Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
High BMI is associated with decreased response to initial combination therapy in recent onset RA patients
Background/Purpose: A diminished response to combination treatment with a fixed dose of TNF-blocker infliximab (IFX) has been reported in patients with established RA and a high BMI. The association between BMI and response to therapy might also exist for other treatment regimens through inflammation and/or pain.
The association between high body mass index (BMI) and treatment response was assessed in a treat to target cohort with recent onset RA patients.
Methods: All patients from the BeSt study (n=508), in which patients were randomized to initial monotherapy or combination therapy with prednisone or infliximab (IFX) were included in the analyses. Response (DAS≤2.4) to disease activity steered treatment (first dose and after 1 year) was compared between patients with a BMI <25 and ≥25, using Poisson regression analyses. Several components of disease activity and functional ability during the first year were compared using linear mixed models. Joint damage progression in year 1 and over 8 years of treatment was compared using radiographs scored with the Sharp/van der Heijde Score.
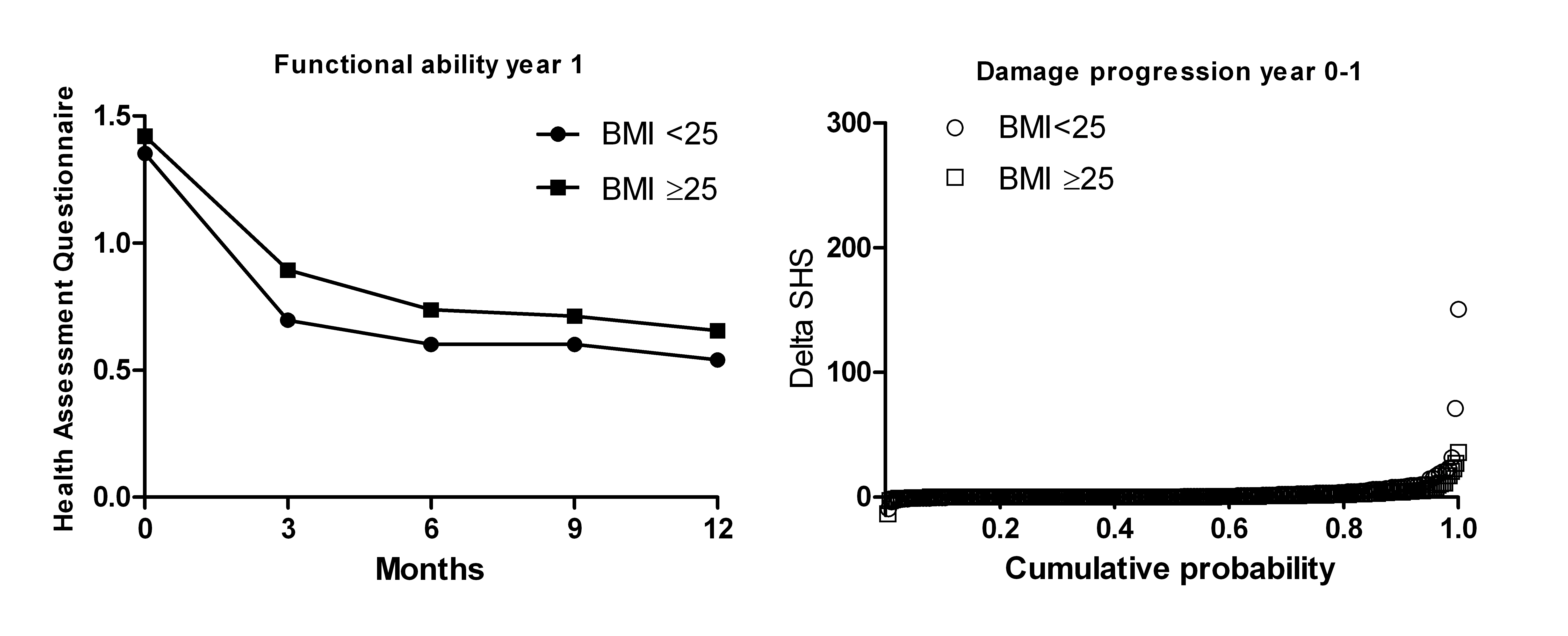
Results: High BMI was independently associated with decreased treatment response to initial therapy, RR: 1.20 (95% C.I. 1.05-1.37). After stratification for initial treatment group, the effect was found for combination therapy with prednisone: RR 1.55 (1.06-2.28) and for combination therapy with IFX, RR 1.42 (0.98-2.06). The RRs for failure after one year in these groups were 1.46 (0.75-2.83) and 2.20 (0.99-4.92) respectively. A similar association was found for response to delayed combination therapy with IFX, after adjustment for selection bias related to previous failure on DMARDs. In the first year of treatment, patients with a high BMI had higher disease activity and worse functional ability, with more tender joints and a higher VAS global health, but not more swollen joints and similar systemic inflammation. Patients with high BMI did not have more damage progression over time.(figure 1)
Conclusion: High BMI was independently associated with decreased response to initial combination therapy with prednisone and to initial and delayed treatment with infliximab, During DAS≤2.4 targeted treatment, patients with a high BMI experienced more pain, but not more swelling or systemic inflammation. Joint damage progression over 8 years was similar for patients with high and normal BMI.
Figure 1: functional ability and joint damage progression in year 1 for patients with normal and high BMI
Disclosure:
M. van den Broek,
None;
L. Heimans,
None;
S. le Cessie,
None;
B. Siegerink,
None;
H. K. Ronday,
None;
K. H. Han,
None;
P. J. S. M. Kerstens,
None;
T. W. J. Huizinga,
None;
W. F. Lems,
None;
C. F. Allaart,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-body-mass-index-is-associated-with-decreased-response-to-initial-combination-therapy-in-recent-onset-ra-patients/