Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterised by progressive destruction of joint bone and loss of periarticularbone mineral. Hand bone loss (HBL) measured by Digital X-ray Radiogrammetry (DXR) has been proposed as a sensitive outcome measure for treatment effect and as a potential predictor of subsequent radiographic progression in RA patients. We aimed to investigate the effect of adding adalimumab to a methotrexate and intra-articular triamcinolone treat-to-target strategy on one-year hand bone loss (HBLone-year) in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to determine if HBL6months is associated with radiographic progression after two years.
Methods: In a clinical trial (OPERA) of 180 treatment-naive early RA patients (1), bone mineral density (BMD) was estimated from hand radiographs with Digital X-ray radiogrammetry (DXR) at baseline, after 6 months (n=90) and 12 months (n=70) of follow-up. Baseline and two-year radiographs were scored according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. Baseline characteristics and HBL6months (0-6 months changes in DXR-BMD) were investigated as predictors of structural damage by univariate linear (DTotal Sharp/van der Heijde Score (TSS) as dependent variable) and logistic (+/-radiographic progression (DTSS>0) as dependent variable) regression analyses. Variables with p<0.10 were included in multivariable models.
Results: In 70 patients with available HBLone-year data, HBLone-year was median (InterQuartileRange(IQR)) -1.9 (-3.3;-0.26 mg/cm2) in the placebo-group and -1.8 (-3.6;0.06) mg/cm2 in the adalimumab-group, p=0.98,Mann Whitney (Figure 1). Increased HBL (compared to general population reference values (2)) was found in 26/37 and 23/33 patients in the placebo- and adalimumab-groups, Chi-sq=0.99. In 90 patients with HBL6months data and two-year radiographic data, HBL6months was independently associated with DTSS after two years (β=-0.086 (95% Confidence Interval=-0.15;-0.025) TSS unit/mg/cm2 increase,p=0.006), and borderline associated with presence of radiographic progression (DTSS>0) (OR 0.96(0.92-1.0), p=0.10).
Conclusion: In early RA, adding adalimumab to a methotrexate-based treat-to-target strategy had no impact on HBLone-year, which was increased in both treatment groups. HBL6months was independently associated with DTSS after two years. References: 1) Hørslev-Petersen et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208166. 2) Ørnbjerg LM et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy.2016, 18:53 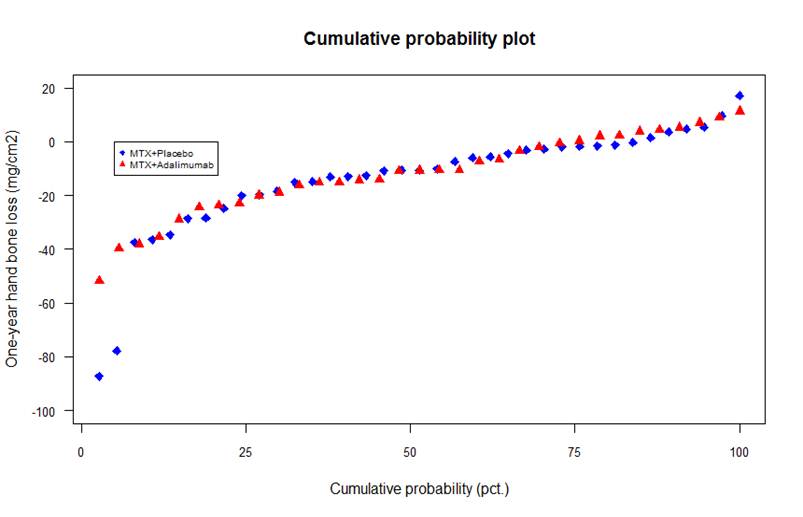
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ørnbjerg LM, Østergaard M, Jensen TD, Hørslev-Petersen K, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Junker P, Ellingsen T, Ahlquist P, Lindegaard H, Linauskas A, Schlemmer A, Yde Dam M, Hansen I, Lottenburger T, Ammitzbøll CG, Jørgensen A, Krintel SB, Raun JL, Lund Hetland M. Hand Bone Loss in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Independent of Adalimumab Treatment – Results from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hand-bone-loss-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-independent-of-adalimumab-treatment-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hand-bone-loss-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-independent-of-adalimumab-treatment-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial/
