Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)-associated retinal toxicity and vision loss are significant challenges, with a 2% prevalence in patients using HCQ for over 10 years and up to 20% for those using doses greater than 5 mg/kg for over 20 years(1). Although regular retinal screening is recommended, compliance varies. The revised 2016 American Association of Ophthalmology (AAO) guidelines recommend a yearly three-component evaluation: a retinal exam, a Humphrey 10-2 visual field test, and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Multifocal-electroretinogram or fundus autofluorescence can also provide useful data(2).
This study aims to determine the proportion of patients within the Allegheny Health Network (AHN) system who comply with AAO retinal screening guidelines and to identify factors influencing this compliance.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational study on patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) who began HCQ treatment. We included patients diagnosed with SLE and using HCQ from January 2016 to December 2023 and assessed whether these patients received a baseline eye exam within one year of starting HCQ and yearly screenings after five years. We analyzed adherence levels against patient demographics, comorbid conditions, and insurance status using chi-square and Wilcoxon (or Kruskal-Wallis) rank sum tests. The study used medical claims data from Highmark Insurance in AHN rheumatology practices to examine adherence to baseline and yearly screening recommendations.
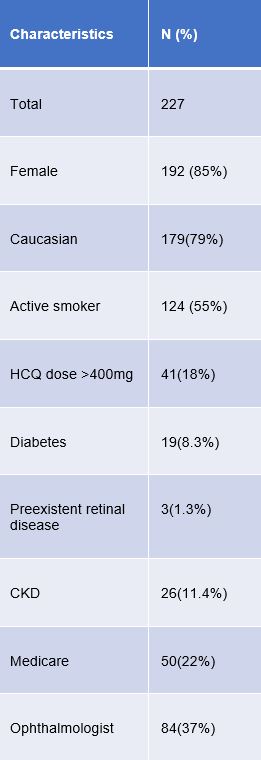
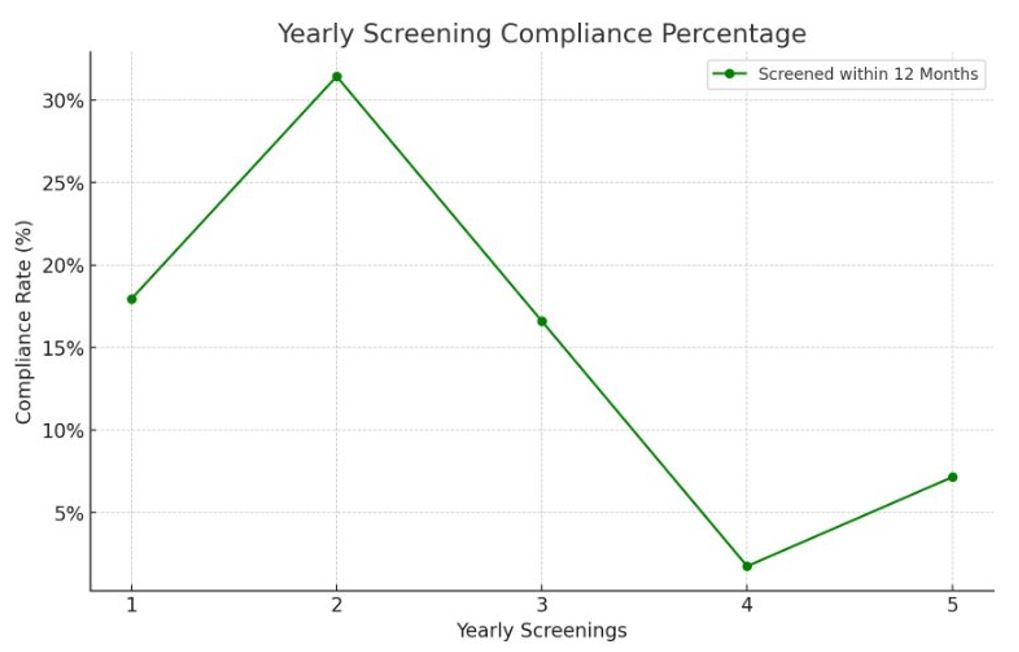
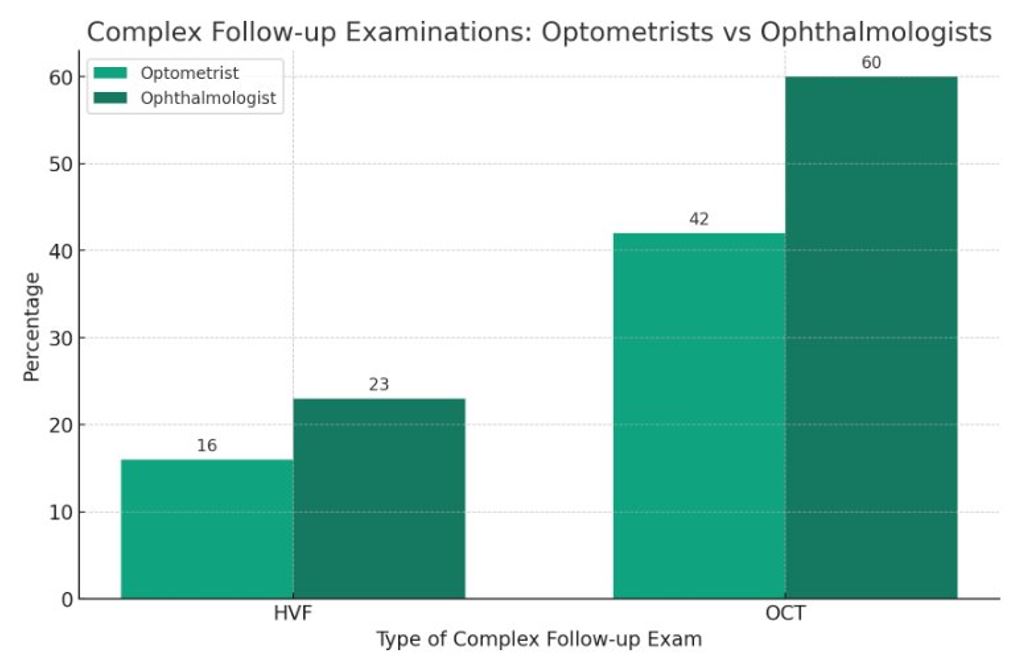
