Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) experience broad systemic symptoms including pain, fatigue, depression, sleep disturbance, poor physical function, and diminished social participation. DISCOVER 1 is a Phase 3 trial (NCT03162796) evaluating the efficacy and safety of guselkumab (GUS), an interleukin 23 inhibitor that binds to the p19-subunit of IL-23, in patients with active PsA. In this study, PROMIS-29 (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System-29), a validated generic health instrument,1 assessed the treatment effect of GUS on symptoms in patients with PsA.
Methods: Patients with active PsA despite nonbiologic DMARDs were enrolled, and ~30% of patients could have previously received ≤2 TNFi. Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to subcutaneous GUS 100 mg at Week 0 (W0), W4 then q8W (n=127), GUS 100 mg q4W (n=128), or PBO (n=126). Concomitant stable use of select csDMARDs, oral steroids, and NSAIDs was allowed. PROMIS-29 consists of 7 domains (Depression, Anxiety, Physical Function, Pain Interference, Fatigue, Sleep Disturbance, and Social Participation) and a pain intensity 0-10 numeric rating scale (NRS). The raw score of each domain is converted into a standardized T-score with a mean of 50 (general population mean) and a standard deviation (SD) of 10. Higher PROMIS scores represent more of the concept being measured. A ≥5-point improvement (1/2 SD of T-score) is defined as clinically meaningful.1
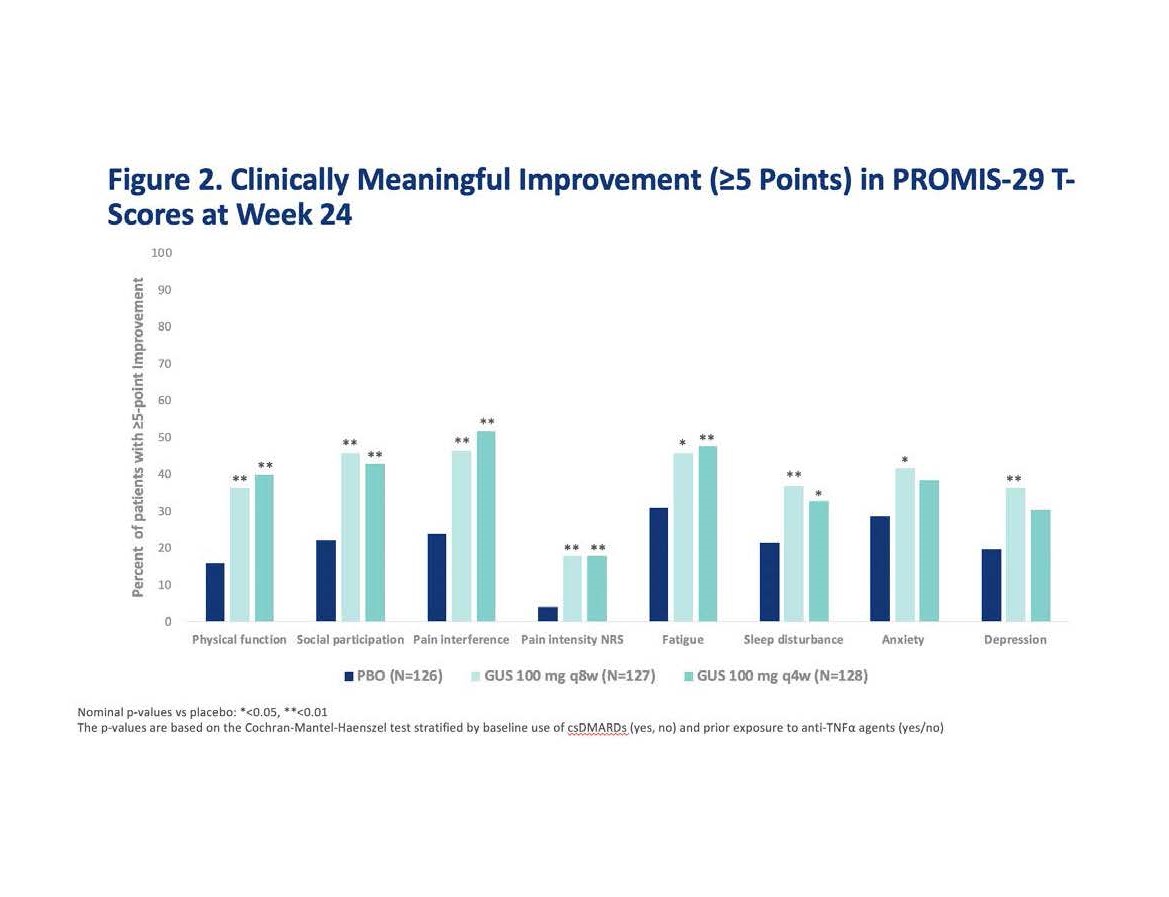
Results: At baseline, mean PROMIS-29 T-scores for physical function, social participation, sleep disturbance, pain, and fatigue were worse than the general US population. At W24, GUS q8W-treated patients achieved greater improvements from baseline in all PROMIS-29 domains vs PBO (p< 0.05) (Table and Fig 1). Results were consistent in the GUS q4W group except for anxiety and sleep disturbance. More patients receiving GUS achieved clinically meaningful improvement vs PBO except for depression and anxiety in the GUS q4W group, which were numerically improved (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Active PsA patients treated with GUS achieved clinically meaningful reduction in symptoms and improvement in physical function and social participation vs PBO at W24
Reference:
