Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Abstracts: Miscellaneous Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) impacts patients’ work productivity (WP) and daily activity.1 DISCOVER-2 (D2), a phase 3 trial of the selective interleukin-23 p19-subunit inhibitor guselkumab (GUS) in biologic-naïve patients with PsA,2 demonstrated significant improvements in patient-reported WP and daily activity following 1 year of GUS treatment.3 This study assessed WP and daily activity impairment in D2 patients through 2 years, estimated indirect savings associated with GUS treatment, and assessed changes in employment status.
Methods: Patients with active PsA received GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at Week (W) 0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO). At W24, PBO patients crossed over to GUS 100 mg Q4W. Work productivity and activity impairment (WPAI)-PsA assesses PsA-related work time missed (absenteeism), impairment while working (presenteeism), and impaired overall WP (absenteeism + presenteeism) for patients employed at baseline (EBL) and daily activity for all patients, including those unemployed at baseline (UBL) during the previous week. Mean changes in WPAI-PsA domains were calculated for each multiple imputation (MI) dataset using an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA); the reported least square (LS) mean is the average of all MI datasets. Significance was defined as p< 0.05. Among patients EBL, potential indirect savings from improved overall WP were estimated using 2020 European Union mean yearly wage estimate (all occupations) combined with LS mean change from BL in WPAI-PsA overall work impairment.4 A shift analysis evaluated proportions of patients employed vs unemployed by treatment group using observed data over time.
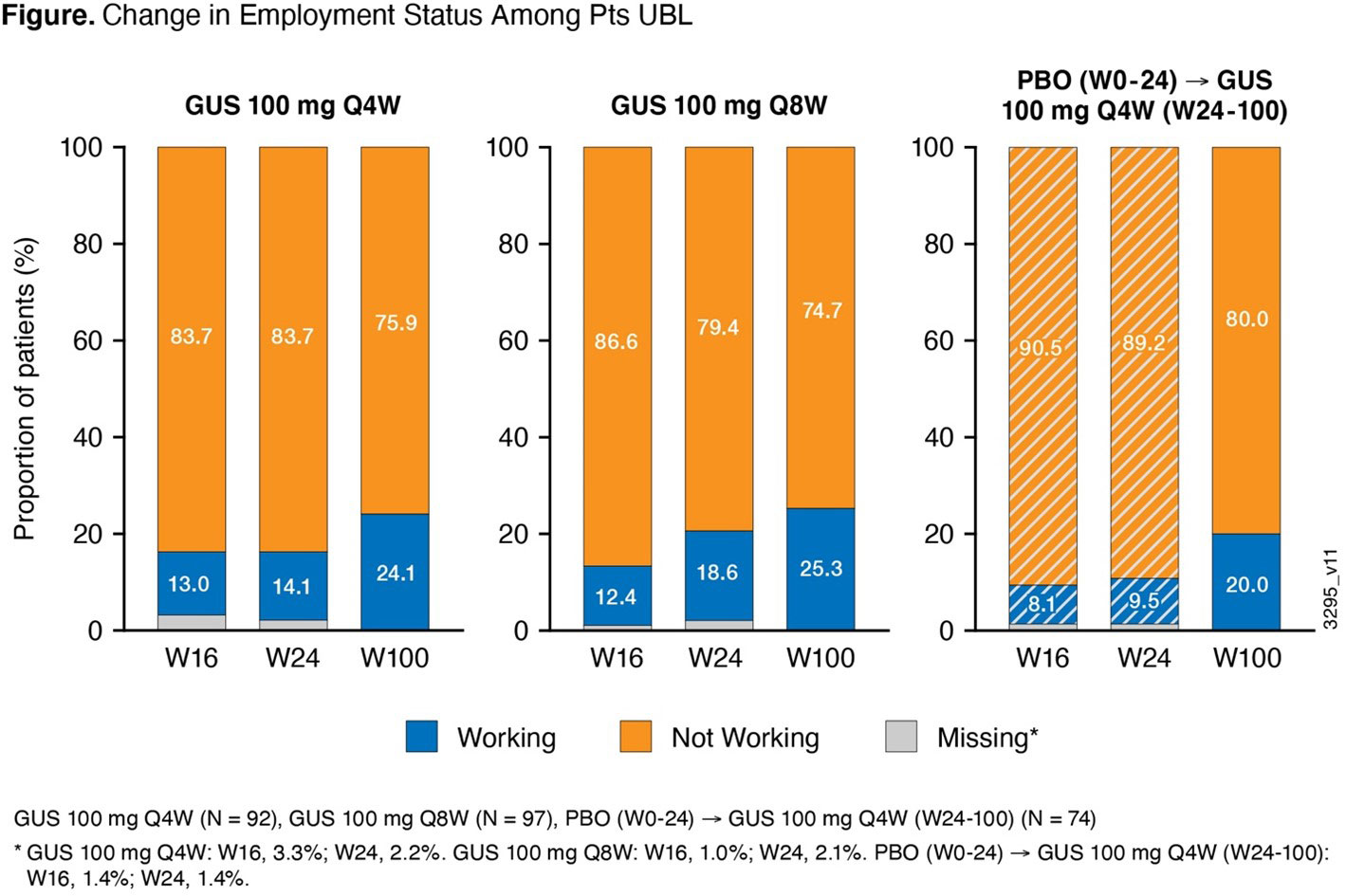
Results: Patients EBL comprised 64% of the analysis cohort. Significant improvements in WP in patients EBL and in daily activity among all patients were observed with GUS Q4W/Q8W vs PBO at W24;3 mean improvements in WP and daily activity increased with continued GUS through 2 years (Table). Potential annual indirect savings from improved overall WP in patients EBL were €10,826 GUS Q4W, €12,712 GUS Q8W, and €10,948 PBO® GUS Q4W at 2 years. Shift analysis showed relatively stable employment in patients EBL with GUS up to 2 years ( >83% continued to work). Among patients UBL (36% of cohort), the proportion of patients employed increased by >20% through 2 years of GUS (Figure).
Conclusion: In GUS-treated bio-naïve PsA patients, robust improvements in WP and daily activity seen at W24 were maintained and increased through 2 years of GUS. Long-term improvements in WP achieved may result in substantial indirect cost savings for GUS-treated patients. Rates of employment remained stable in patients employed and increased in those unemployed at BL.
References:
1. Tillett W et al. Rheumatol (Oxford). 2012;51:275–83.
2. Mease PJ et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1126–36.
3. Curtis JR et al. EULAR, June 2–5, 2021. POS1026.
4. OECD (2020). Average wages (indicator). https://data.oecd.org/earnwage/average-wages.htm
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, McInnes I, Rahman P, Gladman D, Yang F, Peterson S, Kollmeier A, Shiff N, Han C, Shawi M, Tillett W, Mease P. Guselkumab Provides Sustained Improvements in Work Productivity and Daily Activity in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Through 2 Years of DISCOVER-2 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-work-productivity-and-daily-activity-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years-of-discover-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-work-productivity-and-daily-activity-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years-of-discover-2/