Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
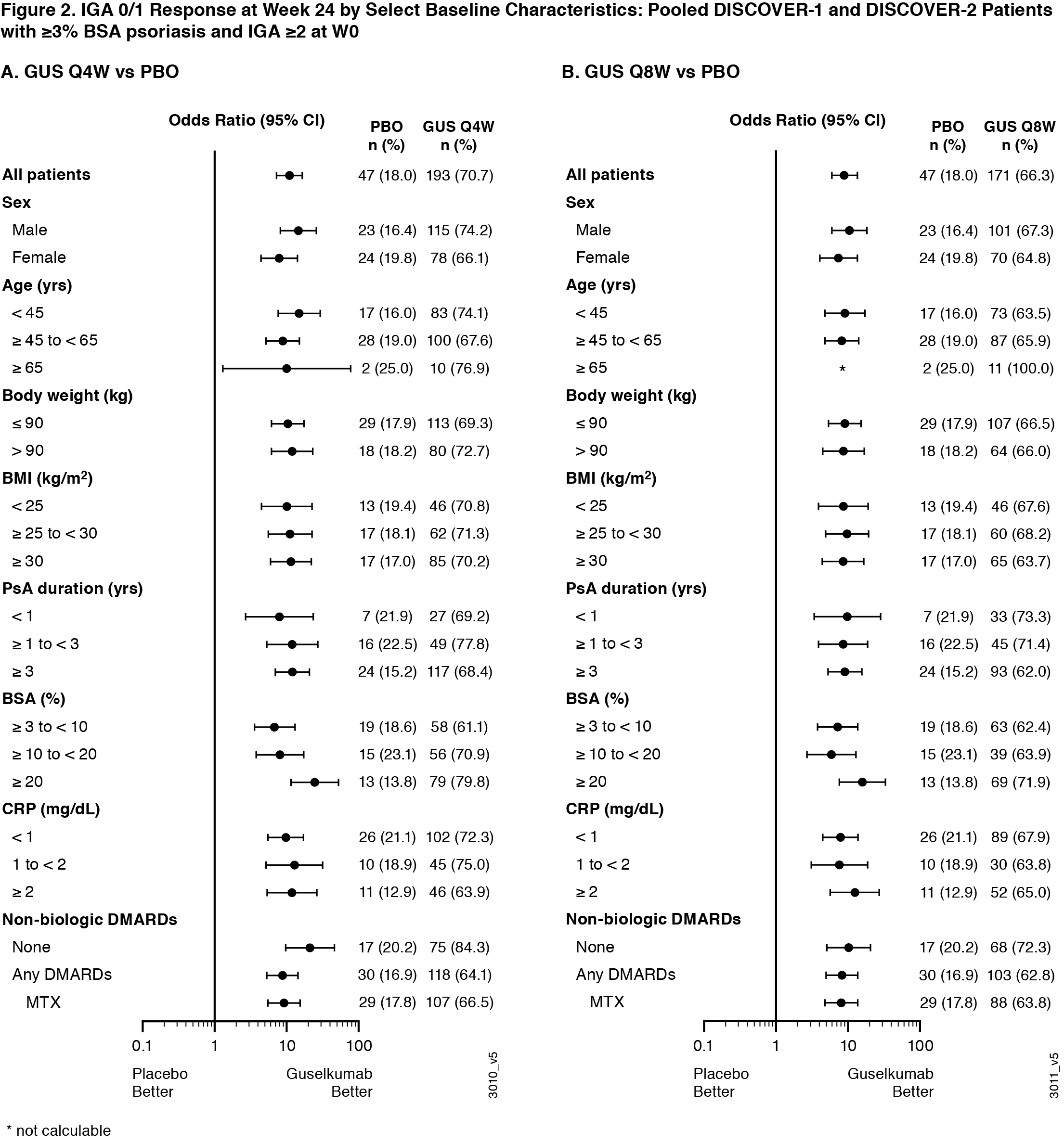
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a human monoclonal antibody targeting the IL-23p19-subunit, has shown consistent efficacy in psoriasis pts regardless of body weight/body mass index (BMI).1 GUS has also shown efficacy across joint and skin endpoints at Week 24 (W24) of the Phase 3 DISCOVER-12 and DISCOVER-2 PsA3 trials. We assessed GUS efficacy at W24 across baseline demographic and disease characteristics subgroups by pooling data across the 2 trials.
