Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was not approved in Japan until 2015 and its therapeutic potential remains poorly understood in the population. In this study, we evaluated the additional therapeutic effect of HCQ in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on maintenance therapy.
Methods: Patients with SLE who visited our hospital from 2015 to 2016 and were taking prednisolone (PSL) at < 20 mg/day were retrospectively evaluated. All patients were divided into 3 groups according to their maintenance treatment regimen: PSL plus immunosuppressant (IS), PSL alone, and no treatment. We compared changes in the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI), PSL dose, and cumulative flare rate between patients who were and were not treated with HCQ.
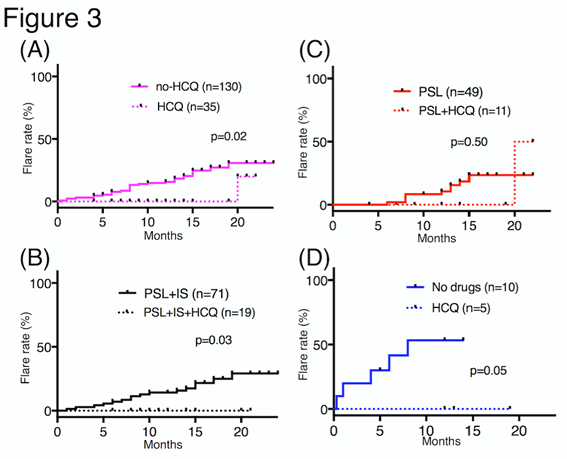
Results: Among the 165 patients evaluated, 35 (21.2%) were treated with HCQ. The mean period of observation did not differ between patients who did and did not receive HCQ (p = 0.3). The SLEDAI (Figure1A) and PSL dose (Figure 1B) were significantly reduced in patients who received HCQ regardless of their background treatment regimen. We next focused on the change in SLEDAI and PSL dose depending IS use (Figure 2). Addition of HCQ on mycophenolate mofetil and azathioprine might have superior efficacy to other combinations and we found less additional therapeutic effect on tacrolimus (TAC) users. The cumulative flare rate was lower in patients who received HCQ compared to those who did not in the PSL plus immunosuppressant and no maintenance treatment groups (p = 0.03 and p = 0.05, respectively) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: The addition of HCQ reduced disease activity and permitted PSL dose reduction regardless of background treatment in Japanese patients with SLE. In the view of combination with IS, however, our results suggested addition of HCQ on TAC might have less additional clinical efficacy than other IS combination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hanaoka H, Iida H, Kiyokawa T, Takakuwa Y, Kawahata K. Hydroxychloroquine Improves Disease Activity and Allows Reduction of Corticosteroid Dose Regardless of Background Treatment in Japanese Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-improves-disease-activity-and-allows-reduction-of-corticosteroid-dose-regardless-of-background-treatment-in-japanese-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-improves-disease-activity-and-allows-reduction-of-corticosteroid-dose-regardless-of-background-treatment-in-japanese-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/