Random Forest, 5-fold cross validation, and Random Forest Gini Scores were used for algorithm development, testing, and variable prioritization.
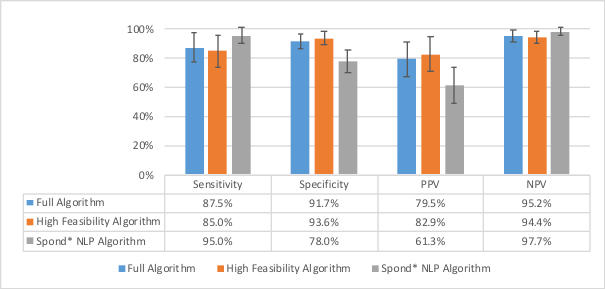
Results: In the testing set, the sensitivity of the Spond NLP Algorithm was 95.0% and the specificity was 78.0%. For the High Feasibility Algorithm, the sensitivity was 85.0% and the specificity was 93.6%. For the Full Algorithm, the sensitivity was 87.5%, and the specificity was 91.7% (Figure 1). The areas under the curve with the receiver operating characteristic analysis for the testing set were 0.86 for the Spond NLP Algorithm, 0.94 for the High Feasibility Algorithm, and 0.96 for the Full Algorithm (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Sensitive and specific algorithms were developed for identifying axSpA patients for big data research. These algorithms offer a range of performance and feasibility attributes that may be appropriate for a broad array of axSpA research.
Figure 1. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of axSpA identification algorithms (n=149)
PPV = positive predictive value, NPV = negative predictive value 
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Overbury RS, Pei S, Penmetsa G, Cannon GW, Clegg DO, Sauer B, Walsh J. Identification of Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients in a Large Dataset: The Development and Validation of Novel Methods [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-in-a-large-dataset-the-development-and-validation-of-novel-methods/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-in-a-large-dataset-the-development-and-validation-of-novel-methods/