Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M105 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Diagnosis & Prognosis II (1929–1934)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients in clinical remission may still develop structural damage that has been attributed to ongoing synovial inflammation, sometimes only detectable by ultrasound or MRI. Here, we assess the clinical features, histologic characteristics, and transcriptional profiles of synovium from RA patients in clinical remission undergoing arthroplasty.
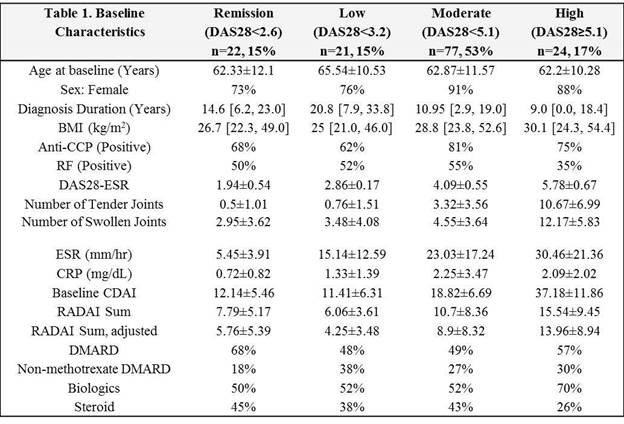
Methods: We studied 144 patients with long-standing RA (median disease duration of 12.5 years) undergoing total hip or knee arthroplasty between 2013 and 2017, and met classification criteria for RA using ACR/EULAR 2010 or 1987 criteria. Baseline data collected included age, sex, comorbidities, duration of disease, and medications. Disease activity was divided into remission (DAS 28 ESR<2.6), low disease activity (≥2.6-3.2), moderate disease activity (≥3.2-5.1), and high disease activity (≥5.1) [12]. Synovium was assessed by histologic analysis and RNA-Seq. Statistical analysis was descriptive. Continuous characteristics are summarized by mean ± standard deviation or median [interquartile range], as appropriate. Categorical variables were compared using Fisher’s exact tests.
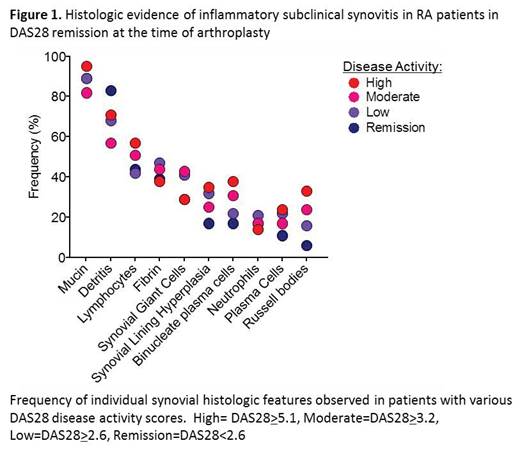
Results: Of 144 participants, 15% (n=22) met DAS criteria for remission, only 1 was drug free. 17%, 53%, and 15% had high, moderate, and low disease activity at baseline as measured by DAS28(TABLE 1). Of the patients in DAS remission: (i) histologic analysis of synovium demonstrated that 45% had moderate to marked lymphocytic infiltrates, 17% had greater than 10% plasma cells, 39% had fibrin deposition, 6% had Russell bodies, 17% had binucleate plasma cells, 17% had neutrophils, and 29% had synovial multinucleated giant cells, all features characteristic of the high inflammatory RA subtype (Figure 1), (ii) RNA-Seq analysis demonstrated that 67% had moderate levels of synovial inflammatory gene expression, and (iii) clinical assessment demonstrated that 36% of all patients in remission prior to surgery, met DAS28 criteria for flare, 6 weeks after joint replacement.
Conclusion: Remission is uncommon in RA patients with long-standing disease undergoing arthroplasty. Of those in remission, synovium may be characterized by ongoing inflammation, and they remain at risk for flares. The notion that RA burns out and that patients undergoing arthroplasty have inactive disease should be re-evaluated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Orange D, Agius P, DiCarlo EF, Mirza SZ, Rozo C, Pannellini T, Figgie MP, Robinson WH, Szymonifka J, Bykerk VP, Donlin LT, Goodman SM. Histologic and Transcriptional Evidence of Subclinical Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Clinical Remission [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/histologic-and-transcriptional-evidence-of-subclinical-synovial-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-clinical-remission/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/histologic-and-transcriptional-evidence-of-subclinical-synovial-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-clinical-remission/