Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19-subunit of IL-23, is approved to treat psoriasis (PsO). At Week 24 of the Phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial in patients (pts) with active PsA who were biologic-naïve or prior TNFα inhibitor (TNFi)-treated (DISCOVER-1), GUS 100 mg, given every 4/8 weeks (Q4W/Q8W), demonstrated efficacy for joint and skin symptoms, physical function, and quality of life vs PBO. Adverse events (AEs) were consistent with GUS safety in PsO. This study assessed GUS efficacy and safety in pts with PsA through 1 year.
Methods: Adults with active PsA (≥3 swollen + ≥3 tender joints; CRP≥0.3 mg/dL) despite standard therapies were eligible. Approximately 30% of pts could have previously received ≤2 TNFi. Pts were randomized 1:1:1, stratified by Week 0 DMARD (Y/N) and prior TNFi use (Y/N), to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at Weeks 0 and 4, and Q8W; or PBO. At Week 24, PBO pts crossed over to GUS 100 mg Q4W (PBO X Q4W). Week 48 marked the last dose of study agent. ACR response rates at Week 52, based on non-responder imputation (NRI) for missing data and as observed in pts still on study agent at Week 24, are shown. Observed data for additional endpoints are shown. AEs were reported through Week 60.
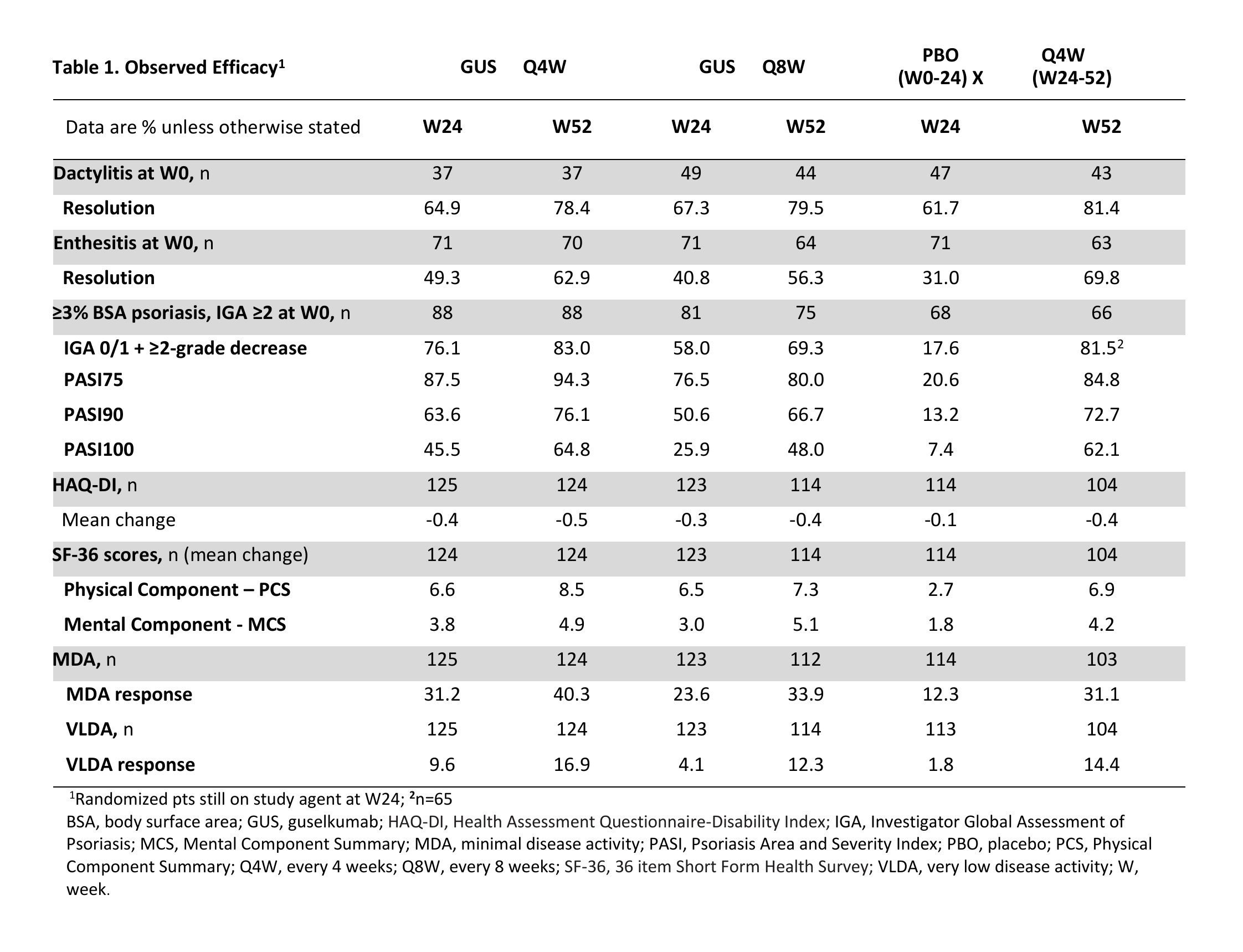
Results: 362/381 (95%) randomized pts continued study agent at Week 24 (125 Q4W, 123 Q8W, 114 PBO X Q4W), 347/381 (91%) pts completed treatment, and 343/381 (90%) completed the study. NRI ACR20 response rates were maintained at Week 52 (Q4W: 73%, Q8W: 60%; Fig. 1A). Similar response patterns were seen for the more stringent ACR50/70 criteria (Fig. 1C, E). Observed ACR responses, overall (Fig. 1B, D, F) and in pts with (Fig. 2A, C, E) and without (Fig. 2B, D, F) prior TNFi use, were also maintained at Week 52. Improvements in other clinical outcomes were also maintained at Week 52, and responses for pts crossing over from PBO X Q4W at Week 24 were generally consistent with other GUS-treated pts by Week 52 (Table 1). Through Week 24, 4 (2%) GUS- and 5 (4%) PBO-treated pts had serious AEs; no GUS-treated and 2 (2%) PBO-treated pts had a serious infection. Through Week 60, serious AEs and serious infections occurred in 4% and 1%, respectively, of all 369 GUS-treated pts. No GUS-treated pt died or had IBD, opportunistic infections or active tuberculosis, or anaphylactic or serum sickness-like reactions.