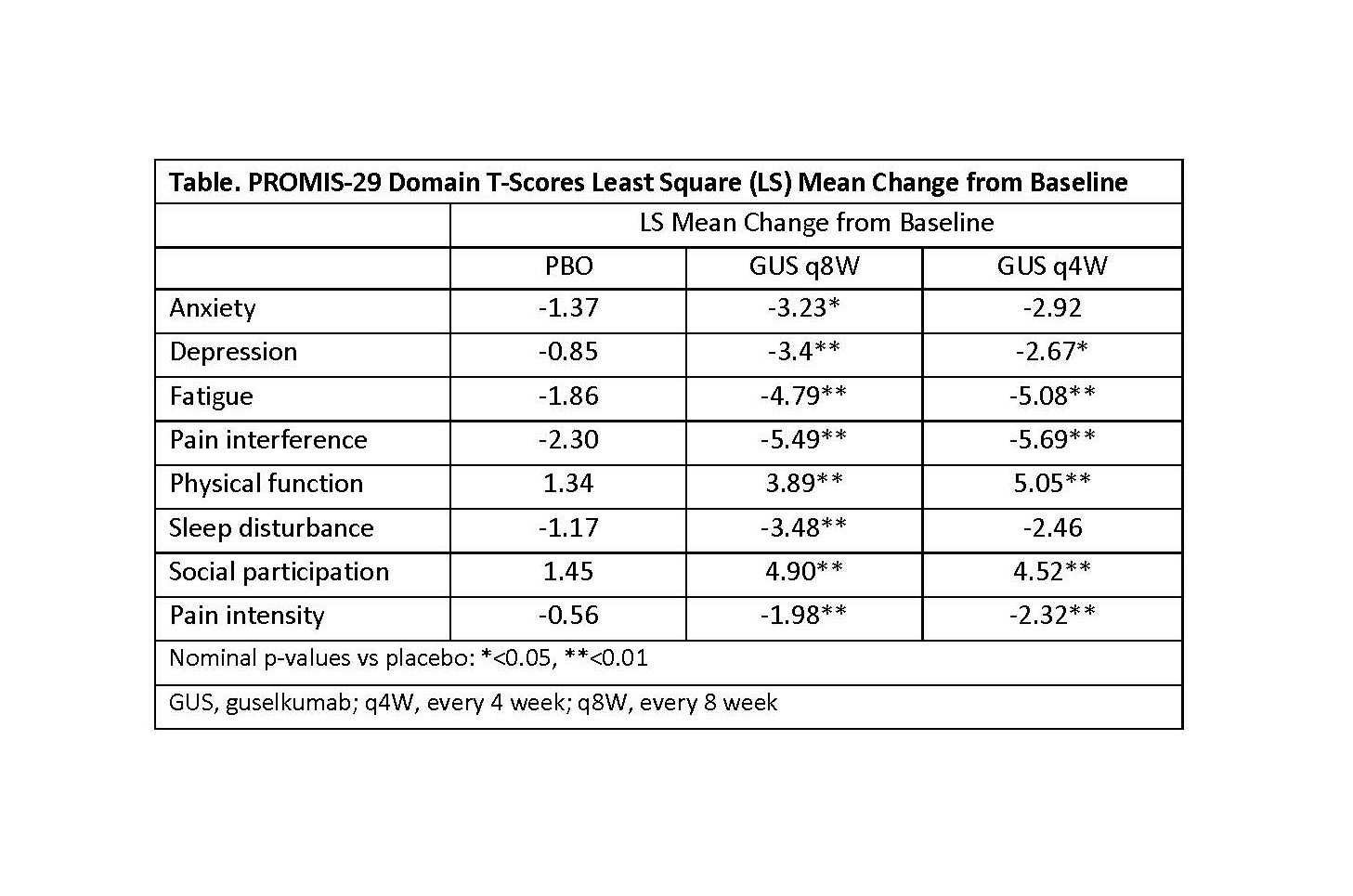 Table: PROMIS-29 Domain T-Scores Least Square (LS) Mean Change from Baseline
Table: PROMIS-29 Domain T-Scores Least Square (LS) Mean Change from Baseline
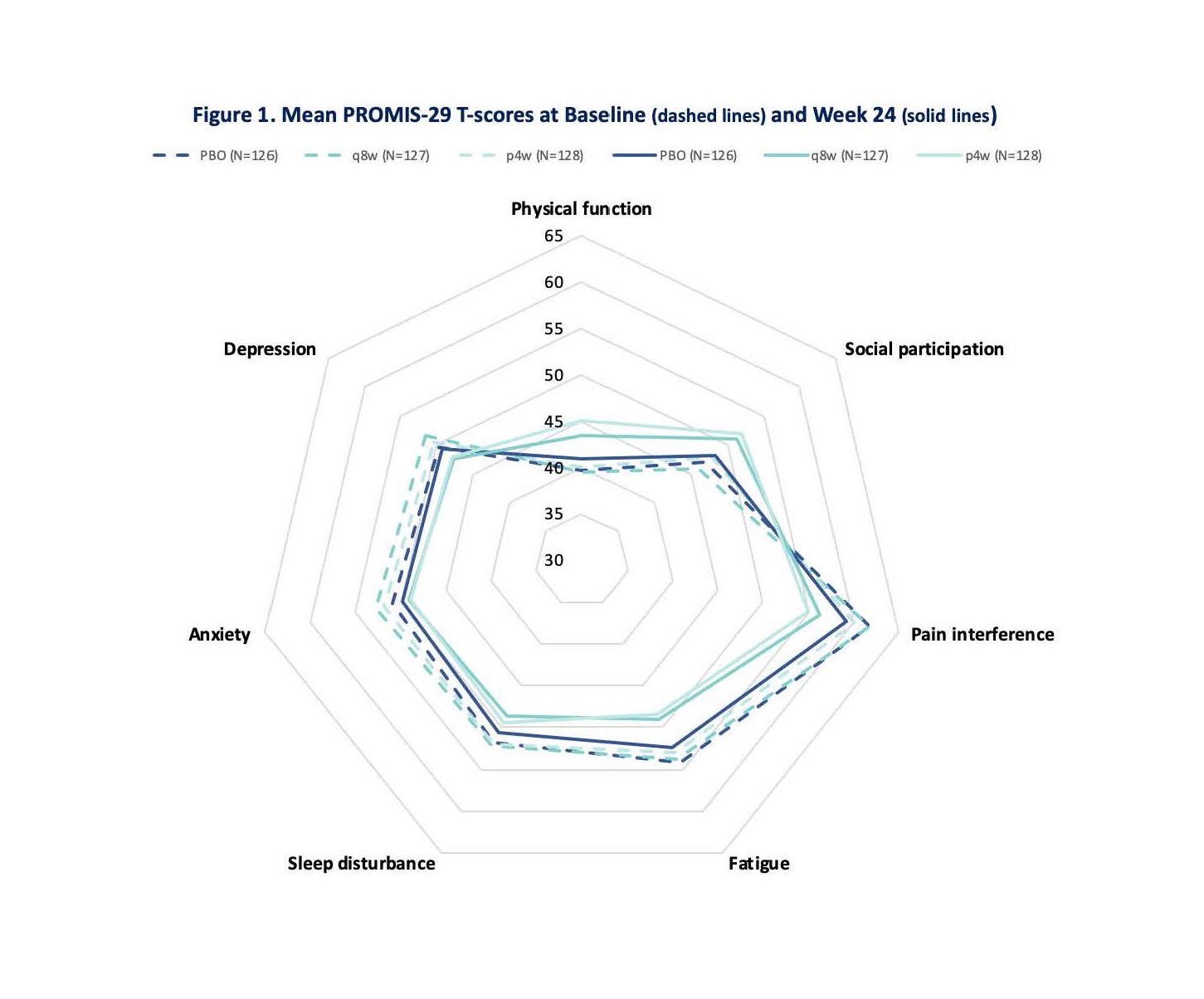 Figure 1: Mean PROMIS-29 T-Scores at Baseline (dashed lines) and Week 24 (solid lines)
Figure 1: Mean PROMIS-29 T-Scores at Baseline (dashed lines) and Week 24 (solid lines)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Orbai A, Coates L, Deodhar A, Helliwell P, Ritchlin C, Kollmeier A, Hsia E, Xu X, Sheng S, Zhou B, Han C. Guselkumab-Treated Patients Achieved Clinically Meaningful Improvement in Systemic Symptoms as Measured with PROMIS Instrument: Results from Phase-3 Psoriatic Arthritis Trial DISCOVER 1 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-treated-patients-achieved-clinically-meaningful-improvement-in-systemic-symptoms-as-measured-with-promis-instrument-results-from-phase-3-psoriatic-arthritis-trial-discover-1/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-treated-patients-achieved-clinically-meaningful-improvement-in-systemic-symptoms-as-measured-with-promis-instrument-results-from-phase-3-psoriatic-arthritis-trial-discover-1/