Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Clinical application of biomarkers to predict response to therapy is the next frontier in RA. Despite the key role of IL-6 in RA, the utility of IL-6 to predict prognosis or treatment response in RA is limited. Post-hoc analyses of MOBIILITY (NCT01061736) and MONARCH (NCT02332590) studies investigated if serum baseline IL-6 level was associated with radiographic and clinical responses to sarilumab versus comparator treatment.
Methods:
Baseline IL-6 levels were measured using a validated assay in 1193 patients (pts) randomized to sarilumab (SC 150 or 200 mg q2w) +MTX or placebo (PBO) +MTX, and 300 randomized to sarilumab 200 mg or adalimumab 40 mg q2w. Efficacy was compared between and within treatment groups according to baseline IL-6 tertile using linear and logistic regression.
Results:
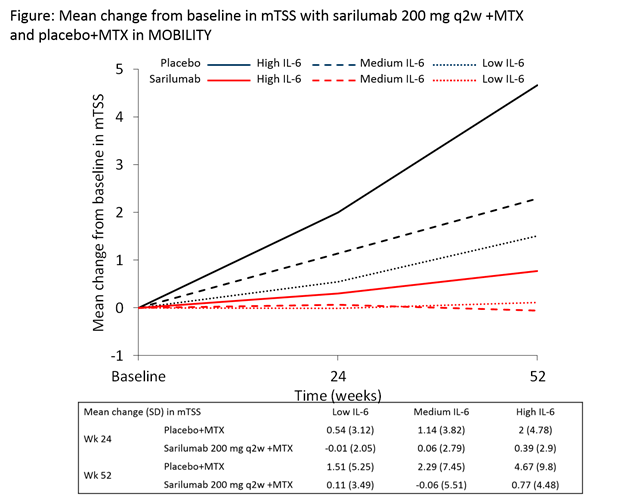
All low tertile pts had normal IL-6 levels (<12.5 pg/mL) and >85% of high tertile pts had IL-6 levels ³3x ULN. At baseline, pts in the high tertile had more joint damage, greater disease activity, and elevated levels of CRP vs the low tertile pts (nominal P<0.05; Tables). In the MOBILITY PBO+MTX group, pts in the high tertile developed more joint damage than pts in the low tertile (mean ± SD mTSS progression 4.67 ± 9.80 vs 1.51 ± 5.25 [Figure]; odds ratio 3.3; 95% CI 1.9, 5.6). Clinical and radiographic efficacy (sarilumab+MTX vs PBO+MTX) in MOBILITY improved with increasing baseline IL-6 tertile (Table 1). In MONARCH, sarilumab efficacy vs adalimumab was greater in the high vs low tertile (Table 2) – ACR20/70 for sarilumab vs adalimumab: 89%/30% vs 52%/4% [high tertile] and 64%/18% vs 58%/18% [low tertile]. Data show that high IL‑6 is better than high CRP at predicting efficacy outcomes. The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events was similar across IL-6 tertiles.
Conclusion:
Across clinical and radiographic endpoints, pts with elevated baseline IL-6 levels had greater response to sarilumab compared with MTX or adalimumab than pts with normal IL-6 levels. Prospective validation is warranted to confirm these data.
Acknowledgements:
Study funding and medical writing support (Matt Lewis, Adelphi) provided by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
|
Table 1 – MOBILITY (pts with an inadequate response to MTX)
|
||||
|
Sarilumab 150 mg q2w/200 mg q2w/PBO q2w (all +MTX), n
|
High IL-6 146/121/131
|
Medium IL-6 129/147/122 |
Low IL-6 126/128/143
|
P value
|
|
IL-6 level (pg/mL), median [range] |
61.0 [31.2–648.7] |
17.3 [9.8–30.7]
|
5.0 [1.6–9.6]
|
|
|
Baseline disease characteristics, mean (SD)
|
|
|||
|
CRP (mg/L)
|
36.4 (30.1) |
18.4 (15.5) |
10.5 (11.6) |
*
|
|
HAQ-DI
|
1.8 (0.7) |
1.6 (0.6) |
1.6 (0.6) |
* |
|
DAS28-CRP
|
6.3 (0.8) |
5.9 (0.8) |
5.6 (0.8) |
* |
|
mTSS
|
56.7 (65.7) |
49.8 (62.1) |
40.8 (56.5) |
* |
|
CDAI
|
43.0 (12.4)
|
40.1 (12.3) |
38.3 (11.6)
|
*
|
|
Mantel-Haenszel odds ratio (95% CI)$ sarilumab 200 mg q2w +MTX versus PBO q2w + MTX (Week 52)
|
||||
|
mTSS progression
|
0.3 (0.1, 0.4)
|
0.6 (0.4, 1.0)
|
0.7 (0.4, 1.1)
|
**
|
|
ACR20
|
4.9 (2.8, 8.3)
|
3.3 (1.9, 5.7)
|
2.0 (1.2, 3.2)
|
**
|
|
ACR50
|
6.4 (3.5, 11.8)
|
3.4 (1.9, 6.2)
|