Methods: Adults with active PsA despite standard therapies were enrolled in DISCOVER-1 (≥3 swollen & ≥3 tender joints; CRP ≥0.3 mg/dL) and DISCOVER-2 (≥5 swollen & ≥5 tender joints; CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL). 31% of DISCOVER-1 pts had received 1-2 prior TNF inhibitors; DISCOVER-2 pts were biologic-naïve. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then every 8 weeks (Q8W); or placebo (PBO). GUS effects on joint (ACR50) and skin (Investigator’s Global Assessment [IGA=0/1 + ≥2-grade reduction from W0] in pts with ≥3% body surface area [BSA] psoriasis and IGA ≥2 at W0) responses were evaluated by pt sex, age, body weight, BMI, PsA duration, tender/swollen joint counts (ACR50 only), % BSA (IGA 0/1 only), CRP, and non-biologic (nb) DMARD/methotrexate (MTX) use at W0. Missing data were imputed as nonresponse. Logistic regression compared GUS vs PBO; odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are shown on a logarithmic scale.
Results: Baseline characteristics of randomized and treated pts in DISCOVER-1 (N=381) and DISCOVER-2 (N=739) were generally well-balanced across groups.1,2 On average, the 1120 pooled pts were 47 yrs and 85 kg at W0; 52% were male; 96% were white. At W24, 34% (127/373) and 31% (116/375), respectively, of pooled GUS Q4W- and Q8W-treated pts achieved ACR50 vs 12% (46/372) for PBO; respective ORs (95% CIs) were 3.7 (2, 5) and 3.2 (2, 5). In subgroups with sufficient sample size, the benefit of GUS Q4W and Q8W over PBO in substantially improving joint signs and symptoms was seen regardless of sex (ORs 3–4), age (2–4), body weight/BMI (3–6), PsA duration (2–7), swollen/tender joint count (2–10), CRP (2–6), or nbDMARD/MTX use (2–5) at baseline. In pooled pts with ≥3% BSA psoriasis and IGA ≥2 at W0, 71% (193/273) and 66% (171/258), respectively, of GUS Q4W- and Q8W-treated pts, vs 18% (47/261) for PBO, had an IGA 0/1 response at W24; respective ORs (95% CIs) were 11 (7, 16) and 9 (6, 14). The benefit of GUS in achieving clear or almost clear skin was seen regardless of sex (ORs 7-15), age (8-15), body weight/BMI (9-12), PsA duration (8-12), % BSA (7-25), CRP (8-13), or nbDMARD/MTX use (8–21) at baseline. Note that small sample sizes in several pt subgroups (eg, pts >65 years, swollen joint count >15) limit their data interpretation. Consistent results were seen for other joint (ACR20/70), skin (PASI90/100), and soft tissue (enthesitis) outcomes.
Conclusion: Conclusions: The benefits of guselkumab 100 mg Q4W and Q8W in substantially improving signs and symptoms of active PsA appeared to be consistent irrespective of the baseline characteristics assessed.
References: 1Armstrong A, et al. World Congress of Dermatology 2019; Poster P524; 2Deodhar A, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1115-25; 3Mease P, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1126-36.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Mease P, Boehncke W, Tesser J, Schiopu E, Chakravarty S, Kollmeier A, Hsia E, Xu X, Shawi M, Jiang Y, Sheng S, Agarwal P, Merola J, McInnes I, Ritchlin C. Guselkumab Efficacy in Adult Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis by Baseline Demographic and Disease Characteristics: Pooled Results of Two Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-efficacy-in-adult-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-by-baseline-demographic-and-disease-characteristics-pooled-results-of-two-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-efficacy-in-adult-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-by-baseline-demographic-and-disease-characteristics-pooled-results-of-two-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-studies/