Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by peripheral arthritis, axial inflammation, dactylitis, enthesitis, and skin/nail psoriasis, is associated with reduced health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study assessed long-term effect of guselkumab (GUS), a human monoclonal antibody that selectively targets the interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit, on HRQoL of bio-naïve PsA patients who participated in the phase 3 DISCOVER-2 trial.1
Methods: Patients with active PsA despite nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) received GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at Week (W) 0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO). At W24, PBO patients crossed over to GUS 100 mg Q4W. HRQoL was assessed using the patient-reported EuroQoL-5 Dimension-5 Level (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire index and EuroQol Visual Analog Scale (EQ-VAS), widely used and complimentary tools that allow patients to provide a global assessment of their HRQoL. The EQ-5D-5L index assesses mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression; an index score is derived ranging from 0 (death) to 1 (perfect health).2 EQ‑VAS assesses patient health state on a scale of 0-100, with higher scores indicating better health. Using mixed effects models for repeated measures (MMRM), least squares (LS) mean changes from baseline in the EQ-5D-5L index and EQ‑VAS through W100 were assessed. Observed changes from baseline were evaluated; in patients who met treatment failure rules before W24 and in patients who discontinued with missing data after W24, changes from baseline were imputed as 0.
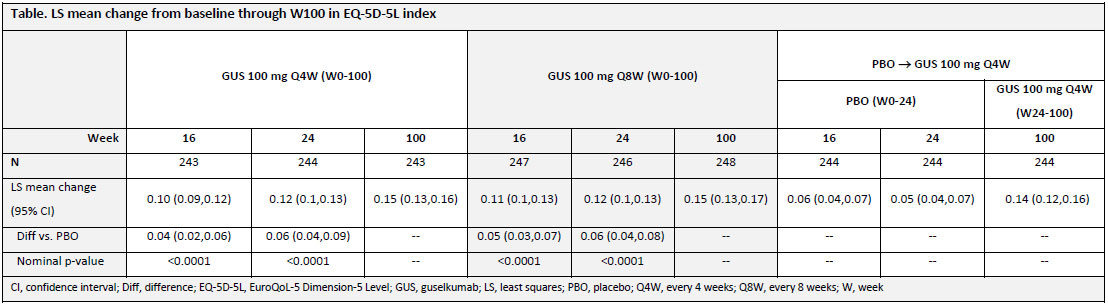
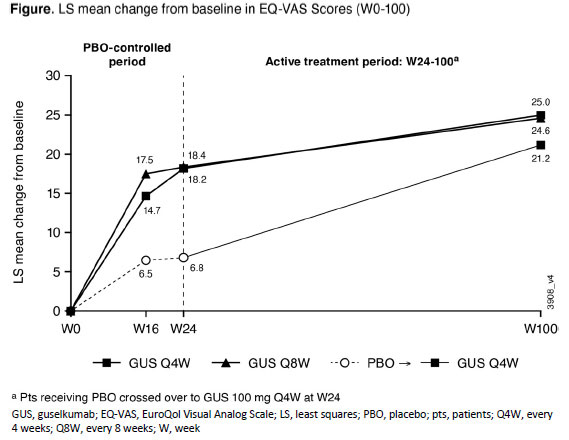
Results: GUS-treated patients achieved greater improvements in patient-reported health status than PBO at both W16 and W24 when evaluated using both the EQ-5D-5L index score and the EQ-VAS. The improvements by GUS in EQ-5D-5L index scores through W24 (0.12 for GUS Q4W/Q8W vs 0.05 for PBO; each nominal p< 0.0001) were maintained with continued GUS through 2 years (0.15 for GUS Q4W/Q8W) (Table). PBO-treated patients who started GUS at W24 reported comparable improvements in their HRQoL by W52 (0.12), with maintenance though W100 (0.14). Similar results were observed with EQ-VAS (Figure). W24 improvements in EQ-VAS scores were greater following GUS treatment (18.2/18.4 GUS Q4W/Q8W) vs PBO (6.8; nominal p< 0.0001). EQ-VAS scores continued to improve with GUS through 2 years (25.0/24.6 GUS Q4W/Q8W). Likewise, PBO-treated patients who crossed over to GUS at W24 experienced improvements in HRQoL by W52 (18.8), with maintenance through W100 (21.2).
Conclusion: In bio-naïve patients with active PsA receiving GUS, earlier improvements (at the first timepoint assessed) in self-reported health-related measures were sustained through 2 years.
References:
1. Mease PJ, et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1126–36.
2. EuroQol Group. Health Policy. 1990;16:199-208.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, McInnes I, Rahman P, Gladman D, Yang F, Peterson S, Kollmeier A, Shiff N, Han C, Shawi M, Tillett W, Mease P. Guselkumab Provides Sustained Improvements in Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Through 2 Years of DISCOVER-2 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years-of-discover-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years-of-discover-2/