Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) that target cytokines and cytokine receptors such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-6 have been established as a standard therapy of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for patients with conventional systemic DMARDs, such as methotrexate (MTX), resistant disease. Currently, TCZ is included as one of the first-line bDMARDs in the latest ACR guideline and European League against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations. However, it is unclear whether the effectiveness of TCZ is depended on previous administration of biologics. Therefore, we focused on the retention rate taking into account of both efficacy and safety under the daily setting care, and this study aimed to investigate optimal treatment strategy with TCZ as a first-line bDMARD treatment in comparison with second-line treatment for RA patients.
Methods: All RA patients who treated with TCZ in Osaka City Universityfs RA registry (including 1070 patients with RA and 353 patients using bDMARDs) were included in this analysis. These patients were divided into two groups that TCZ was used as a first-line bDMARDs (1st group) and a second-line or more treatment (2nd group). Retention rates and clinical efficacy assessed by disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28; on the basis of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR) and clinical disease activity index (CDAI) from week 0 to week 52 were assessed. Retention rates of TCZ were evaluated using Kaplan–Meier analysis. Furthermore, the discontinuation ratio of glucocorticoid was also evaluated.
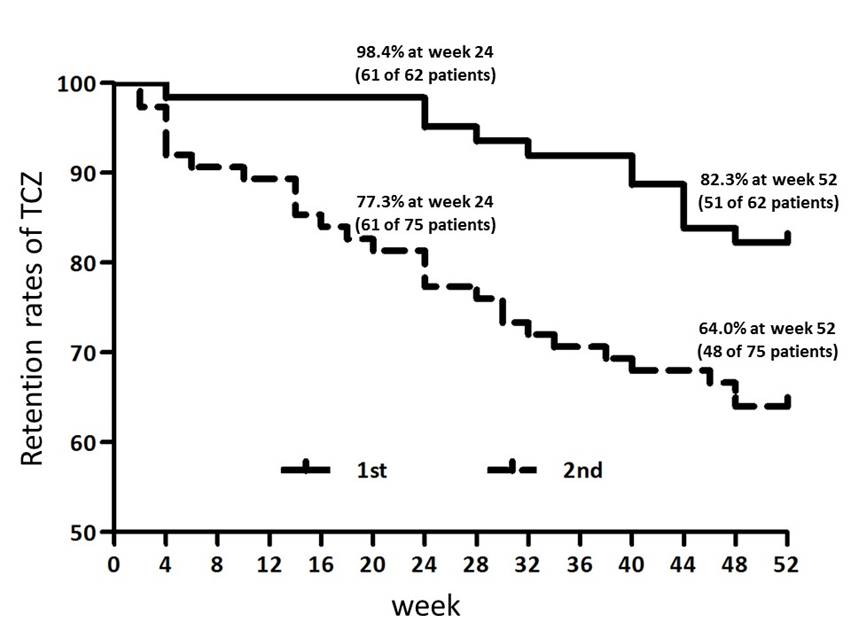
Results: Sixty-two patients in 1st group and 75 patients in 2nd group were analyzed in this study. Retention ratio at week 52 was 82.3% in 1st group and 64.0% in 2nd group (p=0.01). Of 11 discontinued patients in 1st group, only 2 patients were withdrawal due to inadequate response. From the initiation of TCZ use, efficacy of 1st group patients were faster than that of 2nd group patients. DAS28 remission rates were 23.5, 47.0, 49.1, 41.2 and 35.3% in 1st group and 8.3, 22.9, 29.2, 33.3 and 37.5% in 2nd group at week 4, 12, 24, 36 and 52, respectively. Also, CDAI remission rates were 15.7, 13.7, 15.7, 25.5 and 13.7% in 1st group and 0, 6.3, 10.4, 14.6 and 10.4% in 2nd group at week 4, 12, 24, 36 and 52, respectively. During 52 weeks, the dose of glucocorticoid was reduced in 18 patients and withdrawal in 12 patients between 22 patients of 1st group using glucocorticoid at week 0. In 2nd group, the dose of glucocorticoid was reduced in 14 patients and withdrawal in 5 patients between 20 patients of using glucocorticoid at week 0.
Conclusion: High retention rates and clinical efficacy of TCZ as a first-line biologic treatment was found in this research. More than half of glucocorticoid user were able to withdraw glucocorticoid during 52 weeks. This result as 1st line use of TCZ supports for current treatment guidance of the latest ACR guideline and EULAR 2016 recommendations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Okano T, Inui K, Tada M, Sugioka Y, Mamoto K, Koike T, Nakamura H. High Retention Rates and Clinical Efficacy of Tocilizumab As First-Line Biologic Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-retention-rates-and-clinical-efficacy-of-tocilizumab-as-first-line-biologic-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-retention-rates-and-clinical-efficacy-of-tocilizumab-as-first-line-biologic-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/