Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), is a biopsychosocial condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, non-refreshing sleep, and various degrees of anxiety and/or depressive symptoms. Visual analogue scales (VAS) for pain, fatigue, sleep, anxiety, depression, are patient reported, uni-dimensional continuous scales, widely used in FMS as measures of symptom intensity and as outcome measures in drug trials. There is limited data on how well these VAS scales correlate with other “alternative measures” of pain, fatigue, sleep, anxiety and depression and with global measures of FMS severity and impact.
Methods: Consecutive patients diagnosed clinically with FMS were enrolled. Patients completed the following VAS scales: VAS pain, VAS fatigue, VAS waking up unrefreshed, VAS anxiety and VAS depression. As “ alternative measures” we used: for pain the Widespread pain index (WPI), for sleep the mean hours of sleep per night and the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS), for anxiety the Generalized anxiety disorder questionnaire (GAD-7) and for depression the Patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9). The following severity/impact measures were used: Fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQ), the Polysymptomatic distress scale/Fibromyalgianess scale (PSD), calculated as the sum of the Widespread pain index (WPI) and Symptom severity scale (SS), the Health assessment questionnaire (HAQ-DI), and the Pain disability index (PDI). Pearson correlation, r was used to measure two-way linear association between two continuous variables; strong correlations are defined as r ³ 0.7, moderate r ³ 0.5, < 07, weak ³ 03,< 05, and very weak r < 0.3.
Results: We enrolled 763 consecutive patients, 82.4% who met the ACR 2010 criteria for FMS. Patients had the following characteristics: 86.6% were female, 80.3% white, age 44.3 (12.4), PHQ-9 12.7 (8.0), GAD-7 8.8 (6.3), VAS pain 7.1 (2.1), VAS fatigue 7.8 (2.1), VAS waking up rested 7.7 (2.4), VAS anxiety 5.1 (3.3), VAS depression 4.5 (3.3), WPI 11.9 (4.3), hours slept per night 5.9 (2.1), ESS 9.5 (5.6), GAD-7 8.8 (6.3), PHQ-9 12.7 (6.3), FIQ 61.7 (20.3), PSD 20.8 (17.0), PDI 5.5 (2.3), HAQ-DI 1.0 (0.6). Correlations between variables are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion:
We found that VAS pain and WPI are poorly correlated with each other which suggests that they cannot be used interchangeably and probably both should be used when characterizing the pain of FMS patients.
The very poor correlation of VAS waking up unrefreshed with daytime sleepiness measured by ESS and the mean hours of sleep per night, suggests that a more complex and multidimensional measure of sleep is needed to characterize sleep in FMS patients.
The VAS measures of depression and anxiety had moderate and strong correlations with the alternative measures , PHQ-9 and respectively GAD-7, which indicates VAS depression and anxiety can be used as quick measures of current depressive and anxiety symptoms.
Many studiers of FMS severity report only the FIQ total score and use only the VAS components for more specific measures. This analysis suggests that if alternative measures of specific symptoms rather than VAS FIQ components are used, results and/or conclusions may be different.
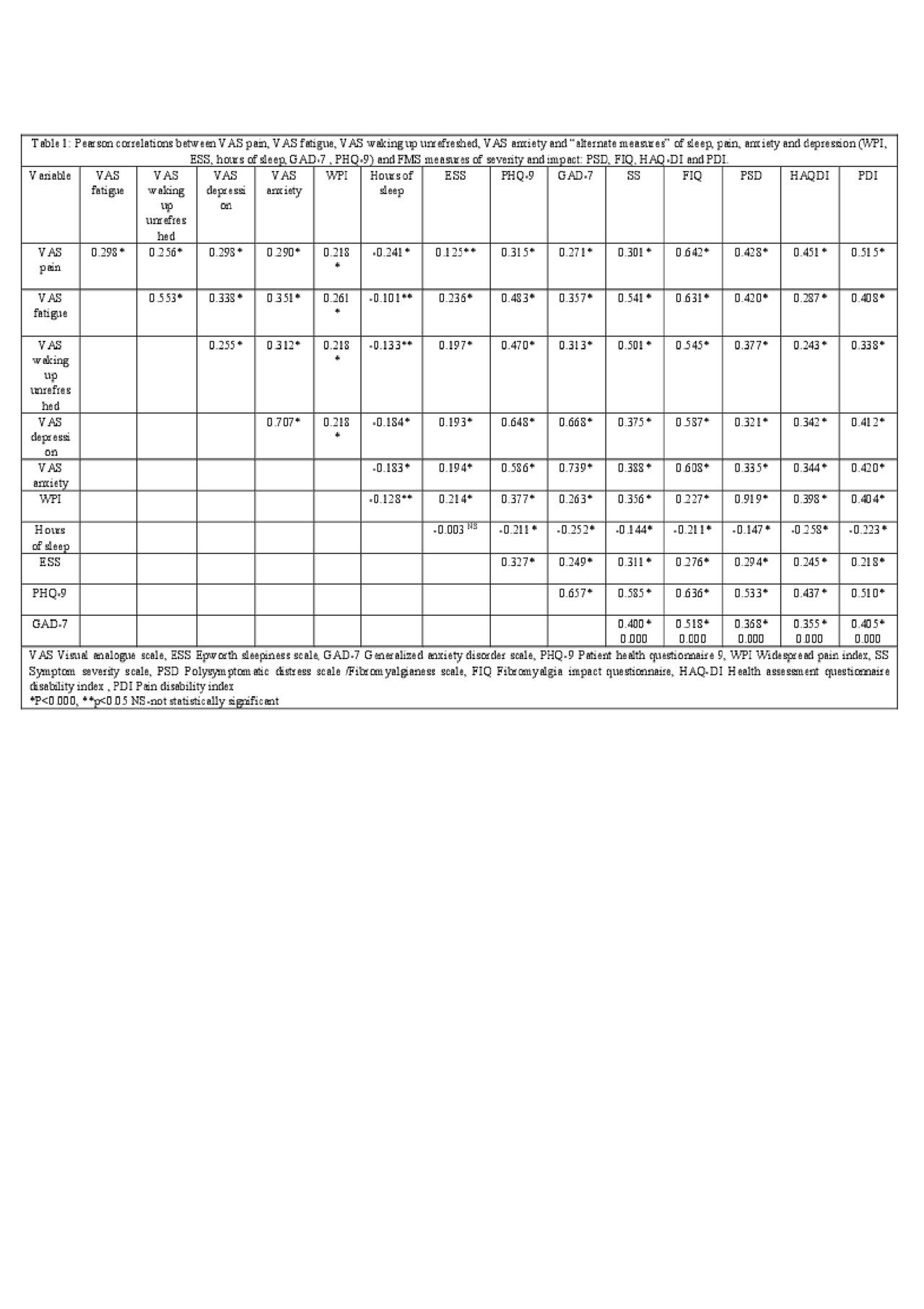
Table for VAS scales abstract May 29
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gota C, Kaouk S, Yaseen K, Jhala N, Wilke W. How Well Do Visual Analogue Scales Used in the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ) Correlate with Other Measures of Pain, Fatigue, Sleep, Sleep Disturbance, Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Fibromyalgia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-well-do-visual-analogue-scales-used-in-the-fibromyalgia-impact-questionnaire-fiq-correlate-with-other-measures-of-pain-fatigue-sleep-sleep-disturbance-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-well-do-visual-analogue-scales-used-in-the-fibromyalgia-impact-questionnaire-fiq-correlate-with-other-measures-of-pain-fatigue-sleep-sleep-disturbance-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with/
