Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Health Services Research Poster II: Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Utilization patterns in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are complex. For targeted interventions, patients with special healthcare needs should be recognized. Our aim was to explore healthcare utilization profiles in RA by cluster analysis.
Methods: The RA patients attending Jyväskylä Central Hospital rheumatology unit, Finland, are as of 2007 enrolled prospectively in a structured digital database, from which we identified patients with rheumatology clinic visits in 2012-2014. We combined this clinical data with well-recorded administrative data on fiscal year 2014 on all public healthcare visits, both in primary and specialty care. For each patient, we considered the median of time dependent clinical variables. Clustering variables were disease activity score (DAS28-3), health assessment questionnaire index (HAQ index, 0-3), pain on visual analogue scale (VAS, 0-100) and total annual health services related direct costs (€), excluding out of pocket medication costs. The number of clusters was set based on dendrogram examination. We applied hierarchical clustering with Ward’s minimum variance method with Euclidean distance.
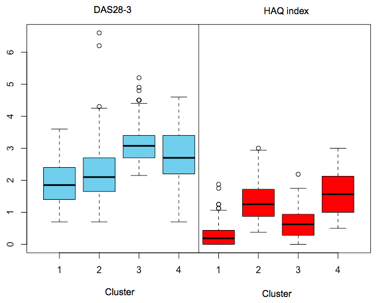
Results: Of 844 patients with RA, complete-case analysis (n = 827) derived four clusters. Descriptive statistics are in Table 1 and distributions for DAS28-3 and HAQ index are in Figure 1. Cluster 1 was the largest cluster constituting relatively young patients with low costs, low disease activity, and minimal disability. Cluster 2 was characterized by high pain levels and disability, despite fairly low average DAS28-3. Compared with cluster 2, patients in cluster 3 had high average disease activity and rheumatic disease -related costs, and biologics were more frequently used. Still, they presented with less pain and disability compared with cluster 2. Cluster 4 was small, heterogeneous and characterized by exceptionally high average costs. These patients had costly and severe comorbidities in addition to RA.
Conclusion: Over half of patients had low costs and favorable outcome measures, whereas a fifth was characterized by high disease activity and active treatment of RA, yielding higher costs. Pain and disability did not necessarily relate to high rheumatic disease -related costs. In all clusters, over half of costs were attributable to comorbidities.
|
|
Cluster 1 |
Cluster 2 |
Cluster 3 |
Cluster 4 |
|
n |
467 |
147 |
180 |
33 |
|
Age (mean ± SD) |
58.2 ± 15.3 |
66.5 ± 11.8 |
63.3 ± 13.9 |
71.1 ± 10.8 |
|
Disease duration (median) |
11.8 ± 8.5 |
16.3 ± 12.6 |
16.0 ± 12.5 |
18.6 ± 12.9 |
|
Pain (mean ± SD) |
15.9 ± 12.2 |
55.2 ± 18.3 |
37.2 ± 15.8 |
47.0 ± 20.9 |
|
RF+ (%) |
65 |
71 |
77 |
90 |
|
Ever biologics (%) |
23.3 |
24.5 |
43.3 |
45.5 |
|
Number of comorbidities |
2.1 ± 2.1 |
3.7 ± 2.8 |
3.4 ± 2.5 |
5.7 ± 3.5 |
|
Mean total costs/patient (€) |
2367 |
3785 |
6772 |
36206 |
|
Mean rheumatic disease costs/patient (%*) |
1054 (48.5) |
1455 (44.8) |
3076 (48.5) |
4323 (13.0) |
*Of recorded healthcare contacs
Table 1. Descriptive statistics.
Figure 1. Distributions for DAS28-3 and HAQ index based on individual time dependent medians.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mars N, Kerola AM, Kauppi MJ, Pirinen M, Elonheimo O, Sokka-Isler T. Healthcare Utilization Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis – a Cluster Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-utilization-profiles-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cluster-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-utilization-profiles-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cluster-analysis/