2.0 (1.2, 3.4)
|
**
|
|
ACR70
|
7.3 (3.3, 16.3)
|
3.5 (1.7, 7.4)
|
1.9 (1.0, 3.8)
|
**
|
|
DAS28-CRP <2.6
|
39.3 (9.4, 163.9)
|
4.4 (2.2, 8.9)
|
2.5 (1.4, 4.7)
|
**
|
|
CDAI ≤2.8
|
42.4 (4.7, 383.4)
|
3.9 (1.6, 9.5)
|
1.8 (0.8, 4.0)
|
**
|
|
HAQ-DI improvement ≥0.3 (Wk 16)
|
3.1 (1.8, 5.2)
|
2.2 (1.3, 3.7)
|
1.1 (0.7, 1.8)
|
**
|
|
Top *Kruskal-Wallis test P<0.05 and bottom **nominal P<0.05 for (high vs low) tertile IL-6-by-treatment interaction (logistic regression with treatment, study randomization stratification factors [prior biological use and region], tertile IL-6 at baseline, and tertile IL-6 at baseline-by-treatment interaction as fixed effects) $Stratified by study randomization stratification factors |
||||
|
Table 2 – MONARCH (pts with an intolerance or inadequate response to MTX)
|
||||
|
Sarilumab/adalimumab, n
|
High IL-6 46/54
|
Medium IL-6 47/53
|
Low IL-6 55/45
|
P value
|
|
IL-6 level (pg/mL), median [range] |
64.7 [39.6–692.3] |
16.2 [7.2–39.5] |
2.4 [1.6–7.1] |
|
|
Baseline disease characteristics, mean (SD)
|
||||
|
CRP (mg/L) |
41.5 (34.1) |
15.2 (17.1) |
5.6 (9.2) |
* |
|
HAQ-DI |
1.8 (0.6) |
1.6 (0.6) |
1.5 (0.6) |
* |
|
DAS28-CRP |
6.5 (0.8) |
6.0 (0.7) |
5.5 (0.8) |
* |
|
CDAI |
46.0 (12.2) |
42.9 (11.4) |
40.6 (11.7) |
* |
|
Mantel-Haenszel odds ratio (95% CI)$ sarilumab versus adalimumab (Week 24)
|
||||
|
ACR20 |
6.6 (2.3, 18.6)
|
1.2 (0.5, 3.0) |
1.4 (0.6, 3.1) |
** |
|
ACR50 |
5.5 (2.3, 13.2) |
1.5 (0.6, 3.5) |
1.6 (0.7, 3.7) |
** |
|
ACR70 |
10.5 (2.3, 48.4) |
1.7 (0.6, 4.6) |
1.1 (0.4, 3.2) |
** |
|
DAS28-ESR <2.6 |
33.9 (3.5, 328.7)
|
5.6 (1.6, 19.4) |
1.5 (0.5, 4.4) |
** |
|
DAS28-ESR <3.2 |
10.5 (3.5, 31.4) |
5.1 (1.8, 14.1) |
2.6 (1.0, 6.7) |
|
|
DAS28-CRP <2.6 |
18.4 (3.8, 90.0) |
4.0 (1.5, 10.9) |
2.0 (0.8, 5.3) |
** |
|
DAS28-CRP <3.2 |
9.2 (3.4, 24.8) |
2.2 (1.0, 5.1) |
3.2 (1.3, 7.6) |
|
|
CDAI ≤10 |
3.6 (1.4, 9.0) |
1.6 (0.7, 3.7) |
3.1 (1.2, 7.7) |
|
|
HAQ-DI improvement ≥0.3 |
4.5 (1.8 , 10.9)
|
1.4 (0.6 , 3.2) |
1.4 (0.6 , 3.2) |
|
|
Top *Kruskal-Wallis test P<0.05 and bottom **nominal P<0.05 for (high vs low) tertile IL-6-by-treatment interaction (logistic regression with treatment, study randomization stratification factors [region], tertile IL-6 at baseline, and tertile IL-6 at baseline-by-treatment interaction as fixed effects) $Stratified by study randomization stratification factor |
||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boyapati A, Msihid J, Schwartzman S, Choy E, Genovese MC, Burmester GR, Lam G, Kimura T, Sadeh J, Graham NMH. High Baseline Serum IL-6 Identifies a Subgroup of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Rapid Joint Damage and Clinical Progression and Predicts Increased Sarilumab Treatment Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-baseline-serum-il-6-identifies-a-subgroup-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-rapid-joint-damage-and-clinical-progression-and-predicts-increased-sarilumab-treatment-response/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-baseline-serum-il-6-identifies-a-subgroup-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-rapid-joint-damage-and-clinical-progression-and-predicts-increased-sarilumab-treatment-response/