Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Superior rates of sustained glucocorticoid (GC)–free remission were shown in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) treated with weekly (QW) or every-other-week (Q2W) subcutaneous (SC) tocilizumab (TCZ) 162 mg + 26-week GC taper (TCZ+26) for 52 weeks compared with placebo + 26-week or 52-week GC taper (PBO+26 or PBO+52) in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial (GiACTA). Improvements in patient-reported SF-36 Physical Component Summary (PCS) score and Patient Global Assessment (PtGA) of disease activity were also reported for TCZ vs PBO+52 (Stone JH et al, N Engl J Med, in press). QW TCZ was recently approved for the treatment of patients with GCA.
Methods: Exploratory analysis of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) was performed in patients treated with QW TCZ+26 (n = 100) vs PBO+52 (n = 51) for 52 weeks based on observed data. Analyses included mean PROs based on a repeated-measures model that included all patients and post-escape data. Post hoc exploratory analyses were based on proportions of patients, and those who withdrew were classified as nonresponders at week 52.
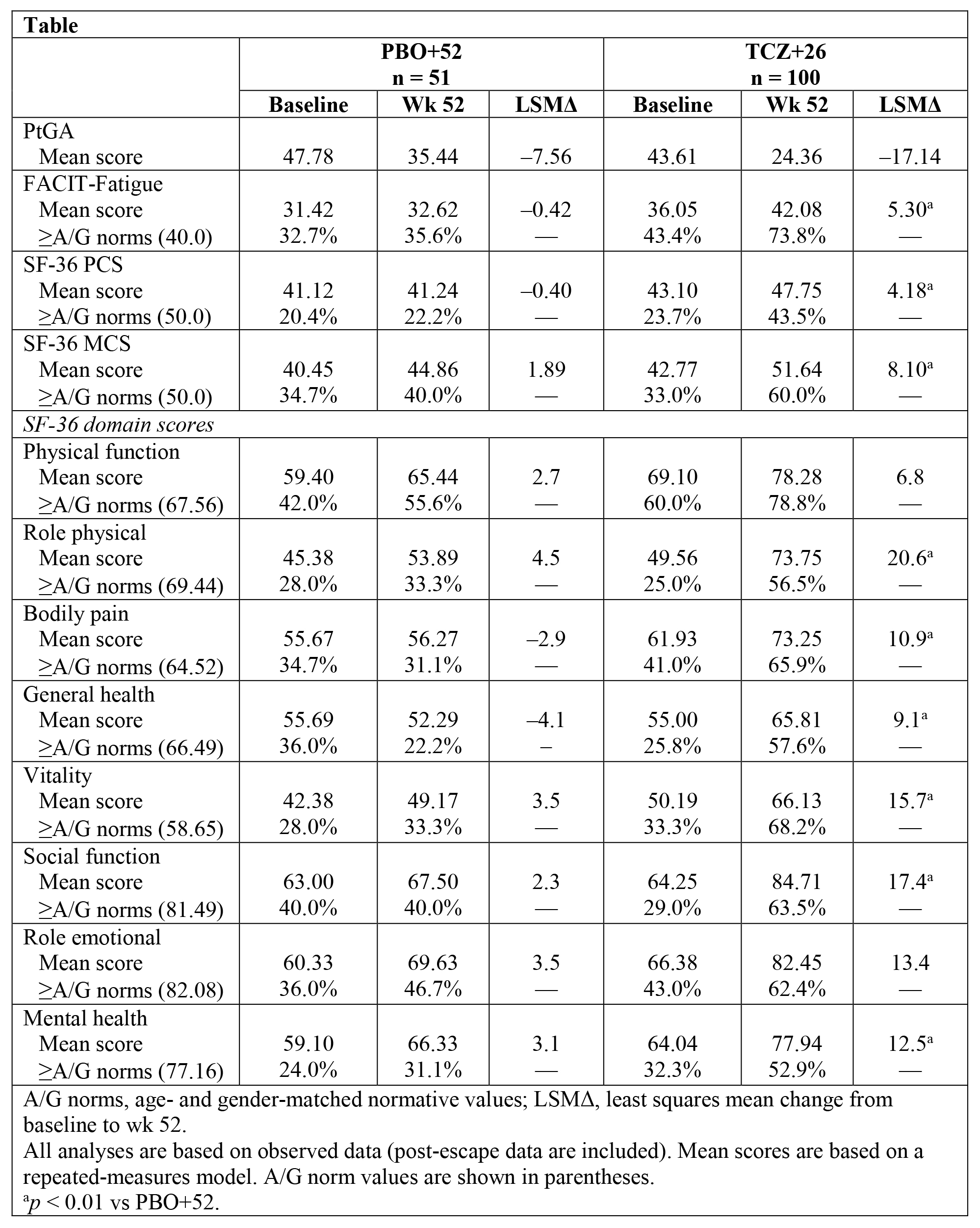
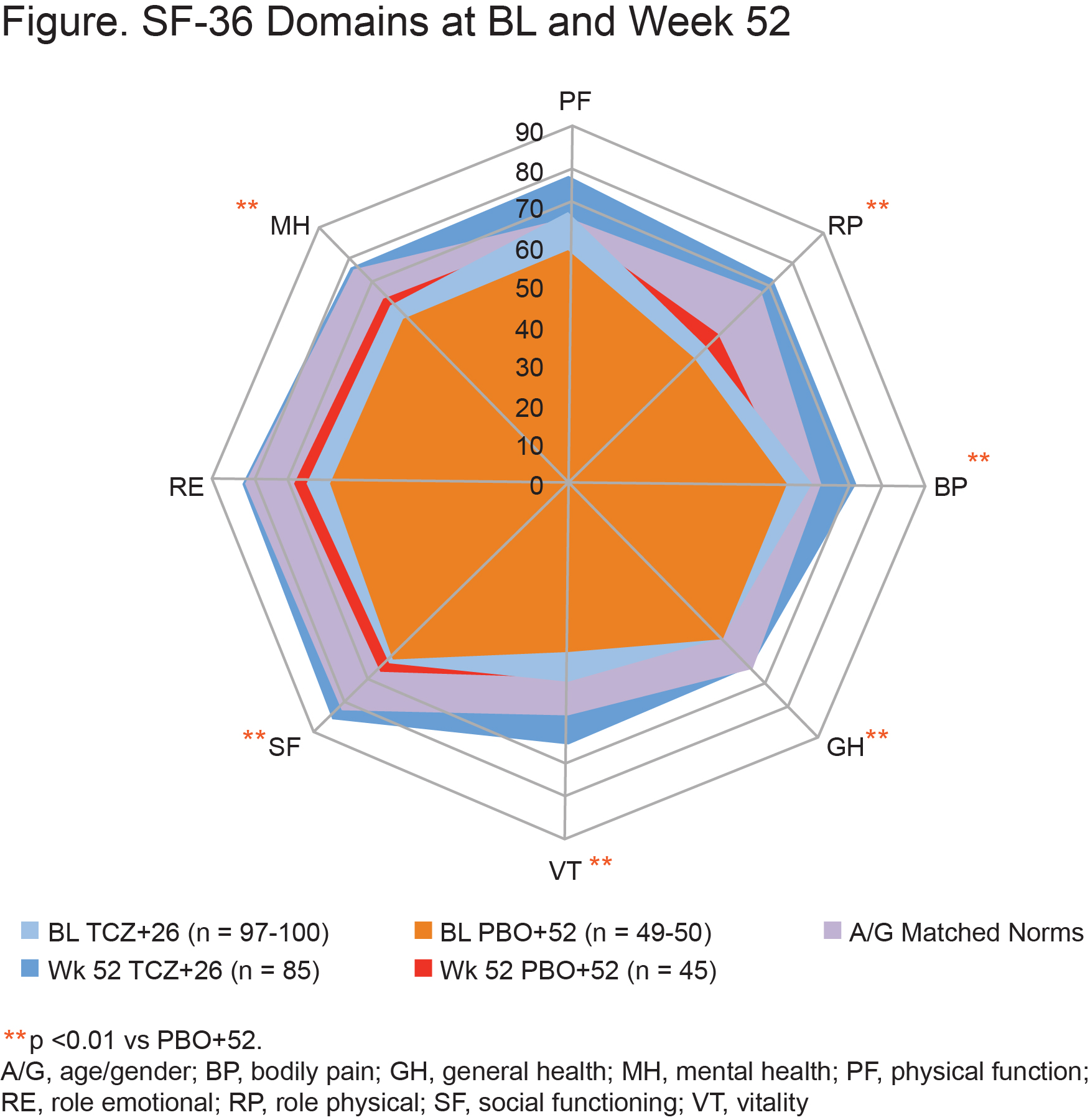
Results: Improvements in SF-36 Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores, 6 of 8 domains, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)–Fatigue at week 52 were statistically greater with QW TCZ+26 than PBO+52 (descriptive p < 0.01; Table, Figure); similar trends were observed vs PBO+26 (not shown). At week 52, mean scores exceeded age and gender (A/G)–matched normative scores with QW TCZ+26; higher proportions of patients reported scores ≥A/G norms in SF-36, PCS, MCS, all domains, and FACIT-Fatigue scores (Table). The median cumulative prednisone dose over 52 weeks was lower with QW TCZ+26 (1862.0 mg) than with PBO+52 (3817.5 mg) (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Patients with GCA treated with weekly TCZ 162 mg and a 26-week taper reported greater improvements in health-related quality of life and fatigue than those treated with a 52-week prednisone taper alone, in part ascribed to lower prednisone doses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Dimonaco S, Tuckwell K, Klearman M, Collinson N, Stone JH. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis Treated with Tocilizumab in a Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-treated-with-tocilizumab-in-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-treated-with-tocilizumab-in-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/