Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To find the effect of HCQ treatment on expression of S100 proteins which were reported to reflect the activity of SLE including lupus nephritis or skin lesion.
Methods: We enrolled 51SLE patients treated without additional immunosuppressive therapy more than 3 months before HCQ treatment in our institute from Jan 2016 to Dec 2017. Serum levels of S100A8 and S100A9 proteins were measured by ELISA (CircuLex ELISA Kit, MBL) at the screening, 3 months and 6 months after HCQ administration. Disease activity of SLE was measured using the SLENA-SLEDAI 2011. Cutaneous disease activity was evaluated by Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index (CLASI). Immunological activity of SLE was also evaluated by the measurement of serum complement level (C3, C4, CH50), anti-dsDNA anti-body titer and blood cell count.
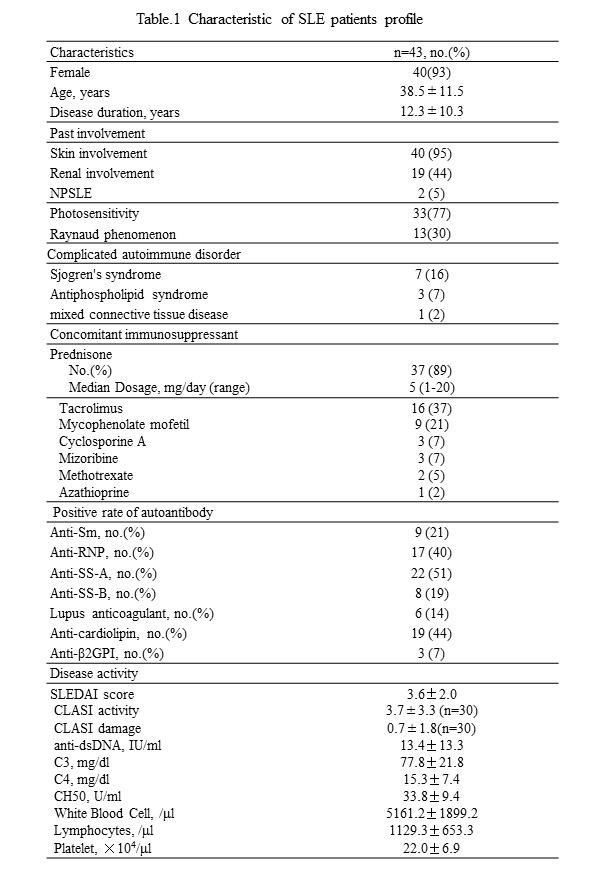
Results: 43 patients were enrolled in this study (M:F; 3:40, average age; 38.5}11.5)(Table.1).
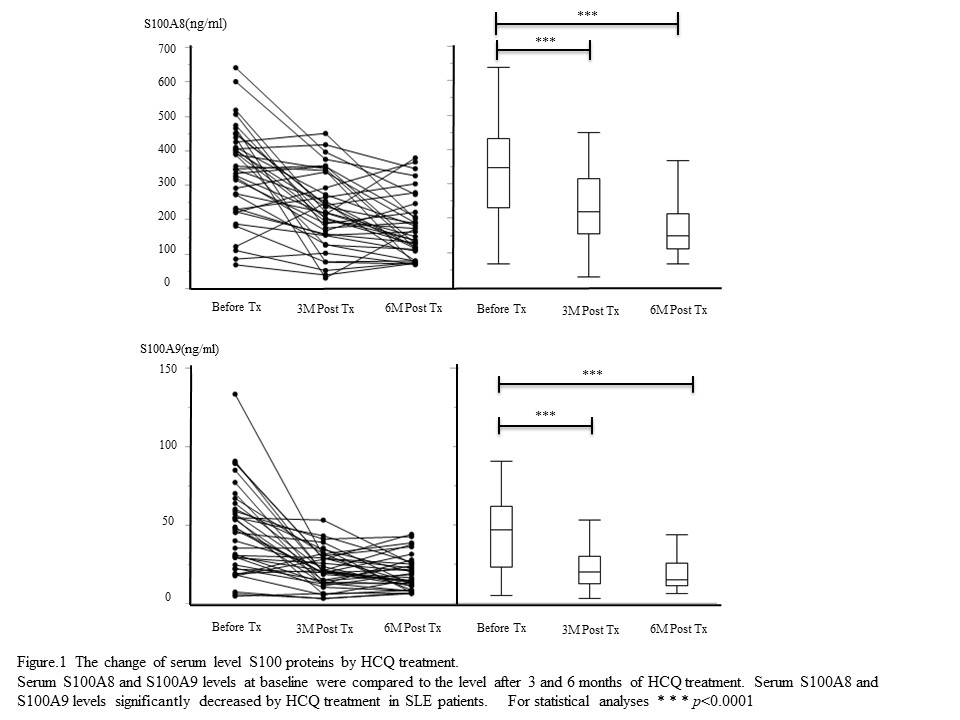
At the screening before HCQ administration, serum levels of S100A8 and S100A9 proteins were significantly elevated in SLE patients with the history of renal involvement. These S100 proteins expression were decreased significantly after 3 and 6 months of HCQ treatment (Figure.1).
