Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is known to increase the risk of cytopenias, but the prevalence of hematologic abnormalities among patients taking low dose MTX is poorly defined. We conducted a systematic literature review and meta-analysis to estimate the prevalence of anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia associated with MTX plus folic acid supplementation among non-oncology patients.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, PubMed, and Embase from inception to August 2016 for all randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) with a MTX monotherapy arm. We excluded RCTs for cancer and included only double-blind studies that reported on hematologic adverse events. Studies were excluded if patients did not receive folic acid or leucovorin supplementation. Most trials used MTX as the comparator arm against newer therapies. Full text articles were assessed by two independent reviewers. Risk of bias was assessed per Cochrane Risk of Bias guidelines including selection, performance, detection, attrition, and reporting bias. Pooled prevalence estimates were calculated using random-effects models. The heterogeneity across studies was tested using Cochran’s Q and I2.
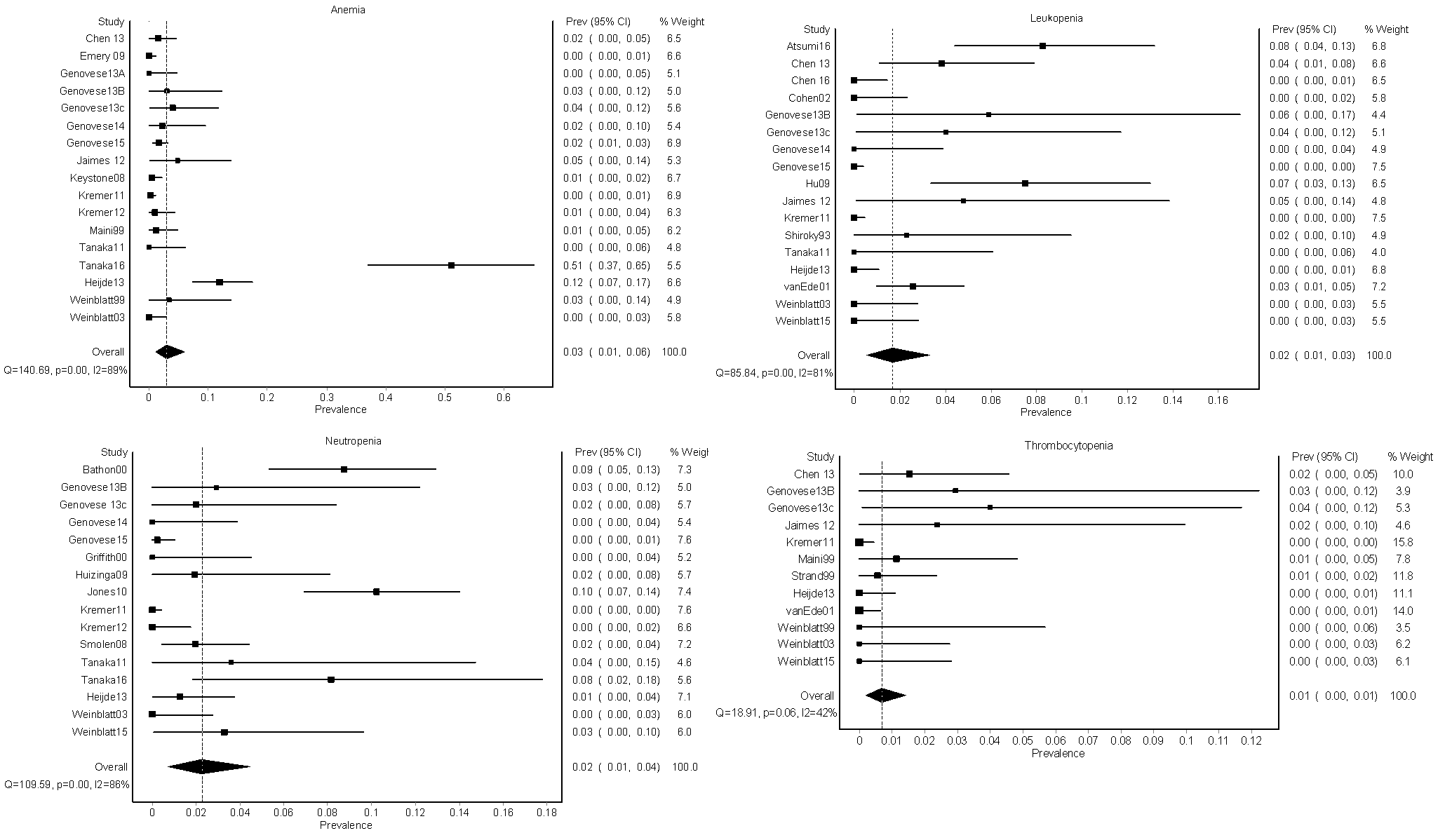
Results: Of 1601 studies identified, 30 (1.87%) were included that contained data from 3,858 patients with RA; no other rheumatologic conditions were represented. Seventeen trials reported on anemia (N=2,032), 17 reported on leukopenia (N=2,220), 16 reported on neutropenia (N=2,202), and 12 reported on thrombocytopenia (N=1,507). The mean dose of methotrexate was 15.4 (± 4.5) mg/week with a maximum dose of 30 mg/week, and 41.9% of subjects were using oral corticosteroids. Trial duration ranged from 12-62 weeks with a mean of 32 (±17) weeks. The pooled prevalence for anemia was 3.05% (95% CI 1.04-5.95%), leukopenia 1.67% (95% CI 0.55-3.31%), neutropenia 2.25% (95% CI 0.74-4.48%), and thrombocytopenia 0.67% (95% CI 0.18-1.42%)(Figure). Severe anemia was reported in 4 patients (0.20%), severe neutropenia was reported in 3 patients (0.14%), and no cases of severe leukopenia or thrombocytopenia were reported. The risk of bias assessment showed that most methodological limitations came from a failure to describe randomization procedures (N=23, 76.7%) and selective reporting of only severe hematologic adverse events (N=8, 26.7%). Significant statistical heterogeneity existed across studies for all cytopenias. The I2 (percentage of variation due to heterogeneity rather than chance) was high: I2 89% for anemia, 81% for leukopenia, 86% for neutropenia, 42% for thrombocytopenia.
Conclusion: Cytopenias are an uncommon side effect of low-dose MTX with folic acid supplementation among RA patients. Randomized controlled clinical trials vary widely in their reporting of hematologic adverse events, with many failing to report mild and moderate cases. Further research is needed to reach a more precise estimate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanni K, Zhang Z, Corrigan C, Solomon DH. Hematologic Abnormalities during the Use of Low Dose Methotrexate for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hematologic-abnormalities-during-the-use-of-low-dose-methotrexate-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hematologic-abnormalities-during-the-use-of-low-dose-methotrexate-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/