Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Recent guidelines from the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) recommend that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) therapy achieve lowest possible disease activity across 6 key domains and related conditions.1 In the DISCOVER-1&2 trials, guselkumab (GUS) significantly improved signs and symptoms of PsA at Week (W) 24. We evaluated GUS efficacy through W100 of DISCOVER-2 across GRAPPA-recommended PsA domains (peripheral arthritis, skin, dactylitis, enthesitis, axial disease) and related conditions of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and uveitis (nails not evaluated).
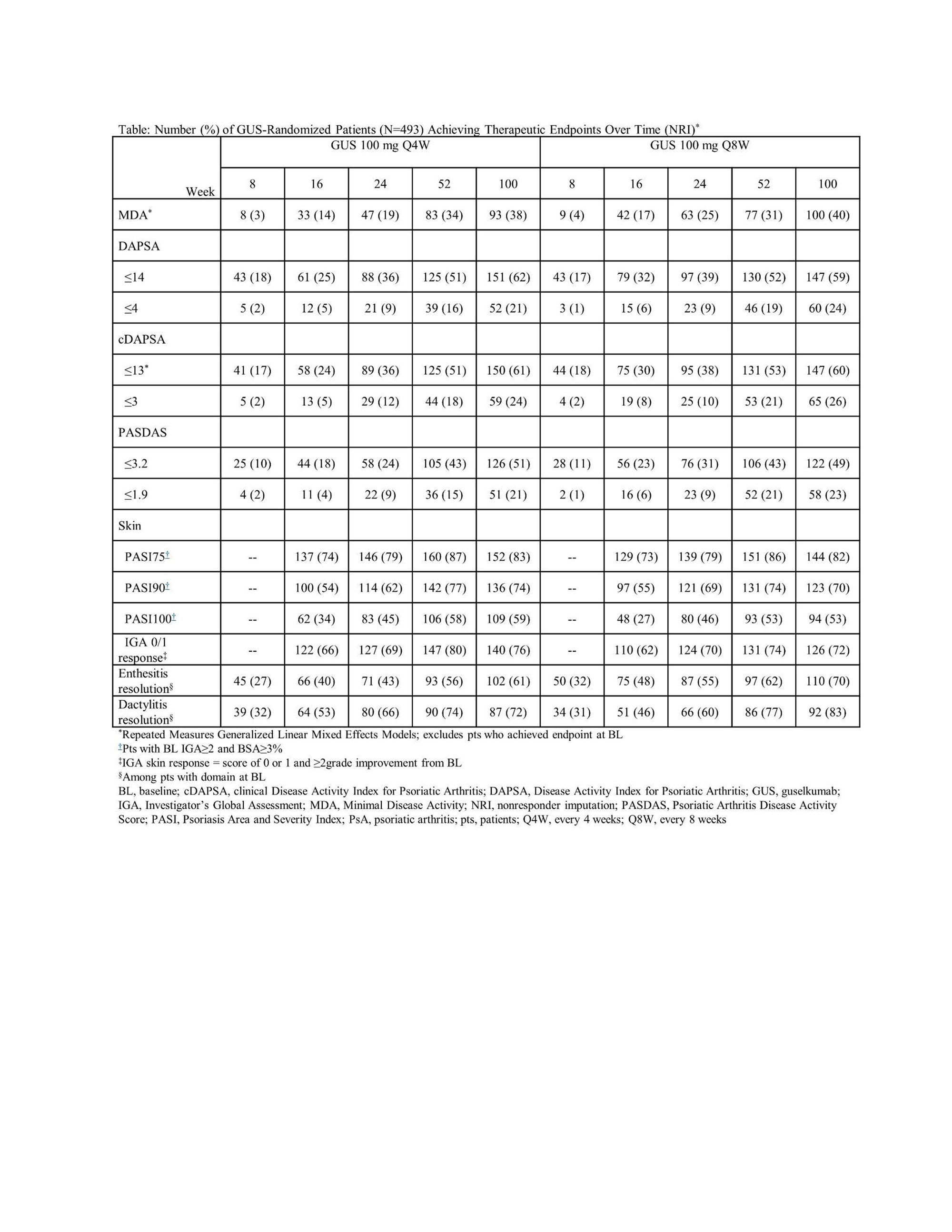
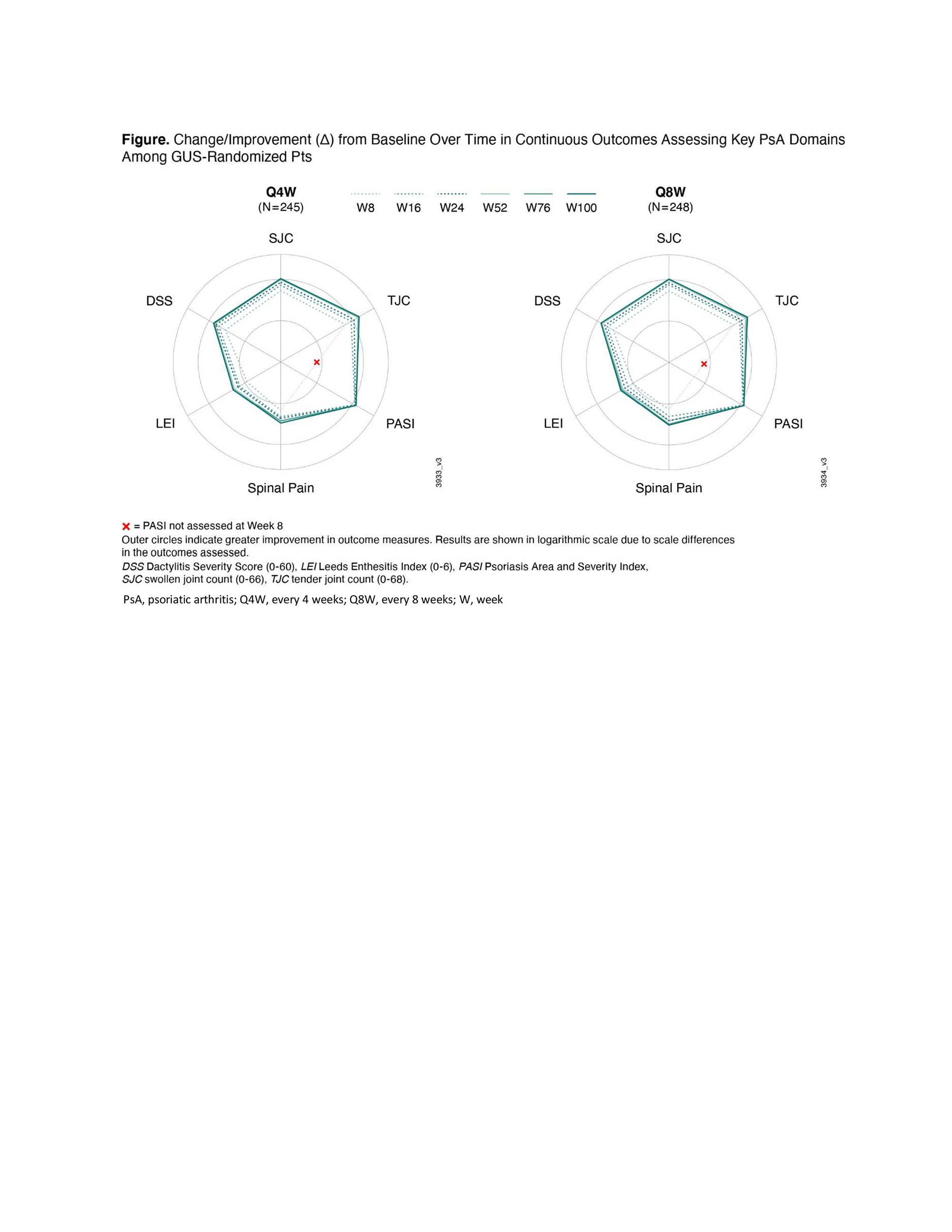
Methods: Enrolled adults had active PsA, were naïve to biologics/Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and had ≥5 swollen and ≥5 tender joints and C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥0.6 mg/dL. Randomized (1:1:1) patients received GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO); PBO patients crossed over to GUS 100 mg Q4W at W24. Outcomes selected aligned with GRAPPA-recommended domains/conditions: overall disease activity (Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score [PASDAS], Minimal Disease Activity [MDA]), peripheral arthritis (changes in Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis [DAPSA] and clinical DAPSA [cDAPSA]), skin (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index [PASI], Investigator’s Global Assessment [IGA] of psoriasis), dactylitis (Dactylitis Severity Score [DSS]), enthesitis (Leeds Enthesitis Index [LEI]), axial disease (spinal pain) and IBD/uveitis (adverse events [AEs]). Among 493 GUS-randomized patients, change from