Results: Among 227 patients, 85% were female with an average age of 53. Demographically, 70% were White, 20% Black, and 10% other ethnicities(Table 1). Only 35% of patients received appropriate baseline retinal testing, and adherence to yearly screening after five years was just 11.8%. Significant relationships to adherence included insurance type and provider specialty, with Medicare Advantage members showing higher adherence than those with commercial insurance, and baseline exams with an ophthalmologist being associated with higher adherence(Figure 1,2). Factors like chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, diabetes, prior retinal disease, and rurality were not associated with increased adherence.
Conclusion: Adherence to baseline and yearly retinal screening for HCQ toxicity in SLE patients is low. Enhancing education for providers and patients about the importance of regular surveillance is crucial to mitigate retinal toxicity risks. Implementing quality improvement initiatives, such as targeted educational programs, streamlined referral processes, and robust tracking systems, can ensure guideline adherence. Further research should explore barriers to adherence and develop strategies to improve patient outcomes and quality of care.
1.Melles R, Marmor M. The risk of toxic retinopathy in patients on long-term hydroxychloroquine therapy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014 Dec;132(12):1453 doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.3459
2. Marmor M, Kellner U, Lai T, et al. AAO Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy. Ophthalmol. 2016 Jun;123(6):1386. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.058
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shahid S, Barrett T, Manocha S, Bichile T. Hydroxychloroquine Screening Adherence: Insights from Highmark Claims Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-screening-adherence-insights-from-highmark-claims-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-screening-adherence-insights-from-highmark-claims-data/