Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment - Poster III: Biomarkers and Nephritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with SLE have a broad clinical and immunological phenotype in which multiple immune pathways may be sequentially or simultaneously activated. No reliable biomarkers exist to identify active disease across the spectrum of lupus patients. Cytokine expression in serum is often at low levels and therefore traditional ELISA methods have inadequate sensitivity. Custom high sensitivity Multiplex arrays offer the opportunity to measure multiple cytokines within a single serum sample. We aimed to investigate the association between cytokine expression and disease activity in patients with established SLE and determine whether clusters of patients could be identified.
Methods: Female healthy subjects and patients with SLE (≥4 ACR criteria) were recruited between 2007 and 2013 from Central Manchester NHS Foundation Trust. Disease activity was measured using the SLEDAI-2K and BILAG-2004 indices. Active disease was defined as presence of any of: SLEDAI score >4, 1 BILAG “A” score, or 2 BILAG “B” scores. The expression of 10 cytokines (covering B cell, T cell and innate immune pathways) was measured in serum by high sensitivity bead-based Multiplex ELISA (Aeirtec Ltd, UK). Principle component analysis (PCA) of the cytokines followed by unsupervised K-means clustering was used to identify patient groups according to cytokine expression.
Results: We recruited 13 healthy control (HC) subjects and 96 SLE patients with median (IQR) age of 40 (32, 49) and 51 (44, 59) years respectively. The SLE group was 77% (74/96) Caucasian with a median disease duration of 11.7 (6.8, 21.4) years. 22/96 (23%) patients had active disease. The median dose of steroids was significantly higher amongst patients with active disease (12.5 [7.5, 17.5] vs. 0 [0, 5]mg/day, p<0.001) but there were no differences in frequency of antimalarial or immunosuppressant use. Compared to HCs, SLE patients had significantly increased levels of CXCL10 and CXCL13. Patients with active SLE had significantly increased levels of BLys, IL-18, CXCL10, IL-17 and pentraxin-3 compared to inactive patients. Cluster analysis revealed 3 groups (high chemokines, including CXCL13 [n=10]; high inflammation initiators including Blys and IFNα [n=6]; all cytokines low [n=93]). All HCs were in group 3. SLE patients in group 1 and 2 had higher disease activity with 7/10 (70%) and 4/6 (67%) active patients compared to group 3 (11/80, 14%). Multinomial logistic regression models identified that group membership was associated with clinical subgroup (HC/inactive SLE/active SLE) and steroid use, but not age, ethnicity or disease duration.
Conclusion: Cytokine profiles are variable in active SLE but at least 2 distinct subgroups are apparent. Patients with inactive SLE have similar profiles to healthy controls. Our findings suggest that distinct immunophenotypes may exist amongst SLE patients and may be detected using multiplex ELISA. 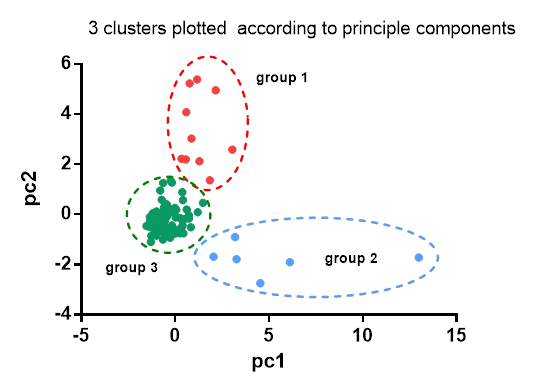
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reynolds JA, Haque S, McCarthy EM, Sergeant JC, Lee E, Holling Lee E, Kilfeather S, Parker B, Bruce IN. High Sensitivity Multiplex ELISA Reveals Cytokine Expression Heterogeneity in Active SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-sensitivity-multiplex-elisa-reveals-cytokine-expression-heterogeneity-in-active-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-sensitivity-multiplex-elisa-reveals-cytokine-expression-heterogeneity-in-active-sle/