baseline (BL) through W100 in continuous outcomes were analyzed by Repeated Measures Generalized Linear Mixed Effects Models adjusting for respective BL score and GUS regimen. Achievement of therapeutic endpoints was summarized by descriptive statistics using nonresponder imputation (NRI) for missing categorical data.
Results: Approximately 90% of GUS-randomized patients completed treatment at W100. For continuous outcomes, improvements over time in key PsA domains extended through W100 of GUS (Figure). Therapeutic endpoint response rates also increased incrementally through W100 (Table). Mean improvements and response rates were consistent across key domains with no significant difference between GUS regimens. For related conditions in GUS patients, 1 patient with IBD and 4 with uveitis were reported at BL and had AE of exacerbation through W100. No patient developed IBD through W100 (vs 1 PBO patient through W24); 1 GUS patient had AE of iridocyclitis through W100 (vs 1 PBO patient through W24).
Conclusion: In DISCOVER-2 bio-naïve PsA patients, both GUS regimens provided continued improvements in key GRAPPA-recommended domains of PsA through up to 2 years of treatment.
Reference:
1 Coates et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80 (suppl 1):139.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, Gossec L, Contré C, Shawi M, Rampakakis E, Shiff N, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Nash P, Mease P, Helliwell P. Guselkumab Provides Continued Improvement in Key Domains of Psoriatic Arthritis Through 2 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-continued-improvement-in-key-domains-of-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-provides-continued-improvement-in-key-domains-of-psoriatic-arthritis-through-2-years/