Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We have already reported that baseline levels of soluble interluekin-6 receptor (sIL-6R), target of tocilizumab, predicted response to tocilizumab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. However, there is a report that interleukin (IL)-6 is also one of predictors. The aim of this study is to investigate the association of baseline levels of both IL-6 and sIL-6R with clinical and radiographic response to tocilizumab in patients with RA.
Methods: Consecutive RA patients at our institution who received tocilizumab as the first biologic agent from April 2010 to April 2013 were included. Serum levels of sIL-6R and IL-6 were measured by electrochemiluminescence assay at week 0, 4, 24, and 52. According to baseline levels of sIL-6R and IL-6, patients were divided into 3 groups using K-means clustering. Clinical response and radiographic progression were compared among the 3 groups. Differences among 3 groups were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA)
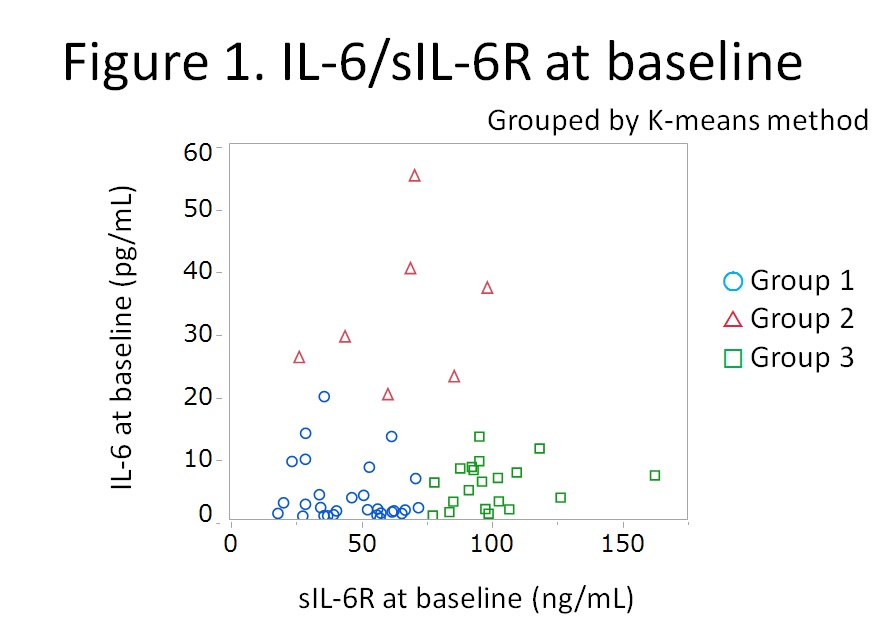
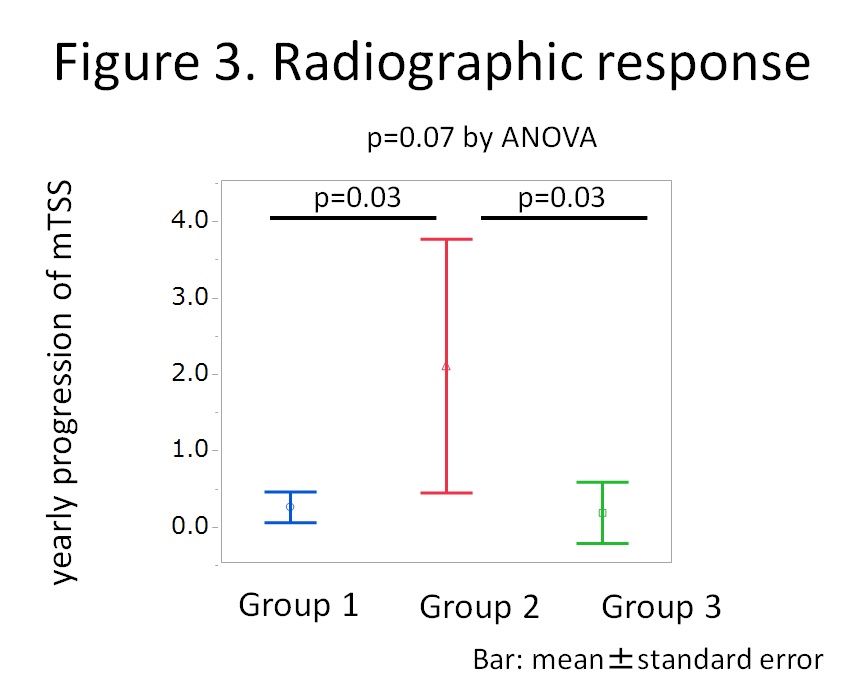
Results: Fifty six patients were enrolled. Distribution of sIL-6R and IL-6 at week 0 is shown in Figure 1 and the clusters were named as Group 1, 2 and 3. Mean levels of sIL-6R and IL-6 of Group 1 (n=29) were 46.2 ng/mL and 3.9 pg/mL; Group 2 (n=7), 65.4 ng/mL and 32.8 pg/mL; and Group 3 (n=20), 100.4 ng/ml and 5.6 pg/mL, respectively. Baseline characteristics were comparable among the groups except for RA activity. Mean disease activity score (DAS28-ESR) was higher in Group 2 compared to Group 1 and 3 (4.9 vs 6.2 vs 5.0 for Group 1, 2, and 3, respectively; p=0.02 by ANOVA). Time course of mean DAS28-ESR is shown in Figure 2. Although significant difference was observed only at week 24, mean DAS28-ESR of Group 2 tended to be higher than those of Group 1 and Group 3 (p=0.21, 0.02, and 0.08, respectively at week 4, 24, and 52). Mean yearly progression of van der Heijde modified total Sharp score was worse in Group 2 but without statistical significance (0.2 vs 2.1 vs 0.2, for Group 1, 2, and 3, respectively; p=0.07) as shown in Figure 3.
Conclusion: Despite lower levels of sIL-6R, patients with very high levels of IL-6 showed worse clinical and radiographic response to tocilizumab in RA. IL-6 as well as sIL-6R could be strong indicators for the effectiveness of tocilizumab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nishina N, Kaneko Y, Yoshimoto K, Takeuchi T. Higher Levels of Interleukin-6 As Well As Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor Leads to Worse Clinical and Radiographic Prognosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Tocilizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-levels-of-interleukin-6-as-well-as-soluble-interleukin-6-receptor-leads-to-worse-clinical-and-radiographic-prognosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tocilizumab/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-levels-of-interleukin-6-as-well-as-soluble-interleukin-6-receptor-leads-to-worse-clinical-and-radiographic-prognosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tocilizumab/