Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Immune response in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) is compromised. As SARS-CoV-2 vaccine trials excluded patients on immunosuppressive therapy, data about vaccination efficacy in this patient group was insufficient.
To evaluate humoral response to SARS-CoV2 vaccination and breakthrough COVID-19 disease in IMID patients on biological therapy compared to healthy individuals.
Methods: Consecutive patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n=65), axial spondyloarthritis (n=30), psoriasis (n=23), psoriatic arthritis (n=20), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (n=17), ANCA-vasculitis (n=4), ulcerative colitis (n=3), systemic lupus erythematosus (n=3) and suppurative hidradenitis (n=1) were included. Control group (n=232) consisted of healthy volunteers.
Medical and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination history was collected and disease activity evaluated. Breakthrough COVID-19 infection was monitored for 12 months. Antibodies (Ab) against SARS-COV-2 Spike protein were measured at 3 and 6 months after full vaccination course using Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S electrochemiluminescence immunoassay.
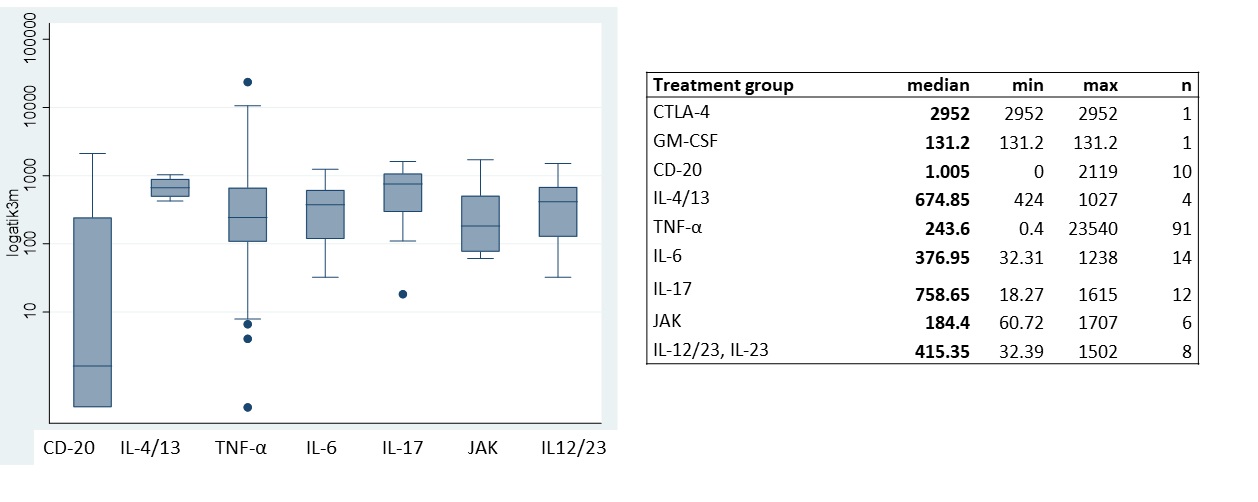
Results: Treatment groups included (n; %) TNFi (110; 64.7), IL-6i (15; 8.8), IL-17i (12; 7), CD-20i (12; 7), IL-12/23/IL-23i (8; 4.7), JAKs (6; 3.5), IL-4/13i (4; 2.3), CTLA-4 (2; 1.1) and GM-CSFi (1; 0.6).
CsDMARD monotherapy was used in 73 (42.9%), combination in 9 (5.3%) patients and glucocorticoids (GC) in 21 patients (12.3%).
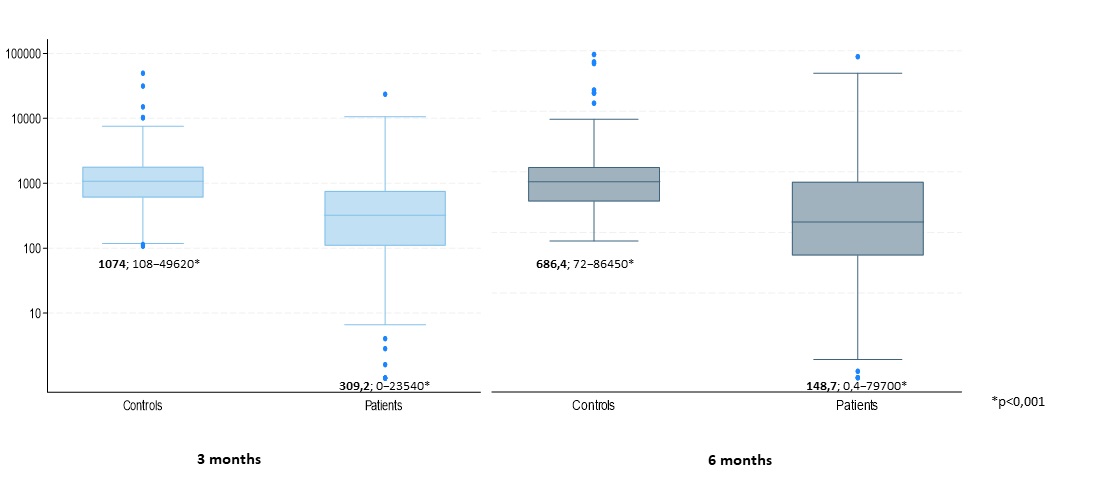
The median level of SARS-CoV-2 anti S-protein Abs in patient and control group at month 3 was 309.2 (0-23540) and 1074 (108-49620) U/ml (p< 0.001), respectively, and 148.7 (0.4-79700) vs 686.4 (72-86450) U/ml (p< 0.001) at month 6 (Fig 1). According to linear regression model adjusted to age, sex and BMI, Ab level in patient group was 46% lower.
Age influenced significantly Ab levels in both groups, with every additional year Ab level being 1% lower. Antibody levels were not influenced by sex, BMI, smoking, or concomitant diseases.
Biological treatment influenced antibody levels significantly (Fig 2). No effect of diagnosis, disease activity, GC or csDMARD use was observed.
Breakthrough COVID-19 infection occurred in 44 patients (26%) and 56 controls (24%), p=0.689. The Ab level in the infected individuals was 1522 and non-infected 1246 U/ml (p=0.5254).
Six patients and no controls needed hospitalization due to severe COVID-19 infection. Hospitalized patients were older (66.8, SD=9.9; 56-83), had lower median Ab levels (2.85 (0.4-133.4) vs 287.5 (0 – 105708 U/ml), p=0.002) and at least one concomitant disease. Three patients had been treated with rituximab, 2 with adalimumab and 1 with abatacept.
Conclusion: In SARS-CoV-2 vaccinated IMID patients on biological therapy, the levels of anti-S-protein Ab was significantly lower and rate of severe COVID-19 infection requiring hospitalization significantly higher than in the control group, correlating with lover levels of anti-S Abs, higher age, and presence of concomitant disease.
Lower Ab levels were associated with rituximab-therapy and older age. Disease activity, csDMARD or CS use had no effect.
Despite full course of vaccination IMID patients on biological therapy are less protected against severe COVID-19 infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raussi E, Eisen M, Palk K, Kütt M. Humoral Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Breakthrough COVID-19 Disease in Patients with Immune-mediated Inflammatory Diseases Receiving Biological Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-response-to-sars-cov-2-vaccination-and-breakthrough-covid-19-disease-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-receiving-biological-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-response-to-sars-cov-2-vaccination-and-breakthrough-covid-19-disease-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-receiving-biological-treatment/