Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The pivotal GO AFTER study [1] and the ongoing observational GO BEYOND study investigate GLM efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who previously received biologics. However, clinical studies of GLM in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) are lacking. Using data from the GO PRACTICE study, we examined GLM persistence in patients with axSpA.
The primary objective of the study was to estimate GLM persistence at 2 years from initial prescription, as a first line of treatment (in biologic naïve patients: BN) and as a second or further line of treatment (in biologic pretreated patients: BP). Secondary outcomes included evaluations of changes over 2 years in 1) clinical disease activity, and 2) patient-reported disease activity, pain, functional ability and quality of life (QoL).
Methods: This was an observational, prospective, multicenter French study, that recruited adult patients with RA, psoriatic arthritis or axSpA, who were newly prescribed GLM. Patients were followed-up over 2 years; data were collected at baseline, 1 year and 2 years. This abstract presents findings originating from the axSpA cohort of the GO PRACTICE study. GLM persistence was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. Clinical disease activity was assessed with the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) and patient-reported disease activity was evaluated with the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI). Pain was evaluated using a visual analogue scale (VAS), functional ability with the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and QoL with the EQ-5D and SF-12 questionnaires.
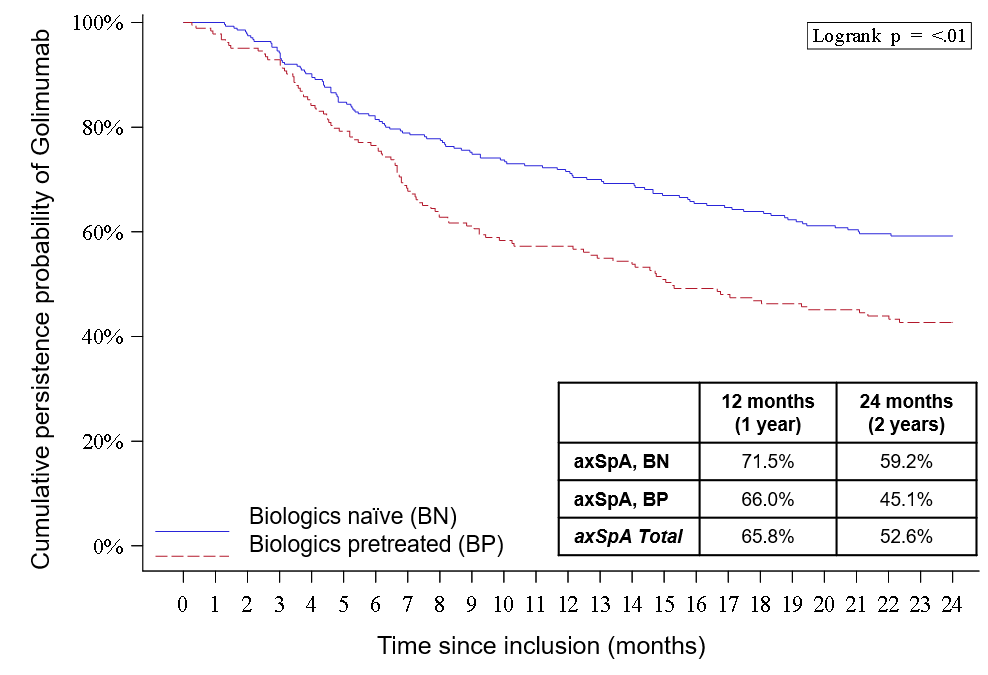
Results: From January 2015 to March 2016, 478 axSpA patients (constituting 63% of the total cohort) from 134 sites were included in the study. Mean age was 43 years and 55% were female; 61% were BN (n=291) and 39% were BP (n=187). Mean duration of axSpA illness was 5.5 and 10.7 years in BN and BP patients, respectively (p < .001). At baseline, most were prescribed 50 mg GLM monthly (97%); DMARDs, corticosteroids and NSAIDs or analgesics were co-prescribed to 34%,17% and 90% of axSpA patients, respectively. GLM persistence over 2 years was significantly higher in BN than BP patients (59.2% vs 45.1%, logrank p < .01). For BN and BP patients persisting on GLM at 2 years, disease activity (Table 1) and patient-reported outcomes showed significant improvements, with improvements being more important in BN patients. GLM was well tolerated in axSpA patients (n=478), with 46 (9.6%) discontinuing due to intolerance. In the BN group, 18 patients (6.2%) discontinued GLM due to primary treatment failure, compared to 28 BP patients (15%). GLM was re-prescribed to 213 (88%) of the 241 patients persisting on GLM at 2-years. Post-hoc multivariate analysis showed that being female was a risk factor for GLM discontinuation in axSpA (HR1.9, IC95% 1.4-2.6).
Conclusion: Golimumab is associated with clinical improvements and good persistence in patients with axial spondyloarthritis, especially those who are biologic naïve
References:
1.Smolen JS, et al; Arthritis research & therapy 2015,17:14
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flipo R, Tubach F, Ouaniche J, Goupille P, Lespessailles E, Gouyette N, Harid N, Fayette J, Bertin P, Fautrel B. Golimumab Persistence in Biologic Naive and Non-Naive Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results of the GO PRACTICE Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/golimumab-persistence-in-biologic-naive-and-non-naive-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-of-the-go-practice-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/golimumab-persistence-in-biologic-naive-and-non-naive-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-of-the-go-practice-study/