Conclusion: GUS Q4W and Q8W maintained improvements in joint symptoms through 1 year in pts with active PsA who were biologic-naïve or previously TNFi-treated. In pts continuing in the study, improvements in skin symptoms, dactylitis, enthesitis, physical function, and quality of life were also maintained through 1 year. GUS 100 mg Q4W and Q8W were safe and well-tolerated through study completion and consistent with GUS safety in PsO.1
Reference: 1. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) Prescribing Information. Janssen Biotech, Inc. 2017. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/761061s000lbl.pdf
 GUS, guselkumab; NRI, non-responder imputation; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q8W, every 8 weeks; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
GUS, guselkumab; NRI, non-responder imputation; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q8W, every 8 weeks; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
 GUS, guselkumab; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q8W, every 8 weeks; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
GUS, guselkumab; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q8W, every 8 weeks; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ritchlin C, Helliwell P, Boehncke W, Hsia E, Kollmeier A, Subramanian R, Xu X, Sheng S, Jiang Y, Zhou B, Deodhar A. Guselkumab, an IL-23 Inhibitor That Specifically Binds to the IL23p19-Subunit, for Active Psoriatic Arthritis: One Year Results of a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Patients Who Were Biologic-Naïve or TNFα Inhibitor-Experienced [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-an-il-23-inhibitor-that-specifically-binds-to-the-il23p19-subunit-for-active-psoriatic-arthritis-one-year-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-of-pati/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-an-il-23-inhibitor-that-specifically-binds-to-the-il23p19-subunit-for-active-psoriatic-arthritis-one-year-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-of-pati/