Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent joint disease that is characterized by the destruction of articular cartilage, although the disease process affects all joint tissues. Understanding the biology of joint homeostasis and the mechanisms of disease will increase our understanding of OA, particularly as it relates to aging. This long-term study aims to integrate genomic, epigenetic, transcriptomic and proteomic data on both normal and OA joint tissues to build a multidimensional molecular profile for OA and aging. The first phase of this project explores the gene expression profiles of articular cartilage from normal and OA human knee joints. In this study, we identified differentially expressed genes between normal and OA articular cartilage using RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) to discover key biological pathways that are dysregulated in OA.
Methods: We extracted total RNA from full-thickness articular cartilage from 10 human donors (5 normal and 5 severe OA) using the Ambion RNAqueous Kit and prepared RNA libraries for sequencing using the NuGen Encore Complete RNA-Seq DR Multiplex System. Sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 (single-end, 100bp reads). Raw data were checked for quality using FASTQC, and the raw FASTQ files were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using TOPHAT2. Aligned transcripts were assembled with CUFFLINKS2 and differentially expressed (DE) transcripts were determined using CUFFDIFF2 with a false discovery rate q-value of 0.05, fragment bias correction and upper quartile normalization. We conducted a signaling pathway impact analysis using the Bioconductor packages SPIA and Graphite with the KEGG, Reactome, BioCarta and National Cancer Institute/Nature Pathway Interaction Databases (NCI/NPID) to identify potential functional pathways dysregulated in OA.
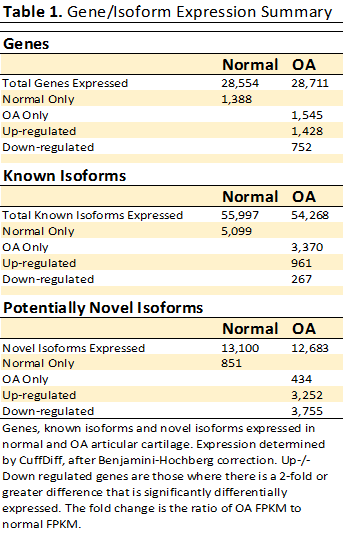
Results: A total of 2,180 DE genes were discovered between OA and normal human cartilage. Of these DE genes, 1,428 were significantly up-regulated in OA and 752 were significantly down-regulated in OA (Table 1). The five DE genes with the largest fold-change that were up-regulated in OA include COL1A1, THY1, TGFBI, CLDN7, and SLPI. The five DE genes with the largest fold-change that were down-regulated in OA include ADM, CHPF2, HILPDA, SERPINA10 and NRF1. Signaling pathway impact analysis revealed 11 significantly perturbed pathways in OA (Table 2).
Conclusion: This transcriptome analysis of OA articular cartilage reveals complex gene expression patterns and pathways that are involved in the disease. These results provide preliminary insights into an integrated, molecular understanding of OA.
|
Table 2. Pathways identified as significantly dysregulated in Osteoarthritis by signaling pathway impact analysis. |
|||||||||||
|
Pathway |
Database |
pSize |
NDE |
pNDE |
tA |
pPERT |
pG |
pGFdr |
pGFWER |
Status |
|
|
ECM-receptor Interaction |
KEGG |
85 |
11 |
2.1E-06 |
2.8E+01 |
5.0E-06 |
2.8E-10 |
3.4E-08 |
3.4E-08 |
Activated |
|
|
Hypoxic and oxygen homeostasis regulation of HIF-1-alpha |
NCI/NPID |
74 |
13 |
5.8E-09 |
0.0E+00 |
1.0E+00 |
1.2E-07 |
6.8E-06 |
1.1E-05 |
Inhibited |
|
|
HIF-1-alpha transcription factor network |
NCI/NPID |
62 |
12 |
7.1E-09 |
0.0E+00 |
1.0E+00 |
1.4E-07 |
6.8E-06 |
1.4E-05 |
Inhibited |
|
|
Smooth muscle contraction |
Reactome |
24 |
7 |
5.2E-07 |
4.7E+00 |
5.5E-01 |
4.6E-06 |
1.2E-03 |
1.2E-03 |
Activated |
|
|
Focal adhesion |
KEGG |
200 |
15 |
3.1E-05 |
4.8E+01 |
2.6E-02 |
1.2E-05 |
7.4E-04 |
1.5E-03 |
Activated |
|
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
KEGG |
131 |
4 |
3.2E-01 |
2.1E+01 |
5.0E-06 |
2.2E-05 |
9.3E-04 |
2.8E-03 |
Activated |
|
|
HIF-2-alpha transcription factor network |
NCI/NPID |
29 |
7 |
2.1E-06 |
0.0E+00 |
1.0E+00 |
3.0E-05 |
9.7E-04 |
2.9E-03 |
Inhibited |
|
|
Circadian Rhythym |
KEGG |
22 |
6 |
5.4E-06 |
-2.6E-01 |
9.7E-01 |
6.9E-05 |
2.1E-03 |
8.5E-03 |
Inhibited |
|
|
C-MYB transcription factor network |
NCI/NPID |
75 |
9 |
3.3E-05 |
-1.7E+00 |
4.7E-01 |
1.9E-04 |
4.4E-03 |
1.8E-02 |
Inhibited |
|
|
E-cadherin signaling events |
NCI/NPID |
247 |
17 |
2.8E-05 |
-5.2E+00 |
6.8E-01 |
2.3E-04 |
4.4E-03 |
2.2E-02 |
Inhibited |
|
|
Syndecan-4 mediated signaling events |
NCI/NPID |
184 |
11 |
2.2E-03 |
2.0E+01 |
1.4E-02 |
3.5E-04 |
5.7E-03 |
3.4E-02 |
Activated |
|
|
pSize: number of genes in the pathway; NDE: number of DE genes in pathway; pNDE: Probability to observe at least NDE genes in the pathway; tA: observed total perturbation accumulation in the pathway; pPERT: probability to observe a total accumulation more extreme than tA by chance; pG: p-value obtained by combinging pNDE and pPERT; pGFdr: False discovery rate; pGFWER: Bonferroni adjusted global p-values; Status: Direction in which the pathway is perturbed. |
|||||||||||
Disclosure:
K. M. Fisch,
None;
M. Saito,
None;
R. Akagi,
None;
S. Duffy,
None;
A. I. Su,
None;
M. K. Lotz,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-aberrant-pathways-in-osteoarthritis-using-rna-seq/