Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster II: X-ray, MRI, PET and CT
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Radiographic progression is a key outcome parameter in RA1. Manual scoring of joint damage based on the established scoring methods (e. g. Sharp Score) is a very time-consuming process with an average time of 30 minutes per image set2.
The objective of this initial feasibility study is to evaluate a new tool for the computer based documentation of joint damage in RA.
Methods:
15 sets of X-rays of 15 patients with RA (12 female, mean age 70.9 ± 4.8 years) were read for bone erosions, joint space narrowing and bone mineralization in 54 hand areas and 28 feet areas as a consensus-reading by two experienced readers.
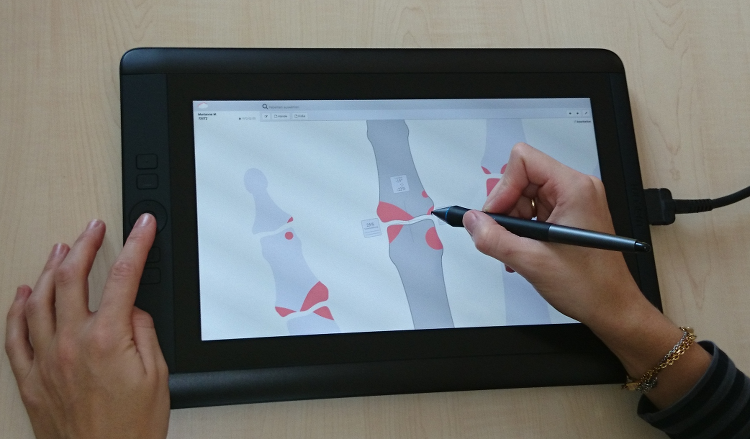
A computer documentation system developed by the first author provides uniform templates of the hands and the feet, into which all identified erosions, joint space narrowing, (sub-)luxation and demineralization were transcribed with a stylus on a tablet (cf. Fig 1). The tool automatically computed the Ratingen3 and Sharp/van der Heijde4 scores from the documented structural changes. The time for the documentation in the computer was measured.
Results:
The mean time for the documentation of the structural changes in all areas was 16.0 ± 6.2 minutes (range 6-31 minutes; median: 15 minutes) per image set. The scores were automatically computed as 17.9 ± 14.1 points (range 1 – 50 points; median: 13 points) for the Ratingen score, as 32.5 ± 28.0 points (range 2 – 97 points; median: 27 points) for the erosion score segment and as 54.7 ± 27.0 points (range 11 – 105 points; median: 52 points) for the joint space narrowing segment of the Sharp/van der Heijde score.
Conclusion:
The tool allows for an easy and fast documentation. In this pilot study, the times to assess and document the structural changes on the hand and foot joints in patients with RA were significantly lower than those reported in the literature2. Multiple scores are computed automatically from the same source data by the system. These points might be of great potential and benefit for X-ray scoring over the time, especially in clinical and research settings.
References:
- van der Heijde DM. Radiographic imaging: the ‘gold standard’ for assessment of disease progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39: Suppl 1:9-16.
- Rau R, Wassenberg S. Bildgebende Verfahren in der Rheumatologie: Scoring-Methoden bei der rheumatoiden Arthritis.Z Rheumatol 2003; 62:555-565.
- Rau R, Wassenberg S, Herborn G, Stucki G, Gebler A. A new method of scoring radiographic change in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1998; 25:2094-2107.
- van der Heijde DMFM. Plain X-rays in rheumatoid arthritis: overview of scoring methods, their reliability and applicability. Baillieres Clinical Rheumatology 1996; 10:435-453.
- Sharp JT, Young DY, Bluhm GB, Brook A, Brower AC et al. How many joints in the hands and wrists should be included in a score of radiologic abnormalities used to assess rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum 1985; 28:1326-1335.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Langer A, Böttcher J, Renz DM, Pfeil A, Langer HE. How Can We Reduce the Time for Scoring Radiographic Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Initial Results with a New Computer-Based Documentation Tool [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-can-we-reduce-the-time-for-scoring-radiographic-joint-damage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-initial-results-with-a-new-computer-based-documentation-tool/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-can-we-reduce-the-time-for-scoring-radiographic-joint-damage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-initial-results-with-a-new-computer-based-documentation-tool/