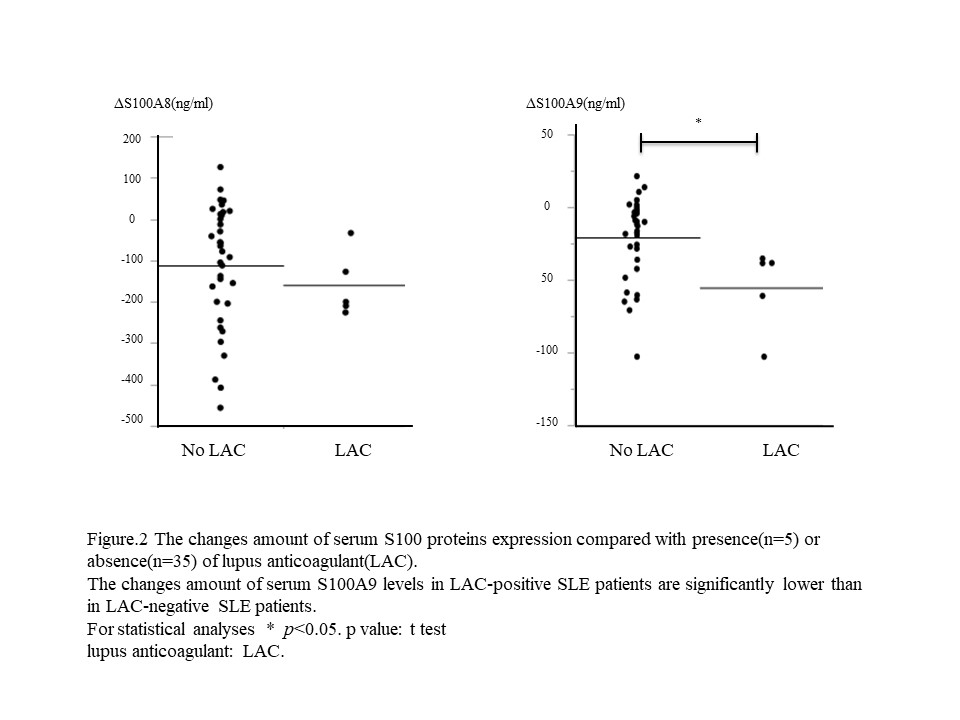
Additionally, this effect of HCQ treatment on serum S100A8 and S100A9 expression was observed in SLE patients with or without the history of renal involvement. As for the correlation with skin involvement, serum S100A8 and S100A9 expressions decreased by HCQ treatment in only SLE patients with improvement of CLASI activity score significantly. The changes of serum S100A9 levels in SLE patients with lupus anti-coagulant (LAC) are lower compared than those without LAC significantly (Figure.2).
We considered these effects on S100 proteins expression were induced by HCQ treatment mainly.
Conclusion: S100 proteins were reported to correlate with the pathogenesis of organ involvements in SLE patients. Our findings could suggest that HCQ affect the improvement of organ improvements in SLE through the modulation of S100 proteins expression especially in renal or skin involvement. Farther investigation is needed to clarify the mechanism of these modulation by HCQ use.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wakiya R, Kameda T, Nakashima S, Shimada H, Kato M, Miyagi T, Ueeda K, Dobashi H. Hydroxychloroquine Could Modulate S100 Proteins Expression, Which Reflect the Activity of Lupus Nephritis or Skin Lesion, in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Low Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-could-modulate-s100-proteins-expression-which-reflect-the-activity-of-lupus-nephritis-or-skin-lesion-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-low-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-could-modulate-s100-proteins-expression-which-reflect-the-activity-of-lupus-nephritis-or-skin-lesion-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-low-disease-activity/