Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The ACR recommends herpes zoster (HZ) vaccination prior to use of non-biologic and biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in RA patients and for those currently on non-biologic DMARD therapy. We evaluated the success rate of HZ vaccination or a documented discussion with eligible RA patients and whether it was affected by educational intervention.
Methods: In June 2015, a lecture on indications for HZ vaccine was given to the rheumatology practice at a single academic center; a pocket guide was provided. Records of RA patients over the age of 60 on medications including those in Table 1 were reviewed. Rates of HZ vaccination or a documented recommendation for the vaccine were compared between August 2014 and August 2015 (before and after the educational lecture). Patients excluded were those with HIV/AIDS, malignancy, tuberculosis therapy, pregnancy, prednisone > 20 mg/day (>/=2 weeks), biologic or contraindicated non-biologic DMARD, or documented fever at the visit. Clinical information was compared between the 2014 and 2015 groups. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the primary outcome in each year. Logistic regression was used to adjust for potential confounders. An anonymous survey was given to identify challenges to HZ vaccination
Results: 91 RA patients met inclusion criteria, 36 in 2014 and 62 in 2015, including 7 duplicate patients (Table 1). In 2014, 25% (9 patients) had a documented discussion or received the HZ vaccine; 22.2% received the vaccine while 33.3% already received it. In 2015, the rate of vaccination or documented discussion increased to 37% (23 patients). 8.7% received the vaccine (23% already received it). The difference in rates did not reach statistical significance. In multivariate analyses, the primary outcome not significantly affected by age, gender, race, year (surrogate for educational intervention), and clinic location. Only individual physician as a factor was significant (p=0.01).
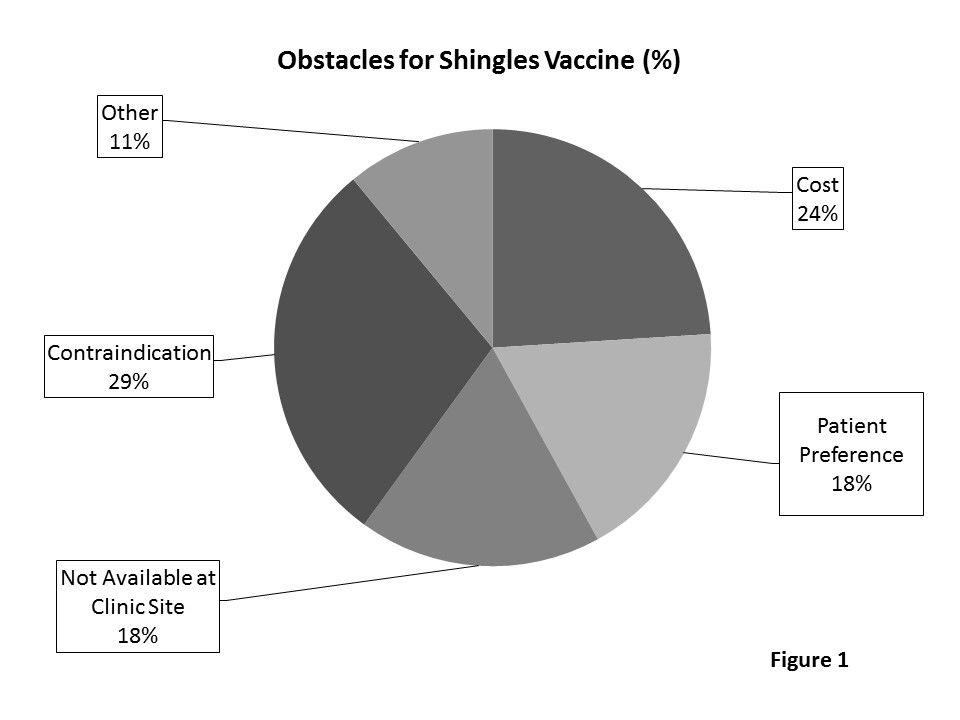
Conclusion: Compliance rates were low for HZ vaccine in eligible RA patients despite educational intervention. Based on survey results, contraindication was the top reason for not giving the vaccine (Figure 1). However, 71.6% patients met criteria for vaccination. Ways to improve compliance include innovative use of electronic medical systems, creation of specialty prevention clinics, improved availability of the HZ vaccine, and increased education for practitioners. Additional studies are warranted to explore ways to improve HZ vaccination rates in eligible RA patients. Disclosures: H. Chaudhry, None; R. Ostrowski, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostrowski RA, Chaudhry H. Herpes Zoster Vaccine: A Quality Improvement Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/herpes-zoster-vaccine-a-quality-improvement-study-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/herpes-zoster-vaccine-a-quality-improvement-study-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/